Solar System Explorer Gizmo Answer Key
Onlines
Mar 25, 2025 · 7 min read
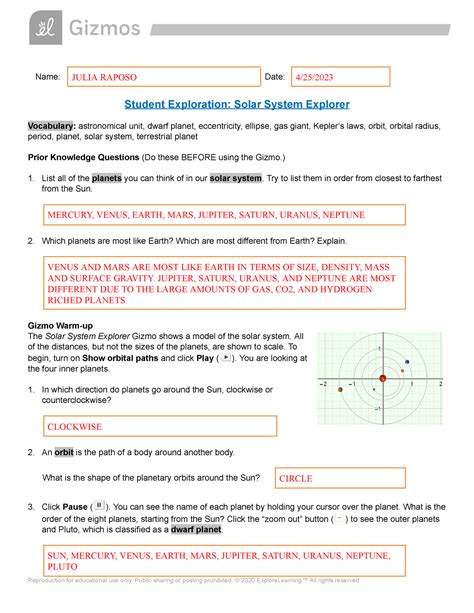
Table of Contents
Solar System Explorer Gizmo Answer Key: A Comprehensive Guide
The Solar System Explorer Gizmo is a fantastic educational tool that allows students to delve into the intricacies of our solar system. It offers a dynamic, interactive experience, fostering a deeper understanding of planetary characteristics, orbital mechanics, and celestial relationships. However, many students find themselves needing assistance navigating the Gizmo and understanding the concepts it presents. This comprehensive guide serves as a detailed answer key and explanation for the Solar System Explorer Gizmo, helping students master the material and solidify their understanding of our solar system.
Understanding the Gizmo Interface
Before diving into specific answers, it's crucial to understand the Gizmo's interface. Familiarizing yourself with the various tools and options will make navigating the activity much easier. The Gizmo typically includes controls for:
- Planet Selection: Allows you to focus on a specific planet and explore its properties in detail.
- Data Display: Provides access to information like mass, orbital period, distance from the sun, and atmospheric composition.
- Orbital Simulation: Allows you to visualize the planets' orbits and understand their movements relative to the sun.
- Comparison Tools: Enables you to compare different planets based on their characteristics.
- Zoom Functionality: Lets you zoom in and out to examine the planets and their features in varying levels of detail.
Exploring Planetary Characteristics: A Detailed Answer Key
This section will address common questions and provide detailed answers based on typical activities within the Solar System Explorer Gizmo. Remember, the specific questions might vary slightly depending on the version of the Gizmo, but the underlying principles remain consistent.
1. Inner Planets vs. Outer Planets:
Question: Compare and contrast the inner (terrestrial) and outer (gas giant) planets in terms of size, composition, atmosphere, and number of moons.
Answer:
-
Size and Composition: Inner planets (Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars) are relatively small and rocky, composed primarily of silicates and metals. Outer planets (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune) are significantly larger and are gas giants, composed mainly of hydrogen and helium, with traces of other elements.
-
Atmosphere: Inner planets have diverse atmospheres. Earth has a nitrogen-oxygen atmosphere, while Venus has a dense carbon dioxide atmosphere. Mars has a very thin atmosphere composed primarily of carbon dioxide. The outer planets have thick, dynamic atmospheres, characterized by powerful storms and atmospheric bands.
-
Number of Moons: Inner planets have few or no moons. Earth has one, Mars has two small moons, while Mercury and Venus have none. Outer planets boast a large number of moons, with Jupiter and Saturn possessing dozens, if not hundreds.
-
Other Key Differences: Inner planets have solid surfaces, while outer planets lack clearly defined surfaces. Outer planets also have extensive ring systems composed of ice, dust, and rock.
2. Orbital Characteristics:
Question: Explain the relationship between a planet's distance from the sun and its orbital period.
Answer: Kepler's Third Law of Planetary Motion states that the square of a planet's orbital period is directly proportional to the cube of its semi-major axis (average distance from the sun). In simpler terms, planets farther from the sun have longer orbital periods (take longer to orbit the sun) than planets closer to the sun.
3. Planetary Atmospheres:
Question: Describe the differences in atmospheric composition and pressure among various planets. What are the implications of these differences for the possibility of life?
Answer:
- Earth: A relatively thin atmosphere, primarily nitrogen and oxygen, with moderate pressure, ideal for supporting life as we know it.
- Venus: Extremely dense carbon dioxide atmosphere, resulting in a runaway greenhouse effect and extremely high surface temperatures, making it inhospitable to life.
