The Arbor Vitae Refers To ________.
Onlines
Mar 15, 2025 · 6 min read
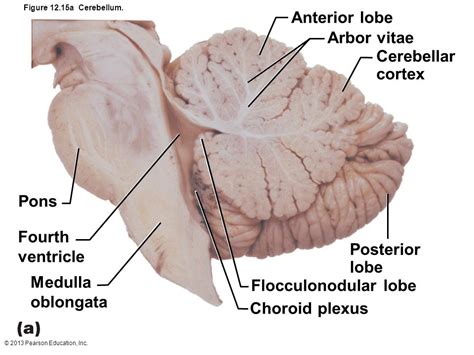
Table of Contents
The Arbor Vitae Refers to: A Deep Dive into the Tree of Life
The phrase "arbor vitae" literally translates from Latin to "tree of life," a name evocative of its intricate, branching structure. However, the term "arbor vitae" doesn't refer to a single entity. Instead, it's used in several distinct contexts, each referencing a structure resembling a tree in its complexity and appearance. This article will explore the various meanings of "arbor vitae," delving into the anatomical, botanical, and historical contexts where this evocative phrase is employed.
Arbor Vitae in Anatomy: The Cerebellar Structure
In the field of neuroanatomy, the arbor vitae refers to the white matter of the cerebellum. This distinctive pattern, visible in both dissected specimens and medical imaging, is crucial for understanding the cerebellum's function and structure. The branching pattern resembles the branches of a tree, hence the name.
The Cerebellum and its White Matter:
The cerebellum, a major part of the brain located at the back of the skull, plays a vital role in motor control, coordination, balance, and posture. It receives sensory input from various parts of the body and uses this information to fine-tune movements, ensuring smooth, coordinated actions. The cerebellum's outer layer, the cerebellar cortex, is composed of grey matter, densely packed with neurons responsible for processing information. Beneath the cortex lies the white matter, which consists primarily of myelinated axons – nerve fibers that transmit signals between different parts of the cerebellum and other brain regions.
Anatomy of the Arbor Vitae:
The arbor vitae's distinctive tree-like appearance arises from the arrangement of these myelinated axons. They radiate outwards from the cerebellar peduncles, which are bundles of nerve fibers connecting the cerebellum to the brainstem. These fibers branch and subdivide, creating a complex network that allows for efficient communication between various parts of the cerebellum. The branching pattern is highly organized, reflecting the functional organization of the cerebellum. The central part of the arbor vitae, the medullary center, is relatively denser, giving it a slightly different appearance compared to the branching pattern of the white matter tracts.
Clinical Significance:
The arbor vitae's integrity is essential for normal cerebellar function. Damage to this structure, resulting from trauma, stroke, or other neurological conditions, can lead to a range of motor impairments, including ataxia (lack of coordination), tremor, dysmetria (inability to judge distance), and difficulties with balance. Medical imaging techniques like MRI and CT scans can visualize the arbor vitae, allowing clinicians to assess its structural integrity and detect any abnormalities that may indicate underlying neurological conditions. The arbor vitae's appearance on these scans can provide important clues to the location and extent of cerebellar lesions. Changes in the appearance of the arbor vitae, such as irregularities or blurring, might indicate pathologies such as tumors or demyelinating diseases.
Arbor Vitae in Botany: The Thuja Species
In botany, the term "arbor vitae" most often refers to trees belonging to the genus Thuja, commonly known as cedars or arborvitae. These evergreen conifers are valued for their aromatic wood, and they are commonly grown as ornamental trees or used in landscaping. The name reflects the scale-like leaves, arranged in overlapping, feathery sprays, which resemble the branching patterns of the anatomical arbor vitae.
Thuja Species and Their Characteristics:
Several Thuja species exist, each with slightly different characteristics, including variations in size, foliage color, and hardiness. These trees are generally characterized by their pyramidal or conical shape, their strong, aromatic wood, and their scale-like leaves. The leaves, tightly pressed against the branches, are usually dark green but can have hints of yellow or gold, depending on the species and cultivar. Thuja species are widespread, with various species growing in different parts of North America, Asia, and Europe.
Uses of Thuja Trees:
Thuja species have been used for various purposes throughout history. Their wood, resistant to rot and decay, is used in construction, crafting, and furniture making. The aromatic oils extracted from the leaves and wood have been used in traditional medicine and as an ingredient in perfumes and cosmetics. Some species are also valued for their ornamental appeal, used in landscaping and gardening to create hedges, screens, and accent pieces.
Medicinal Properties and Caution:
While some historical and traditional uses exist for the oils and extracts of Thuja species, it's crucial to note that many Thuja species contain thujone, a potentially toxic compound. Ingesting large quantities of thujone can lead to serious health consequences. Therefore, the use of Thuja for medicinal purposes should be approached with caution, and it is strongly recommended to consult with a healthcare professional before considering such applications. Never self-medicate. Always use commercially prepared products and follow directions carefully. Avoid any home remedies without professional consultation.
Arbor Vitae in History and Culture: Symbolism and Significance
The phrase "arbor vitae" carries symbolic weight beyond its anatomical and botanical meanings. The image of a tree of life, representing immortality, growth, and connection to the divine, is found across many cultures and religions. In some contexts, the term "arbor vitae" can be used figuratively to denote complex, branching systems or networks of knowledge and information.
Arbor Vitae in Medieval Art:
The intricate branching pattern of the anatomical arbor vitae inspired artists and illuminated manuscript creators in the medieval period. Its representation in anatomical drawings and texts reflected the perceived complexity and mystery of the human brain. The visual resemblance to a tree was seen as symbolic, connecting the human body to the natural world and the divine.
Arbor Vitae as a Metaphor:
The evocative phrase "arbor vitae" frequently serves as a metaphor. It can symbolize a vast, interconnected network, like a family tree, an organizational chart, or a knowledge base. Its use in this context underscores the complexity and interconnectedness of the system it describes.
Conclusion: The Multifaceted Meaning of "Arbor Vitae"
The term "arbor vitae" encapsulates a rich tapestry of meaning, extending from the intricate neural pathways of the human cerebellum to the elegant branching structure of the Thuja tree. Its multifaceted nature reflects the enduring fascination with the complexity of living systems, both biological and symbolic. Understanding the different contexts in which this phrase is used provides a deeper appreciation for its varied significance in anatomy, botany, history, and even metaphor. While the literal translation remains constant, the underlying meaning subtly shifts depending on the context, making "arbor vitae" a compelling and versatile term. From the microscopic intricacies of the brain to the towering presence of the Thuja tree, the "tree of life" continues to inspire and intrigue. Remember always to consult with qualified professionals when dealing with health or botanical matters. The information provided here is for educational purposes and should not be considered medical or botanical advice.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A 35 Year Old Woman Is In The Hospital
Mar 15, 2025
-
Figurative Language Worksheet 2 Answer Key
Mar 15, 2025
-
Correctly Label The Following Major Systemic Arteries
Mar 15, 2025
-
The Graph Of The Relation S Is Shown Below
Mar 15, 2025
-
Which Sentence Most Clearly Uses A Stereotype
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Arbor Vitae Refers To ________. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
