Section 3 Topic 3 Adding And Subtracting Functions
Onlines
Mar 05, 2025 · 6 min read
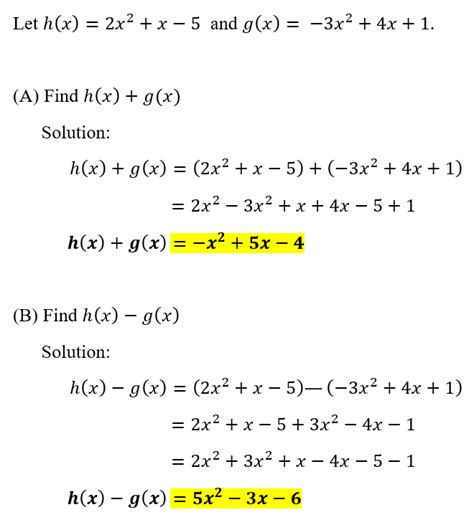
Table of Contents
Section 3, Topic 3: Adding and Subtracting Functions – A Comprehensive Guide
Adding and subtracting functions might seem like a straightforward concept at first glance, but a deeper understanding reveals its significant role in various mathematical applications and real-world scenarios. This comprehensive guide will explore this topic thoroughly, covering fundamental concepts, practical examples, and advanced applications. We'll also explore how these operations relate to function composition and other key mathematical ideas.
Understanding Function Operations: Addition and Subtraction
At its core, adding or subtracting functions involves performing the arithmetic operation on their output values for a given input. Let's define two functions: f(x) and g(x).
-
Addition of Functions: The sum of two functions, denoted as
(f + g)(x), is obtained by adding the outputs of each function for the same input value:(f + g)(x) = f(x) + g(x). -
Subtraction of Functions: The difference of two functions, denoted as
(f - g)(x), is obtained by subtracting the output ofg(x)from the output off(x)for the same input value:(f - g)(x) = f(x) - g(x).
Important Note: The domain of the resulting function (f + g)(x) or (f - g)(x) is the intersection of the domains of f(x) and g(x). This means the input values must be valid for both original functions.
Illustrative Examples: Adding and Subtracting Functions
Let's solidify our understanding with some practical examples.
Example 1: Polynomial Functions
Let f(x) = 2x² + 3x - 1 and g(x) = x² - 2x + 5.
-
Addition:
(f + g)(x) = (2x² + 3x - 1) + (x² - 2x + 5) = 3x² + x + 4 -
Subtraction:
(f - g)(x) = (2x² + 3x - 1) - (x² - 2x + 5) = 2x² + 3x - 1 - x² + 2x - 5 = x² + 5x - 6
In this case, both f(x) and g(x) have a domain of all real numbers, so the resulting functions also have a domain of all real numbers.
Example 2: Rational Functions
Let f(x) = 1/x and g(x) = x + 1.
-
Addition:
(f + g)(x) = 1/x + x + 1. This function is not easily simplified further. -
Subtraction:
(f - g)(x) = 1/x - (x + 1) = 1/x - x - 1. Again, this doesn't simplify significantly.
The domain of f(x) is all real numbers except 0 (x ≠ 0). The domain of g(x) is all real numbers. Therefore, the domain of both (f + g)(x) and (f - g)(x) is all real numbers except 0.
Example 3: Radical Functions
Let f(x) = √x and g(x) = √(4-x).
-
Addition:
(f + g)(x) = √x + √(4 - x). -
Subtraction:
(f - g)(x) = √x - √(4 - x).
The domain of f(x) is x ≥ 0. The domain of g(x) is 4 - x ≥ 0, which implies x ≤ 4. Therefore, the domain of both (f + g)(x) and (f - g)(x) is the intersection of these domains: 0 ≤ x ≤ 4.
Graphical Representation of Function Addition and Subtraction
Visualizing function addition and subtraction graphically provides valuable insights. The graph of the sum (or difference) of two functions can be obtained by adding (or subtracting) the corresponding y-coordinates of the original functions for each x-value.
Imagine plotting f(x) and g(x) on the same coordinate plane. To find the y-coordinate of (f + g)(x) at a specific x-value, you would add the y-coordinates of f(x) and g(x) at that x-value. Similarly, for subtraction, you would subtract the y-coordinate of g(x) from the y-coordinate of f(x).
This graphical method is particularly useful for understanding the overall behavior and characteristics of the resulting function, like its intercepts, maxima, minima, and overall shape.
Applications of Adding and Subtracting Functions
The ability to add and subtract functions has far-reaching applications in various fields:
-
Physics: Combining forces, velocities, or other vector quantities often involves adding or subtracting functions representing these quantities.
-
Economics: Modeling total cost, revenue, or profit often involves adding or subtracting different cost components or revenue streams.
-
Engineering: Analyzing complex systems often requires combining functions that represent different aspects of the system. For example, analyzing the combined effect of multiple forces on a structure.
-
Computer Science: In computer graphics, adding and subtracting functions can be used for image manipulation, such as blending colors or creating special effects.
Advanced Concepts and Extensions
Let's delve into some more advanced aspects related to function addition and subtraction:
Function Composition vs. Function Addition/Subtraction
It's crucial to differentiate between function composition and function addition/subtraction. While both involve combining functions, they do so in fundamentally different ways.
Function composition ((f ∘ g)(x) = f(g(x))) involves applying one function to the output of another. In contrast, function addition and subtraction involve adding or subtracting the output values of the functions directly for the same input value.
For example, if f(x) = x² and g(x) = x + 1, then:
(f + g)(x) = x² + x + 1(addition)(f ∘ g)(x) = f(g(x)) = f(x + 1) = (x + 1)² = x² + 2x + 1(composition)
Notice the distinct results. Function composition creates a nested operation; the output of one function becomes the input to another. Addition and subtraction operate on the outputs directly, at the same x-value.
Linear Combinations of Functions
Adding and subtracting functions are special cases of forming linear combinations of functions. A linear combination of functions f(x), g(x), h(x), etc., is an expression of the form:
a*f(x) + b*g(x) + c*h(x) + ...
where a, b, c, etc., are constants. Adding and subtracting functions are merely linear combinations where the constants are 1, -1, or 0.
Applications in Calculus
Adding and subtracting functions plays a crucial role in calculus. The derivative and integral of a sum (or difference) of functions is simply the sum (or difference) of the derivatives (or integrals) of the individual functions. This property greatly simplifies the computation of derivatives and integrals of complex functions.
Conclusion
Adding and subtracting functions is a fundamental concept in mathematics with broad applications across various disciplines. Understanding these operations, their domains, graphical representations, and their distinction from function composition provides a solid foundation for tackling more advanced mathematical concepts and real-world problems. By mastering these fundamental operations, you gain a powerful tool for analyzing and modeling complex systems and phenomena. Remember to always carefully consider the domain of the resulting function, ensuring the intersection of the domains of the original functions. This attention to detail is critical for accuracy and avoiding errors in your calculations and interpretations.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Punnett Square Riddle Dragon Answer Key
Mar 06, 2025
-
List The Advantages And Disadvantages Of The Manriki Kusari
Mar 06, 2025
-
From The Book Pre Lab Unit 16 Activity 4 Question 1
Mar 06, 2025
-
Precalculus Mathematics For Calculus 7th Edition Answers
Mar 06, 2025
-
Poli 150 01f International Relations And Global Politics
Mar 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Section 3 Topic 3 Adding And Subtracting Functions . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
