The Decision Making Process In Driving Is Known As
Onlines
Mar 18, 2025 · 6 min read
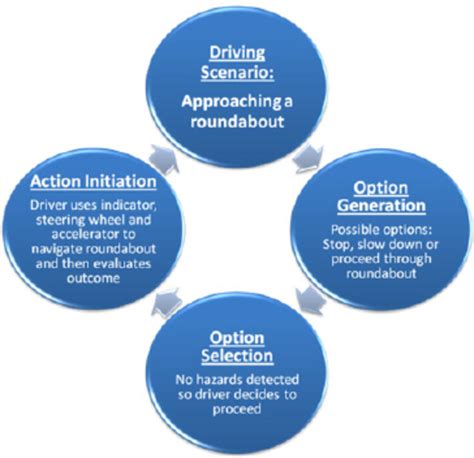
Table of Contents
The Decision-Making Process in Driving: A Deep Dive into Situational Awareness and Risk Assessment
Driving is far more than just operating a vehicle; it's a continuous process of decision-making. Every second behind the wheel presents a new set of variables requiring rapid, accurate judgments. This complex cognitive process, often unconscious for experienced drivers, involves a multifaceted interplay of perception, assessment, and response. Understanding the intricacies of this decision-making process is crucial for improving driving skills, enhancing safety, and reducing accidents. This article explores the key elements involved, from initial perception to final action.
1. Perception: The Foundation of Driving Decisions
The first stage in any driving decision is perception. This refers to the driver's ability to actively gather information from their environment using all available senses:
-
Vision: This is paramount, providing information on road conditions, other vehicles, pedestrians, signage, and more. Peripheral vision plays a vital role in detecting potential hazards outside the direct line of sight. Effective visual scanning techniques are essential for comprehensive perception.
-
Hearing: Sounds like horns, sirens, screeching tires, or engine noises can alert drivers to potential dangers or the actions of other road users.
-
Touch: Feeling the steering wheel, the road surface through the vehicle's suspension, and even the vibrations of the engine contribute to the overall sensory input.
-
Proprioception: This internal sense provides information about the vehicle's position, speed, and movement relative to the surroundings. It's the unconscious awareness of your body's position in space.
Enhancing Perception: Techniques for Safer Driving
Several techniques can significantly improve perceptual skills:
-
Regular Eye Checks: Avoid fixating on a single point. Constantly scan the road ahead, checking mirrors frequently, and being aware of blind spots.
-
Defensive Driving Techniques: Always anticipate potential hazards and assume other drivers might make mistakes.
-
Minimize Distractions: Cell phones, loud music, and passengers can severely impair perception.
-
Maintain Vehicle Awareness: Regularly check your speed, tire pressure, and overall vehicle condition.
2. Information Processing: Making Sense of the Data
Once information is perceived, the brain must process it quickly and efficiently. This involves:
-
Identifying Relevant Information: Filtering out irrelevant sensory input and focusing on crucial details like approaching vehicles, pedestrians, traffic signals, and road conditions.
-
Assessing Risk: Evaluating the potential dangers associated with different courses of action. This is a critical stage, and misjudging risk is a major cause of accidents.
-
Predicting Outcomes: Anticipating the likely consequences of each decision and choosing the option that minimizes risk. This requires a degree of experience and pattern recognition.
Cognitive Biases in Driving
Cognitive biases are systematic errors in thinking that can affect decision-making. Common biases in driving include:
-
Confirmation Bias: Seeking out information that confirms pre-existing beliefs and ignoring contradictory evidence. For example, a driver might underestimate the speed of an oncoming vehicle if they believe it's safe to proceed.
-
Overconfidence Bias: Overestimating one's own driving abilities and underestimating the risks involved.
-
Anchoring Bias: Over-relying on the first piece of information received when making a judgment. This can lead to errors if the initial information is inaccurate.
-
Inattentional Blindness: Failing to notice unexpected events or objects because the driver’s attention is focused elsewhere.
