Skills Module 3.0 Urinary Elimination Posttest
Onlines
Apr 02, 2025 · 5 min read
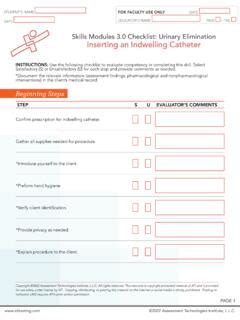
Table of Contents
Skills Module 3.0: Urinary Elimination Post-Test – A Comprehensive Review
This post provides a comprehensive review of the material typically covered in a Skills Module 3.0 post-test focusing on urinary elimination. We will explore key concepts, critical thinking questions, and practical application scenarios to ensure you're fully prepared. This detailed guide is designed to help you not only pass your post-test but also to build a strong foundation in understanding urinary elimination and related patient care. We will cover a wide range of topics, from anatomy and physiology to assessment, interventions, and documentation.
Understanding the Urinary System: Anatomy and Physiology
Before delving into the practical aspects of urinary elimination, it's crucial to have a solid grasp of the urinary system's anatomy and physiology. This foundational knowledge is essential for accurately assessing and addressing urinary issues.
Key Structures and Their Functions:
- Kidneys: These bean-shaped organs filter waste products from the blood, producing urine. Understanding the nephron's role in filtration, reabsorption, and secretion is key.
- Ureters: These tubes transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder. Their peristaltic movements ensure efficient urine flow.
- Bladder: This muscular sac stores urine until it's eliminated. Understanding bladder capacity and its role in continence is vital.
- Urethra: This tube carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body. Differences in the male and female urethra are clinically significant.
The Process of Urine Formation:
A thorough understanding of the three main processes involved in urine formation – glomerular filtration, tubular reabsorption, and tubular secretion – is essential. Knowing how these processes contribute to urine composition and the regulation of fluid and electrolyte balance will greatly enhance your comprehension of urinary elimination.
Assessment of Urinary Elimination: A Systematic Approach
Accurate assessment is the cornerstone of effective patient care related to urinary elimination. A thorough assessment should involve a combination of subjective and objective data collection.
Subjective Data Collection:
- Patient History: Inquire about the patient's voiding habits (frequency, urgency, hesitancy, nocturia), any pain or discomfort during urination (dysuria), changes in urine color or odor, past urinary tract infections (UTIs), and any relevant medical history.
- Symptoms: Thoroughly document the patient's reported symptoms, paying close attention to details like the duration and severity of symptoms.
Objective Data Collection:
- Physical Assessment: This includes assessing skin turgor, mucous membranes, and the presence of edema, all of which can indicate hydration status. Palpating the bladder can help determine its fullness.
- Urine Analysis: Observe the color, clarity, and odor of the urine. Knowledge of common abnormalities and their clinical significance is essential. Understanding the implications of different urine specific gravity readings is also crucial.
- Monitoring Intake and Output (I&O): Accurately measuring fluid intake and urine output is critical for monitoring hydration status and detecting potential problems.
Interventions and Nursing Management: Addressing Urinary Issues
Effective nursing interventions are crucial for promoting optimal urinary elimination and managing related complications.
Promoting Normal Micturition:
- Maintaining Adequate Fluid Intake: Encourage patients to drink sufficient fluids to prevent dehydration and promote adequate urine output.
- Promoting Regular Voiding: Encourage patients to void at regular intervals to prevent bladder distention. Understanding the importance of timed voiding for patients with specific conditions is vital.
- Privacy and Comfort: Provide a comfortable and private environment to facilitate normal voiding.
Managing Urinary Incontinence:
Different types of incontinence (stress, urge, overflow, functional, mixed) require different interventions. Understanding these types and their respective management strategies is critical. This includes knowledge of bladder training exercises, pelvic floor muscle exercises (Kegels), and the use of absorbent products.
Managing Catheterization:
Proper catheter insertion and maintenance are crucial to prevent infection and complications. Understanding sterile techniques and post-catheterization care is paramount. This includes knowledge of different catheter types and their indications.
Monitoring for and Managing UTIs:
Understanding the signs and symptoms of UTIs, including frequency, urgency, dysuria, and fever, is vital. Knowing appropriate nursing interventions and the importance of timely medical intervention is critical.
Documentation: Accuracy and Completeness are Paramount
Accurate and thorough documentation is a legal and ethical responsibility. It ensures continuity of care and facilitates communication among healthcare professionals.
Key Elements of Documentation:
- Intake and Output: Record fluid intake and urine output accurately and consistently.
- Urine Characteristics: Document the color, clarity, and odor of the urine.
- Patient's Subjective Reports: Record the patient's descriptions of symptoms and concerns.
- Interventions and Responses: Document all nursing interventions implemented, as well as the patient's response to these interventions.
Critical Thinking and Clinical Application
The Skills Module 3.0 post-test will likely include scenarios requiring critical thinking and clinical application of knowledge. Here are some examples:
- Scenario 1: A patient reports experiencing frequency and urgency. What assessment data would you collect to determine the cause? What interventions would you implement?
- Scenario 2: A patient with a urinary catheter shows signs of a UTI. What are the immediate nursing actions?
- Scenario 3: How would you educate a patient on performing Kegel exercises? What are the potential benefits and challenges?
- Scenario 4: A patient is experiencing urinary retention. What are the potential causes and nursing interventions? How would you assess the effectiveness of interventions?
Beyond the Post-Test: Continuous Learning
Passing your Skills Module 3.0 post-test is just the beginning of your journey in providing optimal urinary care. Continuing your education through professional development opportunities and staying updated on the latest research and best practices is crucial for providing high-quality patient care.
This comprehensive review covers the key areas likely included in a Skills Module 3.0 urinary elimination post-test. By thoroughly understanding these concepts, mastering the practical skills, and developing strong critical thinking abilities, you will be well-prepared to excel on your post-test and provide safe and effective care for your patients. Remember to always consult your course materials and instructors for specific details and information relevant to your program. Good luck!
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Middle East And South Asia Ii Unit Test
Apr 03, 2025
-
Chapter 2 Pedagogy Of The Oppressed
Apr 03, 2025
-
Which Is Not Recommended When Giving Feedback
Apr 03, 2025
-
A Simple Elevator Ride Can Teach
Apr 03, 2025
-
Penelope 1 Of 1 Muestra Sus Fotos A Mi
Apr 03, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Skills Module 3.0 Urinary Elimination Posttest . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
