The Distal Attachment Point Of A Muscle Is The
Onlines
Mar 18, 2025 · 6 min read
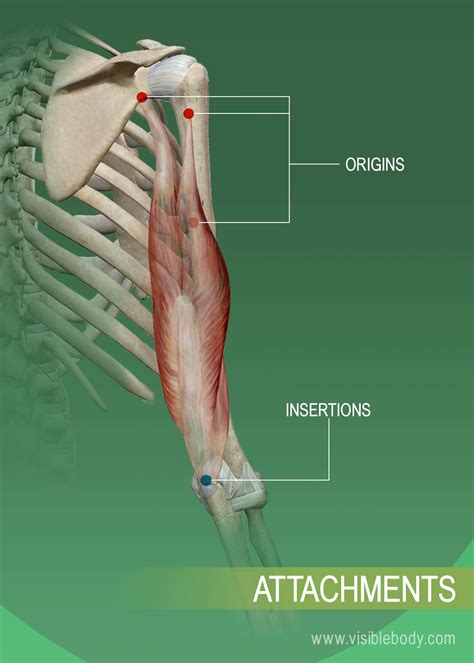
Table of Contents
The Distal Attachment Point of a Muscle Is the...Insertion: A Deep Dive into Muscle Anatomy and Function
Understanding the intricacies of human movement requires a solid grasp of muscle anatomy. One key concept is the distinction between a muscle's origin and insertion points. While the origin is generally considered the relatively stable attachment point, the distal attachment point of a muscle is the insertion. This article delves deep into the meaning of muscle insertion, its significance in movement, and explores various examples across different muscle groups. We'll also touch on clinical implications and the importance of understanding insertions for healthcare professionals and fitness enthusiasts alike.
Defining the Muscle Insertion
The insertion of a muscle is the more mobile attachment point of the muscle to the bone. It's the point where the muscle's contractile force is ultimately transferred, resulting in movement. Think of it as the end of the muscle that moves towards the origin during contraction. Crucially, this definition isn't always static; depending on the movement, the roles of origin and insertion can sometimes reverse. The key is the relative mobility of the attachment points.
Origin vs. Insertion: A Crucial Distinction
It's vital to understand the difference between origin and insertion:
-
Origin: The relatively stationary attachment point of the muscle. Often located closer to the body's midline or on a more stable bone.
-
Insertion: The more mobile attachment point of the muscle. Often located further from the body's midline or on a less stable bone.
Remembering this distinction is crucial for understanding how muscles produce movement. When a muscle contracts, the insertion moves towards the origin.
The Mechanics of Muscle Insertion and Movement
The interaction between a muscle's origin and insertion is the foundation of skeletal movement. Consider a simple example: the biceps brachii muscle.
-
Origin: The coracoid process of the scapula and the supraglenoid tubercle of the scapula. (relatively stable)
-
Insertion: The radial tuberosity of the radius. (more mobile)
When the biceps brachii contracts, the insertion (radial tuberosity) moves towards the origin (scapula), resulting in flexion of the elbow joint. The radius rotates, allowing for supination of the forearm.
Lever Systems and the Role of Insertion
Muscles function using a lever system. The bone acts as the lever, the joint as the fulcrum, and the muscle's force, applied at the insertion, provides the effort. The location of the insertion point relative to the fulcrum significantly impacts the mechanical advantage of the muscle. A further-away insertion point allows for greater range of motion but requires more force, while a closer insertion point allows for greater force production but with a reduced range of motion.
Diverse Examples of Muscle Insertions
The location and nature of muscle insertions vary considerably across the body, reflecting the diverse movements each muscle facilitates. Here are some examples:
Upper Extremity:
- Triceps Brachii: The insertion is on the olecranon process of the ulna, responsible for elbow extension. The stable origin is on the scapula and humerus.
- Deltoid: The insertion is on the deltoid tuberosity of the humerus. Its multiple origins on the clavicle and scapula allow for abduction, flexion, and extension of the shoulder.
- Pectoralis Major: Insertions are on the greater tubercle of the humerus and the crest of the greater tubercle, responsible for adduction, flexion, and medial rotation of the shoulder.
