The Beaks Of Finches Lab Answers Pdf
Onlines
Mar 19, 2025 · 7 min read
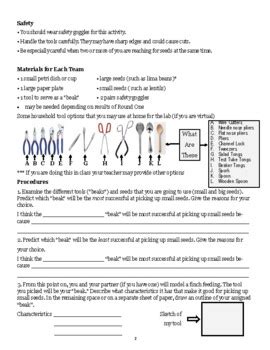
Table of Contents
Decoding Darwin's Finches: A Comprehensive Guide to the Beaks of Finches Lab
The "Beaks of Finches" lab is a staple in biology education, providing a hands-on experience with evolutionary principles and natural selection. This comprehensive guide delves into the lab's objectives, procedures, potential results, and answers, offering a detailed understanding of Darwin's finches and their remarkable adaptations. We will explore the concepts behind the lab, providing a framework for interpreting your results and strengthening your understanding of evolutionary biology. This guide aims to go beyond simple answers, providing context and deeper insights into the fascinating world of Darwinian evolution.
Understanding the Objectives of the "Beaks of Finches" Lab
The primary objective of the "Beaks of Finches" lab is to simulate the process of natural selection, demonstrating how environmental pressures drive evolutionary change in a population over time. Students use different tools (simulating different beak types) to collect "food" (representing different food sources). This simulates the struggle for survival and the selective pressures that favor certain beak adaptations. Through this simulation, students gain a concrete understanding of:
- Natural Selection: The process by which organisms better adapted to their environment tend to survive and produce more offspring.
- Adaptation: The adjustment or changes in an organism, or its parts, that make it better suited to its environment. In this lab, beak shape is the key adaptation.
- Variation: The presence of differences in traits within a population. Different beak types represent this variation.
- Competition: The struggle between organisms for limited resources. The scarcity of food simulates this competition.
- Evolution: The gradual change in the heritable characteristics of a population over successive generations.
Key Concepts to Grasp Before Starting the Lab
Before diving into the lab itself, it's crucial to understand several key evolutionary biology concepts:
- Heritability: Traits must be heritable (passed down from parents to offspring) for natural selection to operate effectively. Beneficial traits are more likely to be passed on, leading to their increase in the population.
- Fitness: Fitness refers to an organism's ability to survive and reproduce in its environment. Organisms with higher fitness are more likely to pass on their genes.
- Environmental Pressure: Factors in the environment that influence the survival and reproduction of organisms. In the lab, the type and availability of food represent the environmental pressure.
The "Beaks of Finches" Lab Procedure: A Step-by-Step Guide
While specific lab procedures might vary slightly depending on the educational institution or resource used, the core elements remain consistent. A typical "Beaks of Finches" lab involves the following steps:
-
Defining the Food Sources: The lab typically uses various types of "food," like beads, seeds, beans, or small pieces of pasta, each representing a different food source available in a particular environment. The size, shape, and hardness of the "food" will represent different challenges for the various "beak" types.
-
Assigning "Beak" Types: Students are assigned different tools to simulate different beak types. These tools might include tweezers, forceps, clothespins, or even spoons, each representing a different beak morphology. This variation mimics the diversity of beak shapes found in Darwin's finches.
-
The "Foraging" Process: Students then compete to collect the most "food" within a set time limit. This simulates the competition for limited resources in the natural environment. The efficiency of each "beak" type in collecting different food sources will vary.
-
Data Collection and Analysis: Students record their results, noting the number of each type of "food" collected by each "beak" type. This data is crucial for analyzing the success of different beak adaptations.
-
Interpreting the Results: After the simulation, students analyze their data to understand which "beak" types were most successful with each type of "food." This analysis directly demonstrates the principle of natural selection—certain beak types are better suited for specific food sources, leading to their greater survival and reproduction.
-
Drawing Conclusions: Finally, students draw conclusions about the relationship between beak shape, food availability, and evolutionary success. They discuss how environmental pressures (the type of food available) drive the evolution of beak morphology in a finch population.
Analyzing the Results and Interpreting the Data
The success of different "beak" types in acquiring different food sources will directly reflect the principles of natural selection. For example:
- Tweezers: Might be most effective at picking up small, delicate seeds.
