Rn Substance Related And Addiction Disorders Assessment
Onlines
Mar 21, 2025 · 6 min read
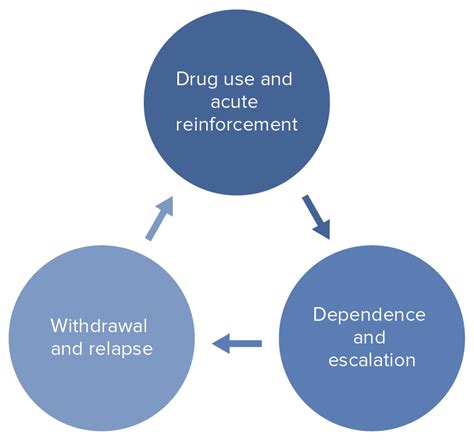
Table of Contents
RN Substance-Related and Addiction Disorders Assessment: A Comprehensive Guide
Registered nurses (RNs) play a crucial role in identifying, assessing, and managing substance-related and addictive disorders. This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted assessment process, equipping RNs with the knowledge and skills necessary to provide effective and compassionate care. We'll explore various assessment tools, interviewing techniques, and crucial considerations for diverse patient populations.
Understanding Substance-Related and Addictive Disorders
Before diving into the assessment process, it's vital to understand the scope of substance-related and addictive disorders. These disorders encompass a broad spectrum of conditions characterized by compulsive drug seeking and use, despite harmful consequences. This includes:
Types of Substances
The range of substances contributing to these disorders is vast and includes:
- Alcohol: Alcohol dependence and alcohol use disorder are significant public health concerns, leading to various physical and mental health issues.
- Opioids: From prescription painkillers to heroin, opioids are highly addictive and carry a high risk of overdose.
- Stimulants: Substances like cocaine, methamphetamine, and amphetamines cause intense stimulation and can lead to severe cardiovascular complications.
- Cannabis: While the perception of cannabis is evolving, its potential for addiction and negative mental health effects cannot be ignored.
- Sedatives, Hypnotics, or Anxiolytics: These drugs, often prescribed for anxiety or sleep disorders, can be highly addictive when misused.
- Hallucinogens: Substances like LSD and psilocybin alter perception and can lead to unpredictable and dangerous behavior.
- Inhalants: These readily available substances, often abused by adolescents, can cause severe neurological damage.
- Tobacco: Nicotine is a highly addictive substance, contributing to significant health problems, including cancer and respiratory diseases.
Diagnostic Criteria
The diagnostic criteria for substance use disorders are outlined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5). The DSM-5 uses a dimensional approach, focusing on the severity of the disorder based on the number of criteria met:
- Mild: 2-3 criteria met
- Moderate: 4-5 criteria met
- Severe: 6 or more criteria met
These criteria include factors like impaired control, social impairment, risky use, and pharmacological criteria (e.g., tolerance, withdrawal).
The RN's Role in Assessment
RNs are often the first point of contact for individuals struggling with substance use disorders. Their role encompasses:
- Identifying potential substance use: Observing behavioral cues, physical signs, and inconsistencies in patient history.
- Conducting a comprehensive assessment: Utilizing standardized tools and interviewing techniques to gather detailed information.
- Collaborating with the interdisciplinary team: Working with physicians, social workers, counselors, and other healthcare professionals to develop a treatment plan.
- Educating patients and families: Providing information about the disorder, treatment options, and support resources.
- Monitoring patients during treatment: Observing for signs of relapse and providing ongoing support.
Assessment Tools and Techniques
A multi-faceted approach is essential for a thorough assessment. This includes:
1. The Clinical Interview
The clinical interview is a cornerstone of the assessment process. It allows the RN to build rapport, gather subjective information, and observe the patient's demeanor. Key areas to explore during the interview include:
- Substance use history: Type of substance, frequency of use, quantity consumed, duration of use, and patterns of use.
- Consequences of substance use: Impact on physical and mental health, relationships, employment, and finances.
- Withdrawal symptoms: Identifying symptoms experienced upon cessation or reduction of substance use.