Lower Extremity:
- Quadriceps Femoris (Rectus Femoris, Vastus Lateralis, Vastus Medialis, Vastus Intermedius): The insertion is on the tibial tuberosity via the patellar tendon, extending the knee. The origins are spread across the femur, and in the case of rectus femoris, also on the ilium.
- Hamstrings (Biceps Femoris, Semitendinosus, Semimembranosus): Insertions are on the proximal tibia and fibula, as well as the ischial tuberosity, responsible for knee flexion and hip extension.
- Gastrocnemius: Insertions are on the calcaneus via the Achilles tendon, responsible for plantarflexion of the foot. Its origins are on the medial and lateral condyles of the femur.
Trunk and Head:
- Rectus Abdominis: The insertion is on the pubic symphysis and pubic crest, responsible for trunk flexion. The origin is on the ribs and sternum.
- Trapezius: Insertions span the occipital bone, acromion, and spine of the scapula, responsible for various movements of the scapula and head. Its origin is very broad.
- Sternocleidomastoid: The insertion is on the mastoid process of the temporal bone, responsible for head rotation and flexion. The origin is on the sternum and clavicle.
Clinical Significance of Muscle Insertion Knowledge
Understanding muscle insertions is crucial in various clinical settings:
- Diagnosis of Muscle Injuries: Knowing the insertion points helps in localizing muscle strains and tears, facilitating accurate diagnosis and treatment. A tear at the insertion point might manifest differently than a mid-belly tear.
- Orthopedic Surgery: Surgeons need precise knowledge of muscle attachments for successful surgeries involving tendons, bones, and muscles. Precise repair of insertions is critical for restoring function.
- Rehabilitation: Physical therapists utilize knowledge of muscle insertions to design effective rehabilitation programs after injury or surgery. Targeted exercises can strengthen the insertion points, promoting healing and restoring muscle function.
- Sports Medicine: Understanding muscle insertions is vital in preventing and managing sports injuries. Proper training techniques and injury prevention strategies can be developed by targeting potential stress points at the insertions.
Practical Applications Beyond the Clinic
Even outside clinical settings, an understanding of muscle insertions is beneficial:
- Fitness Training: Knowing where muscles insert informs the design of effective exercise programs. Exercises targeting specific muscle insertions can enhance strength, power, and muscle growth.
- Bodybuilding: Bodybuilders use this knowledge to optimize training routines, focusing on exercises that effectively stimulate muscle growth at the insertion points.
- Movement Analysis: Coaches, athletes, and movement specialists benefit from understanding the role of muscle insertions in generating movement patterns. Identifying imbalances or inefficiencies can lead to performance improvements.
Insertions: A Dynamic Concept
While we often think of muscle origins and insertions as fixed points, it’s important to remember that the concept is dynamic. The role of origin and insertion can switch depending on the movement being performed. For instance, consider a pull-up. While the biceps brachii's insertion is usually described as the radial tuberosity, during a pull-up, the body's weight acts as a resistance force that pulls the radius downwards and thus towards the origin of the muscle. In this context, the origin is actually the point of less movement, and the relationship is flipped. Therefore, a more comprehensive understanding involves considering the relative movement of the bones involved.
Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding Muscle Insertions
The distal attachment point of a muscle, the insertion, is not merely an anatomical detail. It's a critical component in understanding human movement, injury mechanisms, and the effectiveness of interventions. From clinical diagnosis to fitness training, a thorough grasp of muscle insertions is essential for healthcare professionals, fitness enthusiasts, and anyone interested in the fascinating world of human anatomy and biomechanics. Further research into specific muscle groups and their respective insertions can yield a deeper understanding of individual muscle actions and their combined contribution to coordinated movement. Continuous learning in this field expands our comprehension of the complexity of human motion.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Hamlet Act 3 Scene 2 Summary
Mar 19, 2025
-
Visita Exclusiva Al Museo De Arte Moderno De Nueva York
Mar 19, 2025
-
Project Managers Should Always Reward People Who Work Overtime
Mar 19, 2025
-
The Most Creative Scientists Are Those Who
Mar 19, 2025
-
Does Pearl And Trip Do It
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Distal Attachment Point Of A Muscle Is The . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