3. Decision-Making Strategies: Choosing a Course of Action
Based on the processed information and risk assessment, the driver selects a course of action. This involves:
-
Selecting the Best Option: Choosing the course of action that minimizes risk and maximizes safety while considering legal requirements and ethical considerations.
-
Prioritizing Actions: If multiple hazards exist, the driver must prioritize which threat to address first.
-
Executing the Decision: Translating the chosen course of action into physical actions, such as steering, braking, accelerating, or signaling.
Effective Decision-Making Strategies
Several strategies can enhance driving decision-making:
-
SMOG (Space, Margin, Observation, Grace): A framework emphasizing maintaining adequate space, leaving a margin for error, making continuous observations, and having the grace to react appropriately.
-
SEE (Search, Evaluate, Execute): A systematic process for hazard perception and response.
-
IPDE (Identify, Predict, Decide, Execute): Another widely used approach for safe driving.
4. Execution and Feedback: Refining the Process
The final stage involves executing the chosen decision and receiving feedback from the environment. This feedback loop is essential for continuous improvement:
-
Motor Skills: Executing the decision accurately requires precise control over the vehicle. Practice and experience improve motor skills.
-
Feedback Loop: The environment provides constant feedback, indicating whether the decision was effective. Drivers must continuously adapt based on this feedback.
-
Continuous Learning: Driving is a lifelong learning process. By constantly evaluating decisions and adapting to new situations, drivers can improve their skills and reduce their risk of accidents.
5. Factors Influencing Driving Decision-Making
Numerous factors can influence the decision-making process:
-
Experience: Experienced drivers tend to make quicker, more accurate decisions because they have a larger repertoire of experiences to draw upon.
-
Fatigue: Tired drivers have impaired judgment and slower reaction times.
-
Stress: Stress can impair cognitive function, leading to poor decisions.
-
Emotions: Anger, frustration, or anxiety can negatively impact driving performance.
-
Drugs and Alcohol: These substances significantly impair cognitive function and reaction time, increasing the risk of accidents.
-
Environmental Conditions: Adverse weather conditions like rain, snow, or fog can significantly impact perception and decision-making.
6. Advanced Driving Techniques and Decision-Making
Certain advanced techniques can further enhance decision-making capabilities:
-
Predictive Driving: Anticipating the actions of other road users and adjusting your driving accordingly.
-
Smooth Driving Techniques: Avoiding sudden braking, acceleration, or steering inputs.
-
Maintaining a Safe Following Distance: Providing sufficient space between your vehicle and the vehicle in front.
-
Effective Lane Positioning: Choosing the optimal lane position based on traffic conditions and upcoming maneuvers.
7. Technology's Role in Enhancing Driving Decisions
Technology is increasingly playing a vital role in enhancing driving decisions:
-
Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS): Features like lane departure warning, adaptive cruise control, and automatic emergency braking can help prevent accidents.
-
In-Car Navigation Systems: Providing real-time information about traffic conditions and optimal routes.
-
Vehicle-to-Vehicle (V2V) Communication: Enabling vehicles to exchange information about their speed, position, and intended maneuvers.
8. Conclusion: The Ongoing Evolution of Driving Decision-Making
The decision-making process in driving is a complex and dynamic interplay of perception, cognition, and action. While experience plays a crucial role, continuous learning, the application of effective strategies, and the utilization of advanced technologies are all essential for improving driving skills and enhancing safety. By understanding the intricacies of this process, drivers can become more aware of their own decision-making processes, leading to safer and more efficient driving habits. This ultimately contributes to a reduction in accidents and a safer environment for everyone on the road. The ongoing evolution of both driver training and automotive technology promises to further refine and enhance this crucial aspect of driving. Remaining informed about new advancements and continuously practicing safe driving techniques are vital to staying ahead of the curve and ensuring road safety for years to come.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Nos Alojamos En Un Hotel Malo De La Capital
Mar 19, 2025
-
Apes Unit 8 Progress Check Mcq Part A
Mar 19, 2025
-
Why Did The Elephant Jump Up And Down
Mar 19, 2025
-
2 8a Angles Of Triangles Answer Key
Mar 19, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Not True Regarding Security
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Decision Making Process In Driving Is Known As . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
