Skills Module 3.0 Enteral Tube Feeding Posttest
Onlines
Apr 03, 2025 · 5 min read
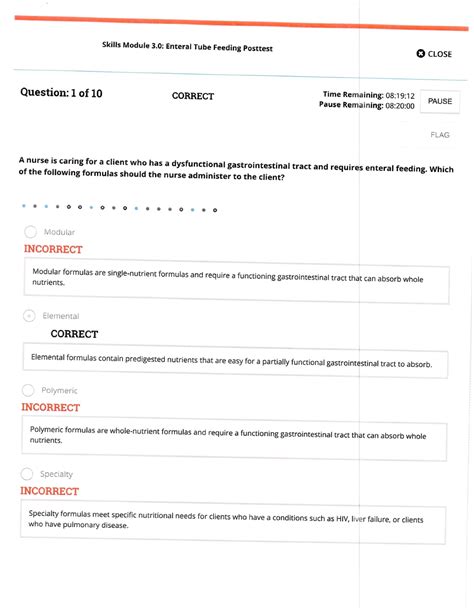
Table of Contents
Skills Module 3.0 Enteral Tube Feeding Post-Test: A Comprehensive Review
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of the Skills Module 3.0 Enteral Tube Feeding Post-Test, providing a detailed review of key concepts and practical applications. We will explore the essential skills required for safe and effective enteral nutrition, addressing common challenges and highlighting best practices. Whether you're a nursing student preparing for your exam or a healthcare professional looking to refresh your knowledge, this resource will serve as your ultimate companion.
Understanding Enteral Nutrition
Enteral nutrition (EN), also known as tube feeding, delivers nutrition directly to the gastrointestinal (GI) tract via a tube. This method bypasses the oral route, proving crucial for patients unable to consume sufficient nutrients orally due to various conditions like stroke, head injury, or critical illness. Successful enteral feeding hinges on meticulous attention to detail, encompassing accurate tube placement verification, appropriate formula selection, and diligent monitoring for complications.
Types of Enteral Access Tubes
Several types of tubes facilitate enteral feeding, each suited to specific patient needs and duration of feeding. These include:
- Nasogastric (NG) tubes: Inserted through the nose and into the stomach. These are typically short-term options.
- Nasointestinal (NI) tubes: Extend beyond the stomach, into the duodenum or jejunum. Used when gastric emptying is compromised.
- Gastrostomy (G-tube) and Jejunostomy (J-tube): Surgically placed tubes directly into the stomach or jejunum, respectively. These are long-term options.
- Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy (PEG) and Percutaneous Endoscopic Jejunostomy (PEJ): Minimally invasive procedures for placing G-tubes and J-tubes.
Skills Module 3.0: Key Areas Covered in the Post-Test
The Skills Module 3.0 Enteral Tube Feeding Post-Test comprehensively assesses your understanding and proficiency across several critical areas. These include, but aren't limited to:
1. Assessment and Planning:
- Patient History and Physical Assessment: Thorough assessment of the patient's nutritional status, swallowing ability, and overall health is paramount. This includes reviewing medical records, assessing weight and height, and evaluating any existing comorbidities.
- Determining Enteral Feeding Needs: Calculating caloric requirements based on individual patient needs. Understanding different formula types and their suitability for various patient conditions (e.g., standard, high-protein, specialized formulas).
- Tube Selection and Insertion: Appropriate selection of tube type based on patient-specific factors. Understanding the procedures for safe and correct tube insertion, including verification of placement.
2. Tube Placement Verification:
This is arguably the most critical aspect of enteral feeding. Incorrect placement can lead to serious complications, including aspiration pneumonia. Verification methods include:
- X-ray: The gold standard for confirming tube location.
- Aspirate pH Measurement: Checking the pH of the aspirate (stomach contents). Gastric aspirate typically has a pH of less than 5.5. However, this method alone isn't entirely reliable.
- Auscultation: Listening for air entry during injection of air into the tube. Not a reliable method on its own.
- Visible marking on the tube: Checking the external marking on the tube against measured distance from the nose or mouth.
