Substance Use And Addictive Disorders Ati Template
Onlines
Apr 01, 2025 · 7 min read
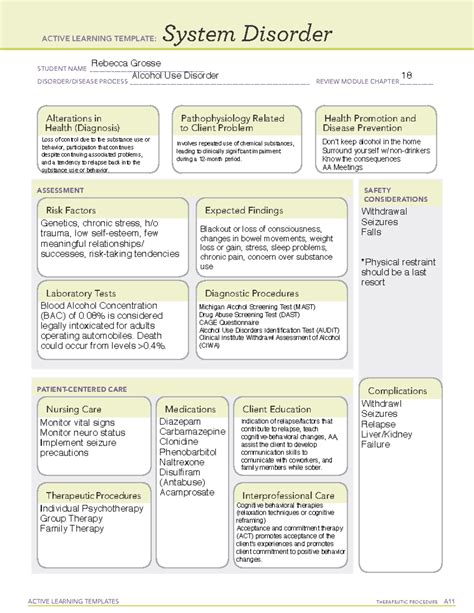
Table of Contents
- Substance Use And Addictive Disorders Ati Template
- Table of Contents
- Substance Use and Addictive Disorders: A Comprehensive Guide Using the ATI Template
- I. Assessment: Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms
- A. History Taking: Unveiling the Story Behind the Addiction
- B. Physical Examination: Detecting the Physical Manifestations
- C. Psychological Assessment: Understanding the Underlying Issues
- II. Planning: Developing a Comprehensive Treatment Strategy
- A. Goals and Objectives: Defining Success
- B. Treatment Modalities: Tailoring the Approach
- C. Relapse Prevention Planning: Preparing for Challenges
- III. Implementation: Putting the Plan into Action
- A. Medication Management: Overseeing the Treatment
- B. Therapeutic Interventions: Facilitating Change
- C. Support Groups and Community Resources: Leveraging External Support
- IV. Evaluation: Measuring Progress and Adapting the Plan
- A. Monitoring Progress: Tracking Key Indicators
- B. Addressing Challenges and Modifying the Plan: Adapting to Changing Needs
- C. Discharge Planning: Preparing for Continued Recovery
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Substance Use and Addictive Disorders: A Comprehensive Guide Using the ATI Template
This article provides a comprehensive overview of substance use and addictive disorders, utilizing a framework inspired by the ATI (Assessment Technologies Institute) template commonly used in nursing education. We'll cover assessment, planning, implementation, and evaluation, focusing on the crucial elements for understanding and managing these complex conditions. This guide aims to equip readers with a strong foundation of knowledge, though it should not be considered a substitute for professional medical advice.
I. Assessment: Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms
Accurate assessment is the cornerstone of effective intervention for substance use and addictive disorders. This stage involves a multifaceted approach, integrating various data sources to create a holistic picture of the individual's situation.
A. History Taking: Unveiling the Story Behind the Addiction
Thorough history taking is critical. This includes:
- Substance Use History: Detailed information about the type of substance(s) used, frequency of use, amount consumed per episode, duration of use, route of administration (e.g., oral, injection, inhalation), and pattern of use (e.g., daily, binge). Past attempts at cessation or reduction are equally important.
- Family History: A strong family history of substance use disorders significantly increases the risk of developing the condition. Exploring this history can provide valuable insight into genetic predispositions and learned behaviors.
- Social History: Examining the individual's social support network, relationships, employment history, and involvement in social activities can help determine contributing factors and potential resources. Isolation and lack of support frequently exacerbate addiction.
- Medical History: Existing medical conditions, including mental health disorders, can influence substance use and treatment options. Comorbid conditions are common and require integrated management. This includes a complete medication history, both prescribed and over-the-counter, to identify potential drug interactions.
- Psychological History: Assessing for underlying psychological conditions like depression, anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), or personality disorders is crucial. These conditions often co-occur with substance abuse and require concurrent treatment.
B. Physical Examination: Detecting the Physical Manifestations
A comprehensive physical examination is necessary to identify the physical effects of substance abuse. This may reveal:
- Signs of withdrawal: Physical symptoms experienced when ceasing substance use, which vary depending on the substance. These can range from mild discomfort to life-threatening complications.
- Organ damage: Prolonged substance use can damage vital organs, such as the liver, kidneys, heart, and lungs. Physical signs may include jaundice, edema, abnormal heart rhythms, or respiratory distress.
- Nutritional deficiencies: Substance abuse often leads to poor nutrition, resulting in weight loss, muscle wasting, and other deficiencies.
- Infections: Individuals who inject substances are at increased risk of infections like HIV, Hepatitis B, and Hepatitis C.
- Trauma-related injuries: Substance abuse can impair judgment and increase risky behaviors, leading to physical injuries.
C. Psychological Assessment: Understanding the Underlying Issues
Assessing the psychological aspects of addiction is equally important. This involves:
- Mental Status Examination: Evaluating cognitive function, mood, affect, and thought processes to identify any underlying mental health conditions.
- Personality Assessment: Understanding personality traits and coping mechanisms can help determine the individual's readiness for change and tailor treatment accordingly.
- Motivation for Change: Assessing the individual's level of motivation to engage in treatment is crucial for determining the success of the intervention.
- Readiness for Change (Stages of Change Model): Understanding the individual's stage of change (precontemplation, contemplation, preparation, action, maintenance) helps tailor interventions to their current level of readiness.