- Forceps: Might excel at picking up slightly larger seeds.
- Clothespins: Might be best suited for larger, harder items.
- Spoons: Might be efficient at scooping up a large quantity of smaller items.
Analyzing the data will reveal which "beak" type was most successful overall, and which were most successful with specific food types. This analysis is key to understanding how environmental pressures shape the evolution of beak morphology. A successful "beak" type will have collected significantly more food than others, demonstrating higher fitness in that simulated environment.
Addressing Potential Questions and Providing Answers
The "Beaks of Finches" lab often leads to insightful questions. Here are some common questions and their answers:
Q: What if some students are naturally better at using certain tools than others?
A: This is a valid concern. To mitigate this, the lab should be conducted multiple times with each student using different "beak" types. Averaging the results across multiple trials reduces the impact of individual skill differences.
Q: How does this lab simulate genetic inheritance?
A: The lab doesn't explicitly model genetic inheritance. However, the success of specific "beak" types represents the selective advantage that certain heritable traits offer. Successful beak types would hypothetically be more prevalent in subsequent generations, mirroring the effect of genetic inheritance in natural selection.
Q: Can the lab perfectly replicate natural selection?
A: No, the lab is a simplified model. It omits factors like mutation, gene flow, genetic drift, and sexual selection, which are all important elements of the evolutionary process. However, it serves as a valuable illustration of the core principles of natural selection.
Q: What are the limitations of this simulation?
A: The main limitations include the simplification of complex evolutionary factors (as mentioned above), the artificial nature of the "food" and "beaks," and the absence of real environmental complexities like predation, disease, and climate change. Nevertheless, the simulation provides a valuable introductory understanding of the underlying processes.
Q: How does this relate to Darwin's finches in the Galapagos Islands?
A: Darwin's finches represent a real-world example of adaptive radiation and natural selection. The different beak shapes observed in these finches are adaptations that evolved in response to the availability of different food sources on the various islands. This lab directly mirrors this process, providing a tangible understanding of Darwin's observations.
Extending the Learning: Further Exploration of Darwin's Finches
The "Beaks of Finches" lab provides a foundation for deeper exploration into the fascinating world of Darwin's finches. Students can investigate:
- The specific species of Darwin's finches: Research the different species of Galapagos finches, their beak morphologies, and their preferred food sources.
- Peter and Rosemary Grant's research: Learn about the long-term studies conducted by the Grants on Daphne Major, which documented the evolutionary changes in finch populations in response to environmental changes.
- The concept of adaptive radiation: Understand how a single ancestral species can diversify into multiple species, each adapted to a specific niche.
- The role of environmental changes in driving evolution: Explore how factors like drought, volcanic eruptions, or introduced species can impact finch populations and their beak morphology.
By exploring these areas, students can gain a more comprehensive understanding of the evolutionary processes that have shaped the remarkable diversity of Darwin's finches.
Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of the "Beaks of Finches" Lab
The "Beaks of Finches" lab provides an engaging and effective method for teaching the principles of natural selection and evolution. By actively participating in the simulation, students gain a deeper and more intuitive understanding of these fundamental concepts than through passive learning. The lab's ability to connect abstract evolutionary principles with a tangible, hands-on experience makes it a valuable tool in science education, leaving a lasting impact on students' understanding of Darwin's legacy and the power of natural selection. This guide aimed to equip you with a thorough understanding of the lab, helping you confidently interpret results and appreciate the fascinating intricacies of evolutionary biology. Remember that this is a simplified model, but its value lies in its ability to bring the abstract concepts of Darwinian evolution to life.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Secondary Math 3 Module 8 Modeling With Functions Answer Key
Mar 20, 2025
-
2 2 5 Practice Illustrating Supply And Demand
Mar 20, 2025
-
Student Exploration Longitudinal Waves Answer Key
Mar 20, 2025
-
Ecuador Divide Los Andes En Varias Regiones
Mar 20, 2025
-
Hoy Voy A Ir De Compras Al 1 Of 1
Mar 20, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Beaks Of Finches Lab Answers Pdf . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