- Mars: A very thin carbon dioxide atmosphere, resulting in low atmospheric pressure and extremely cold temperatures. While liquid water is unlikely on the surface, there's ongoing research exploring the possibility of past or subsurface life.
- Gas Giants: Thick atmospheres composed primarily of hydrogen and helium, with powerful winds and storms. The extreme pressure and lack of a solid surface make them unsuitable for life as we know it.
4. Planetary Surfaces:
Question: Compare the surface features of Mars and Earth.
Answer: Earth's surface features a wide diversity of landforms: mountains, valleys, oceans, and continents, shaped by plate tectonics and erosion. Mars, on the other hand, shows evidence of past volcanic activity, vast canyons (like Valles Marineris), and impact craters, suggesting a less geologically active past compared to Earth. While evidence suggests past liquid water on Mars, its current surface is largely dry and barren.
5. Moons and Rings:
Question: Describe the characteristics of some of the major moons in our solar system. What are the key differences between the ring systems of Saturn and Jupiter?
Answer:
-
Major Moons: Examples include Ganymede (Jupiter's largest moon), Titan (Saturn's largest moon, with a thick atmosphere), and Callisto (Jupiter's second-largest moon, heavily cratered). These moons exhibit diverse features, some with their own unique geological processes.
-
Ring Systems: Saturn’s rings are the most prominent, composed mostly of ice particles. Jupiter also has rings, but they are much fainter and composed primarily of dust. The differences in composition and brightness are primarily due to the size and makeup of the particles comprising the rings.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Concepts and Exploration
The Solar System Explorer Gizmo might also delve into more complex topics, requiring a deeper understanding of physics and astronomy. Here's a look at some of these advanced concepts:
1. Gravity and Orbital Mechanics:
Question: Explain how gravity affects the orbits of planets and moons. How does the mass of a planet influence the orbital characteristics of its moons?
Answer: Gravity is the fundamental force that dictates planetary and lunar motion. The sun's gravity holds the planets in their orbits. The stronger the gravitational force between two celestial bodies, the tighter and faster the orbit. A more massive planet exerts a stronger gravitational pull on its moons, resulting in faster orbital speeds and tighter orbits.
2. Planetary Formation:
Question: Discuss the current scientific theories about the formation of the solar system.
Answer: The currently accepted model is the nebular hypothesis, which suggests that our solar system formed from a rotating cloud of gas and dust (a solar nebula). Gravity caused the nebula to collapse, with the majority of the mass concentrating at the center to form the sun. The remaining material formed a rotating disk, where planetesimals gradually accreted to form the planets.
3. Comparative Planetology:
Question: How can studying other planets help us better understand Earth?
Answer: Comparative planetology involves comparing and contrasting different planets to understand their formation, evolution, and characteristics. By studying planets with vastly different environments than Earth (like Venus's runaway greenhouse effect or Mars's thin atmosphere), we gain valuable insights into the factors that influenced Earth's development and the conditions necessary for habitability.
Tips for Success with the Solar System Explorer Gizmo
To get the most out of the Gizmo, consider these strategies:
- Read Instructions Carefully: Begin by thoroughly reviewing the Gizmo's instructions. This will help familiarize yourself with the controls and objectives.
- Experiment: Don't be afraid to experiment with the Gizmo's features. Try changing parameters, comparing planets, and running simulations.
- Take Notes: Jot down key observations and data points during your explorations.
- Review and Reflect: After completing the activity, take time to review your findings and reflect on what you have learned.
Conclusion
The Solar System Explorer Gizmo is a powerful tool for learning about our solar system. By understanding its interface, exploring the planetary characteristics, and delving into more advanced concepts, students can significantly enhance their comprehension of astronomical phenomena. This comprehensive guide, serving as an answer key and explanation, aims to support students in their learning journey and provide them with a deeper appreciation of the fascinating world beyond our planet. Remember that independent exploration and critical thinking are paramount to a truly enriching educational experience. While this guide provides answers, the process of discovery and understanding remains the key to mastering the concepts presented in the Gizmo.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Chapter 18 Summary Of The Giver
Mar 28, 2025
-
The Cpt Code For Posting Mr Bowdens Payment Is
Mar 28, 2025
-
Tina Jones Cardiovascular Shadow Health Transcript
Mar 28, 2025
-
Art Labeling Activity The Major Systemic Arteries
Mar 28, 2025
-
3 12 Unit Test Nutrition Part 1
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Solar System Explorer Gizmo Answer Key . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
