Skills Module 3.0 Infection Control Posttest
Onlines
Mar 13, 2025 · 6 min read
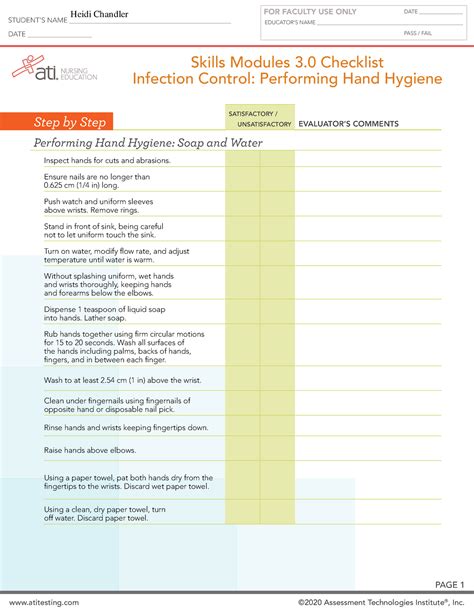
Table of Contents
Skills Module 3.0 Infection Control Post-Test: A Comprehensive Guide
Infection control is paramount in any healthcare setting. The Skills Module 3.0 Infection Control Post-Test assesses your understanding of crucial infection prevention and control practices. This comprehensive guide will delve into the key concepts covered in the module, providing detailed explanations to help you ace your post-test. We'll explore topics ranging from hand hygiene and personal protective equipment (PPE) to the management of spills and waste disposal.
Understanding the Importance of Infection Control
Before diving into the specifics, let's underscore the critical role of infection control. It's not merely a set of procedures; it's a lifeline protecting patients, healthcare workers, and the wider community from preventable infections. Effective infection control measures significantly reduce the incidence of healthcare-associated infections (HAIs), improving patient outcomes and minimizing healthcare costs.
The Chain of Infection: Breaking the Links
Understanding the chain of infection is fundamental. This chain comprises six key links:
- Infectious Agent: The pathogen (bacteria, virus, fungus, etc.) causing the infection.
- Reservoir: The place where the pathogen resides (e.g., humans, animals, environment).
- Portal of Exit: How the pathogen leaves the reservoir (e.g., respiratory droplets, blood, feces).
- Mode of Transmission: How the pathogen travels from the reservoir to the host (e.g., direct contact, airborne droplets, vectors).
- Portal of Entry: How the pathogen enters the susceptible host (e.g., mucous membranes, broken skin).
- Susceptible Host: An individual at risk of infection due to compromised immunity or other factors.
Breaking any link in this chain effectively prevents the spread of infection. This is the cornerstone of infection control strategies.
Key Concepts Covered in Skills Module 3.0 Infection Control
Skills Module 3.0 likely covers a range of infection control procedures and principles. Let's examine some key areas:
1. Hand Hygiene: The Foundation of Infection Control
Hand hygiene is arguably the single most important infection control measure. It involves washing hands with soap and water or using an alcohol-based hand rub. The module likely emphasizes the correct technique, including:
- Timing: Washing hands before and after patient contact, before and after performing aseptic procedures, and after touching contaminated surfaces.
- Technique: Proper scrubbing, covering all surfaces of the hands and fingers, and ensuring sufficient contact time.
- Product Selection: Choosing appropriate soap and water or alcohol-based hand rub based on the situation.
2. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Shielding Against Infection
PPE provides a barrier between healthcare workers and potential sources of infection. The module likely covers:
- Gloves: Types of gloves (sterile, non-sterile), appropriate use, and proper disposal.
- Gowns: When gowns are necessary (e.g., during procedures with potential splashes), correct donning and doffing procedures.
- Masks: Different types of masks (surgical masks, N95 respirators), proper fit and use, and disposal.
- Eye Protection: Goggles or face shields to protect the eyes from splashes or sprays.
Proper donning and doffing procedures are crucial. These procedures ensure that PPE is used effectively and minimizes the risk of contamination. The module likely provides step-by-step instructions for each type of PPE. Remember to always follow the specific protocols established by your institution.
3. Standard Precautions: A Universal Approach
Standard precautions apply to all patients, regardless of their infection status. They aim to reduce the risk of transmission of bloodborne and other pathogens. Key elements include:
- Hand hygiene: As discussed above.