- Severity of Addiction: Utilizing standardized assessment tools to gauge the severity of the addiction helps determine the appropriate level of care.
II. Planning: Developing a Comprehensive Treatment Strategy
The planning phase involves developing a comprehensive and individualized treatment plan based on the assessment findings.
A. Goals and Objectives: Defining Success
Specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals are crucial. These should focus on:
- Substance abstinence: Achieving and maintaining abstinence from the substance(s) of abuse.
- Improved physical health: Addressing any physical health issues resulting from substance abuse.
- Improved mental health: Addressing any co-occurring mental health disorders.
- Enhanced coping skills: Developing healthy coping mechanisms to manage stress and cravings.
- Improved social functioning: Rebuilding social support networks and improving relationships.
- Increased self-esteem: Building self-esteem and a sense of self-worth.
B. Treatment Modalities: Tailoring the Approach
The choice of treatment modalities depends on various factors, including the type of substance, severity of addiction, co-occurring disorders, and individual preferences. Options may include:
- Detoxification: Medically supervised withdrawal from the substance.
- Medication-assisted treatment (MAT): Using medications to manage withdrawal symptoms and cravings. Examples include methadone for opioid addiction, buprenorphine, naltrexone, and acamprosate for alcohol dependence.
- Individual therapy: Providing one-on-one counseling to address underlying issues contributing to addiction.
- Group therapy: Offering a supportive environment where individuals can share their experiences and learn from others.
- Family therapy: Involving family members in the treatment process to improve communication and support.
- Behavioral therapies: Using techniques like cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and motivational interviewing to change thoughts, feelings, and behaviors.
- 12-step programs: Participation in support groups like Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) or Narcotics Anonymous (NA).
C. Relapse Prevention Planning: Preparing for Challenges
Relapse is a common occurrence in addiction recovery. A relapse prevention plan should address:
- Identifying triggers: Identifying situations, people, or feelings that increase the risk of relapse.
- Developing coping strategies: Creating a plan to manage cravings and high-risk situations.
- Building a support system: Establishing a network of supportive individuals to provide assistance during challenging times.
- Developing a crisis plan: Creating a plan to address relapse if it occurs.
III. Implementation: Putting the Plan into Action
Implementing the treatment plan requires a collaborative effort between the individual, healthcare professionals, and support systems.
A. Medication Management: Overseeing the Treatment
Medication management, if prescribed, requires careful monitoring and adjustment based on the individual's response. This includes:
- Dosage adjustments: Adjusting medication dosages based on individual needs and tolerance.
- Adverse effect monitoring: Monitoring for adverse effects and taking appropriate action.
- Medication adherence: Ensuring adherence to the prescribed medication regimen.
B. Therapeutic Interventions: Facilitating Change
Therapeutic interventions are critical for addressing the underlying psychological issues contributing to addiction. This includes:
- Individual therapy sessions: Providing consistent and supportive counseling.
- Group therapy participation: Facilitating participation in group therapy sessions.
- Family therapy sessions: Improving communication and dynamics within the family.
- Behavioral therapy techniques: Implementing techniques such as CBT and motivational interviewing.
C. Support Groups and Community Resources: Leveraging External Support
Utilizing community resources and support groups is crucial for fostering a strong support network:
- 12-step programs: Encouraging active participation in 12-step programs such as AA or NA.
- Support groups for families: Offering support and education for family members affected by addiction.
- Community resources: Connecting individuals with community resources such as housing, employment, and healthcare services.
IV. Evaluation: Measuring Progress and Adapting the Plan
Regular evaluation is essential to assess the effectiveness of the treatment plan and make necessary adjustments.
A. Monitoring Progress: Tracking Key Indicators
Progress should be monitored through:
- Substance use: Tracking abstinence or reduction in substance use.
- Physical health: Monitoring physical health markers.
- Mental health: Assessing mental health symptoms.
- Social functioning: Evaluating social interactions and relationships.
- Quality of life: Measuring overall quality of life.
B. Addressing Challenges and Modifying the Plan: Adapting to Changing Needs
The treatment plan should be flexible and adjusted based on the individual's progress and challenges encountered. This may involve:
- Changing treatment modalities: Adjusting the treatment approach based on the individual's response.
- Increasing support: Providing additional support and resources as needed.
- Addressing relapses: Developing strategies to manage and prevent future relapses.
C. Discharge Planning: Preparing for Continued Recovery
Discharge planning involves developing a plan for continued recovery after the completion of formal treatment. This includes:
- Aftercare planning: Developing a plan for ongoing support and treatment.
- Relapse prevention strategies: Reinforcing relapse prevention techniques.
- Community resources: Connecting individuals with community resources for ongoing support.
This comprehensive guide using an ATI-inspired template provides a foundational understanding of substance use and addictive disorders. Remember, addiction is a complex condition requiring a multifaceted approach involving healthcare professionals, support systems, and the individual's commitment to recovery. This information is for educational purposes and should not substitute professional medical advice. Always consult with qualified healthcare providers for diagnosis and treatment.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Cat On A Hot Tin Roof Big Mama
Apr 04, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Sentences Uses The Active Voice
Apr 04, 2025
-
1 03 Quiz Evaluate Arguments And Fallacious Reasoning
Apr 04, 2025
-
Night Elie Wiesel Chapter 4 Summary
Apr 04, 2025
-
What Happened In Chapter 17 Of The Giver
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Substance Use And Addictive Disorders Ati Template . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
