The Earnings Spread For A Bank Is Equal To:
Onlines
Mar 19, 2025 · 6 min read
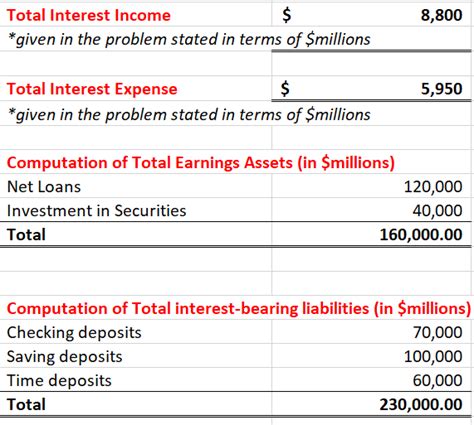
Table of Contents
The Earnings Spread for a Bank: A Comprehensive Guide
The earnings spread, a cornerstone of banking profitability, represents the difference between the interest a bank earns on its assets and the interest it pays on its liabilities. Understanding this spread is crucial for analyzing a bank's financial health, assessing its risk profile, and predicting its future performance. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the intricacies of the banking earnings spread, exploring its components, influencing factors, and implications for investors and regulators alike.
Understanding the Components of the Earnings Spread
The earnings spread, at its core, is a simple calculation:
Earnings Spread = Interest Income on Assets - Interest Expense on Liabilities
However, the simplicity of the formula belies the complexity of its components. Let's break down each element:
Interest Income on Assets
This represents the revenue a bank generates from its interest-earning assets. These assets can include:
- Loans: This is typically the largest component of interest income, encompassing various loan types like mortgages, consumer loans, commercial loans, and credit card receivables. The interest rate charged on these loans significantly influences the overall spread.
- Securities: Banks invest in various securities, including government bonds, corporate bonds, and other marketable securities. The yield on these investments contributes to interest income.
- Other Interest-Earning Assets: This category encompasses less prominent but still important assets, such as repurchase agreements and other short-term investments.
The interest income generated from these assets is affected by several factors, including prevailing interest rates, the credit quality of borrowers, the mix of assets held, and the overall economic climate.
Interest Expense on Liabilities
This represents the cost of funds for a bank. The major components of liabilities include:
- Deposits: This comprises the largest portion of a bank's liabilities. It includes various deposit types such as checking accounts, savings accounts, certificates of deposit (CDs), and money market accounts. The interest rate paid on these deposits directly impacts the interest expense.
- Borrowings: Banks may borrow funds from other financial institutions, the central bank, or through the issuance of debt instruments. The interest rates on these borrowings are critical to the overall spread.
- Other Liabilities: This category includes less common liabilities like subordinated debt and other short-term obligations.
The interest expense is significantly affected by prevailing interest rates, competition among banks for deposits, the bank's funding strategy, and its overall risk profile.
Factors Influencing the Earnings Spread
Several factors exert significant influence on a bank's earnings spread. Understanding these factors is critical for accurately interpreting the spread and predicting its future trajectory.
Interest Rate Environment
The prevailing interest rate environment has a profound impact on the earnings spread. Rising interest rates generally lead to higher interest income on assets, but also to higher interest expense on liabilities. The impact on the spread depends on the sensitivity of the bank's assets and liabilities to interest rate changes (duration gap). A bank with a positive duration gap will generally benefit from rising interest rates, whereas a bank with a negative duration gap may see its spread compressed.
Competition
Intense competition among banks for deposits can lead to higher interest rates paid on liabilities, squeezing the spread. Conversely, less competition can allow banks to maintain lower interest expense, leading to a wider spread.
Credit Risk
The credit risk associated with a bank's loan portfolio directly influences its earnings spread. Higher default rates on loans reduce interest income, negatively impacting the spread. Banks with more conservative lending practices and lower default rates tend to enjoy wider spreads.