3. Formula Preparation and Administration:
- Formula Handling and Storage: Proper handling of enteral formulas to prevent contamination and spoilage. Understanding storage guidelines and expiration dates.
- Calculating and Administering Feedings: Accurate calculation of feeding volumes based on prescribed orders. Understanding different administration methods (bolus, continuous, intermittent).
- Medication Administration Through Enteral Tubes: Correct procedure for administering medications through the feeding tube, including compatibility considerations and potential drug interactions.
4. Monitoring and Managing Complications:
Ongoing monitoring is vital to prevent and manage potential complications. These include:
- Aspiration: The most serious complication. Signs and symptoms include coughing, choking, and respiratory distress.
- Diarrhea: Can lead to dehydration and electrolyte imbalances.
- Constipation: Requires careful monitoring and management.
- Nausea and Vomiting: May indicate intolerance to the formula or tube placement issues.
- Tube Occlusion: Requires prompt intervention to restore patency.
- Electrolyte Imbalances: Careful monitoring of electrolytes is critical.
- Infection: Strict adherence to aseptic techniques minimizes infection risk.
5. Documentation and Communication:
Accurate and meticulous documentation is paramount:
- Recording Feeding Schedule and Volumes: Precise record-keeping of feeding times, volumes administered, and any observations.
- Documenting Assessments and Interventions: Detailed notes on patient assessments, any interventions performed, and the patient's response to treatment.
- Communication with Healthcare Team: Effective communication with other healthcare professionals about the patient's progress and any concerns.
Sample Post-Test Questions and Answers
While the exact questions on the Skills Module 3.0 post-test will vary, understanding the underlying concepts will enable you to answer a wide range of questions. Here are a few examples:
1. What is the most reliable method for verifying enteral tube placement?
- A. X-ray
- B. Auscultation
- C. Aspirate pH Measurement
- D. Visible marking on the tube
Answer: A. X-ray
2. What are the signs and symptoms of aspiration?
- A. Coughing, choking, respiratory distress
- B. Diarrhea, constipation
- C. Nausea, vomiting
- D. Fever, chills
Answer: A. Coughing, choking, respiratory distress
3. What is the appropriate action if a feeding tube becomes occluded?
- A. Attempt to flush the tube with water.
- B. Immediately replace the tube.
- C. Stop feeding and contact the physician.
- D. Attempt to flush the tube with water, and if unsuccessful, contact the physician.
Answer: D. Attempt to flush the tube with water, and if unsuccessful, contact the physician.
Preparing for the Skills Module 3.0 Enteral Tube Feeding Post-Test
Success on the Skills Module 3.0 post-test requires thorough preparation. Here's a structured approach:
- Review Module Materials: Carefully review all provided course materials, including textbooks, handouts, and presentations.
- Practice Skills: Hands-on practice is invaluable. Seek opportunities to practice enteral tube insertion, feeding administration, and other relevant skills under supervision.
- Develop a Study Plan: Create a realistic study plan that allocates sufficient time to cover all relevant topics.
- Use Practice Questions: Use practice questions to assess your understanding and identify areas needing further review.
- Seek Clarification: Don't hesitate to seek clarification from instructors or mentors on any unclear concepts.
Conclusion
The Skills Module 3.0 Enteral Tube Feeding Post-Test assesses your competence in a crucial aspect of patient care. By mastering the concepts outlined in this review, you'll be well-prepared to demonstrate your knowledge and skills. Remember, patient safety is paramount, and meticulous attention to detail is crucial in every stage of enteral nutrition. Good luck with your exam!
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Autumns School Holds A Volunteer Challenge
Apr 04, 2025
-
Sorting Finch Species Click And Learn Answer Key
Apr 04, 2025
-
Summary Of Act 4 The Tempest
Apr 04, 2025
-
What Type Of Current Is Illustrated In The Diagram Below
Apr 04, 2025
-
The Land Ethic Aldo Leopold Summary
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Skills Module 3.0 Enteral Tube Feeding Posttest . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