- Motivation for change: Assessing the patient's readiness to seek treatment and engage in recovery.
- Mental health history: Co-occurring mental health disorders are prevalent among individuals with substance use disorders.
- Social support systems: Evaluating the strength and availability of social support networks.
- Medical history: Identifying any pre-existing medical conditions that may impact treatment.
2. Standardized Assessment Tools
Several standardized tools can aid in the assessment process. These include:
- The Substance Abuse Subtle Screening Inventory (SASSI): A screening tool to detect substance abuse, even when individuals attempt to conceal their use.
- The Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT): A widely used screening tool for alcohol problems.
- The Drug Abuse Screening Test (DAST): A brief screening instrument for drug abuse.
- The CAGE questionnaire: A short questionnaire that screens for alcohol dependence. (While simple, it's important to remember this is only a screening tool and not a diagnostic instrument).
3. Physical Examination
A thorough physical examination is crucial to assess the physical impact of substance use. This may reveal signs of:
- Nutritional deficiencies: Malnutrition is common due to altered eating habits.
- Organ damage: Liver disease, heart problems, and other organ damage can result from long-term substance use.
- Infections: Substance use can increase the risk of various infections.
- Withdrawal symptoms: Physical manifestations of withdrawal can vary depending on the substance.
4. Laboratory Tests
Laboratory tests can confirm substance use and identify potential medical complications. These may include:
- Urine toxicology: Detects the presence of various drugs.
- Blood alcohol content (BAC): Measures the level of alcohol in the blood.
- Liver function tests: Assesses liver function, which may be impaired by substance use.
- Complete blood count (CBC): Evaluates overall blood health.
Specific Considerations
The assessment process requires sensitivity and awareness of diverse factors:
1. Co-occurring Disorders
It's crucial to screen for co-occurring mental health disorders, often referred to as dual diagnosis. Depression, anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and other conditions frequently co-occur with substance use disorders. Treating both conditions simultaneously is essential for successful outcomes.
2. Cultural Considerations
Cultural factors significantly influence substance use patterns and attitudes towards treatment. RNs must be sensitive to these differences and tailor their approach accordingly.
3. Gender-Specific Considerations
Substance use disorders manifest differently in men and women, influencing assessment and treatment strategies.
4. Age-Specific Considerations
The assessment process needs to adapt to the developmental stage of the patient, considering specific challenges and risk factors at different life stages, such as adolescence or older adulthood.
Documentation and Reporting
Accurate and comprehensive documentation is paramount. This includes:
- Patient demographics and history: Detailed information about the patient's background and substance use history.
- Assessment findings: Detailed observations from the clinical interview, physical examination, and laboratory tests.
- Treatment plan: Outline of the proposed treatment strategy, including medications, counseling, and support services.
- Progress notes: Regular updates on the patient's progress and any changes in their condition.
Ethical Considerations
RNs must adhere to ethical guidelines, ensuring patient confidentiality, informed consent, and non-judgmental care. This involves respecting patient autonomy and ensuring the assessment process is conducted in a safe and supportive environment.
Conclusion
The assessment of substance-related and addiction disorders is a complex yet crucial process requiring skillful application of clinical knowledge, assessment tools, and interpersonal skills. By mastering these techniques, RNs become integral members of the healthcare team, providing vital support and guidance to individuals seeking recovery. The journey to recovery is challenging, but with comprehensive assessment and collaborative care, positive outcomes are achievable. Remember, ongoing education and professional development are essential for RNs to stay current with the latest advances in addiction treatment and best practices. This continuous learning ensures the delivery of optimal, compassionate, and effective care to all individuals affected by substance use disorders.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
2 04 What The Bureaucracy Does For You
Mar 22, 2025
-
Life Of Pi How Many Chapters
Mar 22, 2025
-
Bird Island Biodiversity Analysis Questions Answers
Mar 22, 2025
-
In This Excerpt Schlosser Claims That Fast Food Restaurants Are
Mar 22, 2025
-
Match The Behaviors To The Appropriate Species
Mar 22, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Rn Substance Related And Addiction Disorders Assessment . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