- PPE: Using appropriate PPE when necessary.
- Safe handling of sharps: Using appropriate techniques to prevent needlestick injuries and proper disposal of sharps in designated containers.
- Respiratory hygiene/cough etiquette: Covering coughs and sneezes, proper disposal of tissues, and hand hygiene afterward.
- Environmental cleaning and disinfection: Regular cleaning and disinfection of surfaces and equipment.
4. Transmission-Based Precautions: Targeted Strategies
Transmission-based precautions are implemented in addition to standard precautions when a patient is known or suspected to have a specific infectious agent that requires additional control measures. These precautions are categorized based on the mode of transmission:
- Airborne Precautions: Used for infections spread through airborne droplets (e.g., tuberculosis, measles). Requires a negative pressure room and respirators (e.g., N95).
- Droplet Precautions: Used for infections spread through large respiratory droplets (e.g., influenza, rubella). Requires the use of surgical masks.
- Contact Precautions: Used for infections spread through direct or indirect contact (e.g., MRSA, C. difficile). Requires the use of gloves and gowns.
Understanding the specific precautions for each type of infection is essential. The module likely provides detailed guidance on implementing these precautions effectively.
5. Aseptic Techniques: Maintaining Sterility
Aseptic techniques are crucial in preventing the introduction of microorganisms into sterile fields. The module likely covers:
- Sterilization: Methods to eliminate all microorganisms (e.g., autoclaving, gas sterilization).
- Disinfection: Methods to reduce the number of microorganisms on surfaces (e.g., using disinfectants).
- Surgical asepsis: Procedures used in the operating room to maintain sterility.
- Medical asepsis: Techniques used to reduce the number of microorganisms in clinical settings.
6. Waste Disposal and Spill Management: Protecting the Environment and Preventing Transmission
Proper waste disposal and spill management are critical aspects of infection control. The module likely addresses:
- Sharps disposal: Proper disposal of needles, syringes, and other sharps in designated containers.
- Biohazardous waste disposal: Safe disposal of contaminated materials according to established guidelines.
- Spill management: Proper procedures for cleaning up spills of blood, body fluids, or other potentially infectious materials.
7. Documentation and Reporting: Maintaining Accurate Records
Accurate documentation is essential for tracking infection control practices and identifying potential outbreaks. The module likely emphasizes the importance of:
- Recording hand hygiene compliance: Tracking the frequency and adherence to hand hygiene protocols.
- Reporting infections: Promptly reporting suspected or confirmed infections to the appropriate authorities.
- Maintaining accurate records of PPE use and waste disposal: Ensuring a detailed record of all infection control procedures.
Preparing for the Skills Module 3.0 Infection Control Post-Test
To excel in the post-test, thorough preparation is key. Review all materials provided in the module, focusing on the key concepts outlined above. Practice applying the knowledge by visualizing scenarios and considering how you would apply different infection control measures in various situations. Consider using flashcards or creating summary notes to reinforce your understanding. If possible, discuss the material with colleagues or instructors to clarify any areas of uncertainty.
Beyond the Post-Test: Continuous Learning in Infection Control
Passing the Skills Module 3.0 Infection Control Post-Test is just the beginning. Infection control is a constantly evolving field. Continuous learning and staying updated on the latest guidelines and best practices are vital for all healthcare professionals. Attend workshops, conferences, and online courses to further enhance your knowledge and skills. Staying informed will ensure that you're always equipped to provide the safest and most effective care for your patients.
By understanding the chain of infection, mastering hand hygiene and PPE protocols, and adhering to standard and transmission-based precautions, you'll be well-prepared to not only pass the post-test but also contribute significantly to a safer healthcare environment for everyone. Remember, preventing infections is a shared responsibility, and your commitment to infection control plays a crucial role in safeguarding both patients and healthcare providers.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of These Employee Rights Might Affect What You Do
Mar 14, 2025
-
Chapter 12 Summary To Kill A Mockingbird
Mar 14, 2025
-
At Present For Adult Cpr Outside The Hospital
Mar 14, 2025
-
Lewis Medical Surgical Nursing 12th Edition Test Bank
Mar 14, 2025
-
Beauty Professionals Are Permitted And Encouraged To
Mar 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Skills Module 3.0 Infection Control Posttest . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