Liquidity Management
Efficient liquidity management is crucial for maintaining a healthy earnings spread. Banks need to ensure they have sufficient liquid assets to meet their obligations while also maximizing interest income on their overall asset portfolio. Poor liquidity management can force banks to borrow funds at higher interest rates, reducing their spread.
Economic Conditions
The overall economic environment significantly affects the earnings spread. During economic expansions, banks often benefit from higher loan demand and lower default rates, leading to wider spreads. However, during recessions, loan defaults can increase, and competition for deposits can intensify, potentially compressing the spread.
Regulatory Changes
Regulatory changes, such as reserve requirements and capital adequacy ratios, can also impact a bank's earnings spread. These regulations influence a bank's funding costs and the types of assets it can hold, indirectly affecting the interest income and expense components.
Technological advancements
The introduction of new technologies like Fintech has affected how banks operate, impacting both their assets and liabilities. The rise of digital banking has, for example, allowed for lower operating costs and may allow for higher interest offered on deposits, depending on the strategy of the banks involved.
Analyzing the Earnings Spread: Implications for Investors and Regulators
The earnings spread provides valuable insights for both investors and regulators.
For Investors
Investors use the earnings spread as a key indicator of a bank's profitability and financial health. A consistently wide spread indicates strong profitability, while a narrowing or shrinking spread may signal potential problems. Investors also analyze the trends in the spread over time to identify potential risks and opportunities. Understanding the factors influencing the spread helps investors make informed investment decisions.
For Regulators
Regulators use the earnings spread as an important indicator of a bank's financial stability. A narrow spread may indicate that a bank is taking on excessive risks to maintain profitability, potentially threatening its solvency. Regulators also monitor trends in the earnings spread across the banking sector to assess the overall health of the financial system. Supervisory actions may be taken if regulators identify problematic trends in the spread.
Beyond the Basic Spread: Net Interest Margin and Other Metrics
While the earnings spread is a fundamental metric, it's often insufficient on its own for comprehensive analysis. Here are some related metrics that provide a more holistic picture:
- Net Interest Margin (NIM): NIM is a more comprehensive measure of profitability that considers non-interest income and expenses. It is calculated as (Net Interest Income / Average Earning Assets). NIM offers a more nuanced view of bank profitability than the simple earnings spread.
- Return on Assets (ROA): ROA measures a bank's profitability relative to its assets. It is calculated as (Net Income / Average Total Assets). ROA considers all sources of income and expenses, providing a broader picture of bank performance.
- Return on Equity (ROE): ROE measures a bank's profitability relative to its equity. It is calculated as (Net Income / Average Total Equity). ROE focuses on the return generated for shareholders.
Analyzing these metrics in conjunction with the earnings spread provides a more complete understanding of a bank's financial health and profitability.
Conclusion: The Earnings Spread as a Vital Financial Indicator
The earnings spread, though seemingly straightforward, offers valuable insights into the financial performance and health of a bank. Understanding its components, the factors influencing it, and its relationship to other key metrics is crucial for investors, regulators, and anyone seeking to understand the intricacies of the banking industry. By carefully analyzing the earnings spread and related metrics, a more comprehensive assessment of a bank's financial strength and future prospects can be achieved. The spread serves as a vital financial indicator, providing a glimpse into the heart of a bank's profitability and its ability to navigate the ever-changing financial landscape. Its continuous monitoring is paramount for sound financial decision-making and robust regulatory oversight. As the banking industry continues to evolve, understanding the nuances of the earnings spread remains a critical skill for stakeholders at all levels.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Discover Is A Good Example Of A
Mar 19, 2025
-
Topic 3 Assessment Form A Answer Key Savvas
Mar 19, 2025
-
Selecciona La Respuesta Que Mejor Completa Cada Oracion
Mar 19, 2025
-
Cat On A Hot Tin Roof Characters
Mar 19, 2025
-
1 2 Reteach To Build Understanding Answer Key
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Earnings Spread For A Bank Is Equal To: . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
