The Break Even Point Is That Level Of Activity Where
Onlines
Apr 03, 2025 · 6 min read
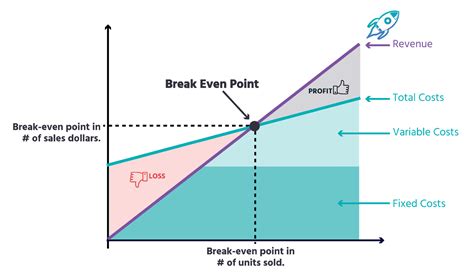
Table of Contents
The Break-Even Point: Where Revenue Meets Costs
The break-even point (BEP) is a crucial concept in business and finance. It represents the level of activity – be it sales units, revenue, or production – where total revenue equals total costs. In simpler terms, it's the point at which a business neither makes a profit nor incurs a loss. Understanding the break-even point is vital for businesses of all sizes, from startups to established corporations, as it provides a benchmark for assessing financial viability and making informed decisions. This comprehensive guide will delve deep into the concept of the break-even point, exploring its calculation, applications, limitations, and importance in strategic business planning.
Understanding the Components of the Break-Even Point
Before we delve into the calculation, let's define the key components involved:
1. Fixed Costs:
These are expenses that remain constant regardless of the level of production or sales. Examples include:
- Rent: Monthly rent for office space or a factory remains the same whether you produce 10 units or 1000 units.
- Salaries: Fixed salaries paid to employees are generally consistent.
- Insurance Premiums: These costs are typically fixed for a specific period.
- Depreciation: The decrease in the value of assets over time is a fixed cost.
- Property Taxes: These taxes remain consistent for a given property.
2. Variable Costs:
These expenses fluctuate directly with the level of production or sales. Examples include:
- Raw Materials: The cost of materials directly used in production increases proportionally with output.
- Direct Labor: Wages paid to production workers are directly related to the number of units produced.
- Sales Commissions: Commissions paid to salespeople are directly tied to the sales volume.
- Packaging and Shipping: These costs increase with the number of units sold or shipped.
3. Contribution Margin:
The contribution margin is the difference between revenue and variable costs. It represents the portion of revenue available to cover fixed costs and contribute to profit. It can be expressed as a per-unit contribution margin or a total contribution margin.
- Per-unit Contribution Margin: Selling price per unit - Variable cost per unit
- Total Contribution Margin: Total Revenue - Total Variable Costs
Calculating the Break-Even Point
The break-even point can be calculated in two ways:
1. Break-Even Point in Units:
This method determines the number of units a business needs to sell to reach the break-even point. The formula is:
Break-Even Point (Units) = Fixed Costs / (Selling Price per Unit - Variable Cost per Unit)
Or, more concisely:
Break-Even Point (Units) = Fixed Costs / Per-Unit Contribution Margin
Example:
Let's say a business has fixed costs of $10,000, a selling price per unit of $20, and a variable cost per unit of $10.
Break-Even Point (Units) = $10,000 / ($20 - $10) = 1,000 units
This means the business needs to sell 1,000 units to cover its costs and break even.
2. Break-Even Point in Sales Dollars:
This method determines the total revenue a business needs to generate to reach the break-even point. The formula is:
Break-Even Point (Sales Dollars) = Fixed Costs / ((Sales Revenue - Variable Costs) / Sales Revenue)
Or, more concisely using the contribution margin ratio:
Break-Even Point (Sales Dollars) = Fixed Costs / Contribution Margin Ratio
Where the Contribution Margin Ratio is: (Sales Revenue - Variable Costs) / Sales Revenue
Example:
Using the same example above, with fixed costs of $10,000, a selling price of $20, and variable costs of $10 per unit:
Contribution Margin Ratio = ($20 - $10) / $20 = 0.5 or 50%
Break-Even Point (Sales Dollars) = $10,000 / 0.5 = $20,000
This means the business needs to generate $20,000 in sales revenue to break even.
Applications of the Break-Even Point Analysis
The break-even analysis is a versatile tool with numerous applications in various business scenarios:
- Pricing Strategies: Understanding the break-even point helps businesses set appropriate prices that ensure profitability. By adjusting pricing, a company can quickly see the impact on its BEP.
- Cost Control: Analyzing the break-even point highlights areas where cost reduction is critical for improving profitability. Identifying and minimizing unnecessary expenses can significantly lower the BEP.
- Sales Forecasting: The break-even point provides a realistic sales target that must be achieved to avoid losses. This informs sales planning and resource allocation.
- New Product Launches: Before launching a new product, businesses use break-even analysis to determine the required sales volume to achieve profitability. This is crucial for assessing the viability of new ventures.
- Investment Decisions: Investors utilize break-even analysis to assess the financial feasibility of potential investments. Reaching the BEP quickly demonstrates the viability of the project.
- Business Planning: Break-even analysis is a vital component of a comprehensive business plan, demonstrating to investors and lenders the financial viability of a business.
Limitations of Break-Even Analysis
While break-even analysis is a powerful tool, it has certain limitations:
- Simplified Model: The analysis assumes a linear relationship between costs and revenue, which may not always hold true in reality. It often overlooks economies of scale and other complexities.
- Static Analysis: The break-even point is calculated at a specific point in time and doesn't account for changes in costs, prices, or demand over time. It's a snapshot, not a moving picture.
- Ignoring Other Factors: The analysis doesn't incorporate factors such as marketing expenses, research and development, and competition, which significantly influence a business's profitability.
- Difficulty in Forecasting: Accurate forecasting of costs and revenue is crucial for reliable break-even analysis. Inaccurate estimations lead to unreliable results.
Improving Accuracy and Practicality of Break-Even Analysis
To overcome the limitations mentioned above, businesses can enhance their break-even analysis by:
- Sensitivity Analysis: Conducting sensitivity analysis by varying assumptions (e.g., sales price, variable costs) provides a range of possible break-even points, offering a more realistic view.
- Scenario Planning: Developing multiple scenarios (best-case, worst-case, and most-likely) helps businesses prepare for different market conditions and refine their strategies accordingly.
- Incorporating Time Value of Money: For long-term projects, incorporating the time value of money (discounting future cash flows) is crucial for a more accurate assessment of profitability.
- Regular Monitoring and Adjustment: The break-even point should be regularly reviewed and adjusted as market conditions and internal factors change.
Beyond the Break-Even Point: Profit Maximization
While achieving the break-even point is essential for survival, the ultimate goal for any business is profit maximization. Understanding the break-even point is the first step towards achieving this goal. By carefully managing costs, setting optimal prices, and increasing sales volume beyond the break-even point, businesses can significantly enhance their profitability.
Conclusion
The break-even point is a fundamental concept in business finance that helps businesses understand the level of activity required to cover their costs. While its calculation is relatively straightforward, understanding its implications and limitations is vital for making informed decisions. By incorporating sensitivity analysis, scenario planning, and regular monitoring, businesses can use break-even analysis as a powerful tool for strategic planning, pricing strategies, cost control, and ultimately, achieving sustainable profitability and growth. Remember that the break-even point is not just a static number; it's a dynamic benchmark that evolves with changing market conditions and business strategies. Continuously analyzing and adjusting your break-even point ensures your business remains on the path to success.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Esta Manana Salimos A Comprar Las Invitaciones
Apr 04, 2025
-
Which Culture Fears Silence Rather Than Embracing It
Apr 04, 2025
-
What Do You Say To A Misbehaving Polar Bear
Apr 04, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Statements About Group Writing Are True
Apr 04, 2025
-
11 3 Practice Problems Continued Chemistry Answer Key
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Break Even Point Is That Level Of Activity Where . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
