Tina Jones Comprehensive Assessment Shadow Health Subjective
Onlines
Mar 06, 2025 · 7 min read
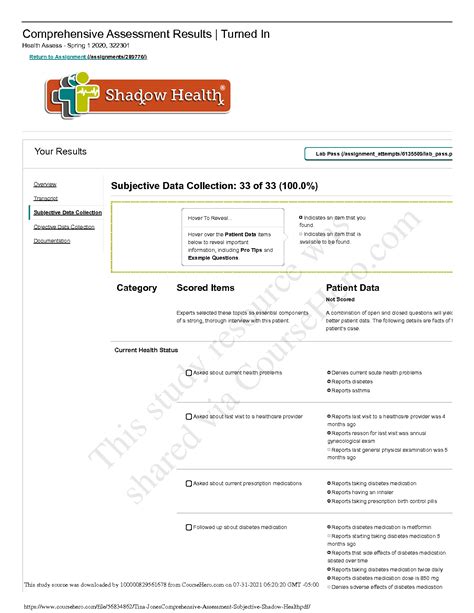
Table of Contents
Tina Jones Comprehensive Assessment: A Deep Dive into Subjective Data in Shadow Health
Shadow Health's Tina Jones virtual patient provides an invaluable opportunity for nursing students to practice comprehensive assessment skills. This article will delve deeply into the subjective data gathered during Tina Jones's assessment, analyzing key findings, potential diagnoses, and the importance of effective communication and critical thinking in this virtual clinical experience. We'll explore the nuances of her history, presenting complaints, and the crucial role of subjective data in formulating a comprehensive care plan.
Understanding Subjective Data in Patient Assessment
Before we dive into Tina Jones's specific case, let's establish the importance of subjective data. Subjective data is information provided by the patient themselves. It includes their feelings, perceptions, and descriptions of their symptoms. This contrasts with objective data, which is observable and measurable by the healthcare provider (e.g., vital signs, physical examination findings). Subjective data is crucial because it forms the foundation of understanding the patient's experience of their illness. It’s the patient's story, and it’s essential for building rapport and creating a comprehensive picture of their health.
Key Components of Subjective Data Collection:
- Chief Complaint (CC): The primary reason for the patient's visit. This is usually stated in the patient's own words.
- History of Present Illness (HPI): A detailed chronological account of the CC, including onset, location, duration, character, aggravating and relieving factors, radiation, associated symptoms, timing, exacerbating/relieving factors, and severity (OLDCARTS).
- Past Medical History (PMH): A summary of previous illnesses, surgeries, hospitalizations, and allergies.
- Family History (FH): Information about the health status of the patient's family members, highlighting any significant illnesses that may have genetic implications.
- Social History (SH): Details about the patient's lifestyle, including occupation, relationships, habits (smoking, alcohol, drug use), and socioeconomic status.
- Review of Systems (ROS): A systematic inquiry about each body system to identify any other potential health problems.
Tina Jones's Subjective Data: A Detailed Analysis
Tina Jones's subjective data in Shadow Health presents a rich tapestry of information crucial for understanding her health status. Let's dissect the key aspects:
1. Chief Complaint:
Tina Jones typically presents with a chief complaint related to her respiratory system, often describing symptoms such as cough, shortness of breath, or chest pain. The exact nature of her CC will vary depending on the specific Shadow Health scenario, allowing for diverse learning experiences. The phrasing of her CC provides initial clues about her perceived health problem and should be meticulously documented.
2. History of Present Illness (HPI):
This section requires careful attention to detail. Tina's HPI will detail the progression of her respiratory symptoms, using the OLDCARTS mnemonic:
- Onset: When did the symptoms begin? Was it sudden or gradual?
- Location: Where is the discomfort or symptom located? Is it localized or widespread?
- Duration: How long have the symptoms lasted? Are they continuous or intermittent?
- Character: What is the nature of the symptoms? (e.g., sharp, dull, aching, stabbing, burning, itchy, etc.)
- Aggravating factors: What makes the symptoms worse? (e.g., exercise, deep breaths, certain positions)
- Relieving factors: What makes the symptoms better? (e.g., rest, medication, specific postures)
- Radiation: Does the pain or discomfort spread to other areas?
- Severity: How severe are the symptoms on a scale of 1-10?
- Timing: How frequently do the symptoms occur? (e.g., constant, intermittent, etc.)
- Associated symptoms: Are there any other symptoms present along with the primary complaint? (e.g., fever, chills, fatigue, etc.)
Analyzing Tina's HPI requires carefully listening to her descriptions and probing for further clarification using open-ended questions. This is crucial for building a complete picture of her illness.
3. Past Medical History (PMH):
Tina's PMH often includes details about previous respiratory infections, allergies, or other relevant medical conditions. Thoroughly documenting this information is vital as it can offer clues to the underlying cause of her present complaint and influence treatment decisions. For example, a history of asthma would significantly impact the assessment and management of her current respiratory symptoms.
4. Family History (FH):
A comprehensive family history should include information about respiratory illnesses (asthma, emphysema, lung cancer) and other relevant conditions that might have genetic components. This information helps determine potential risk factors and guide further investigation.
5. Social History (SH):
Tina's social history provides insight into her lifestyle and potential environmental factors influencing her health. This includes details about her smoking history (pack-years), exposure to environmental pollutants, occupational hazards, diet, exercise habits, and support systems. Her social history often highlights potential contributing factors to her respiratory condition. A detailed smoking history, for example, can greatly inform the diagnosis and treatment plan.
6. Review of Systems (ROS):
A thorough ROS is crucial. While the primary focus is on Tina's respiratory system, exploring other systems (cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, neurological, etc.) can reveal related symptoms or comorbidities that might be contributing to her condition. For instance, a history of cardiac issues could impact the assessment of her shortness of breath.
Interpreting and Applying Subjective Data: Developing a Differential Diagnosis
Once you have carefully gathered Tina Jones's subjective data, the next step is to analyze it critically and develop a differential diagnosis. This means creating a list of possible diagnoses based on the information gathered. For Tina Jones, this often involves considering:
- Acute Bronchitis: Characterized by cough, sometimes with mucus production, and often triggered by a viral infection.
- Pneumonia: A lung infection causing cough, fever, chills, and shortness of breath.
- Asthma Exacerbation: Worsening of asthma symptoms, characterized by wheezing, cough, and shortness of breath.
- COPD Exacerbation: A worsening of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease symptoms, including increased cough, shortness of breath, and sputum production.
- Pleurisy: Inflammation of the lining of the lungs, causing chest pain that worsens with deep breaths or coughing.
The subjective data will significantly influence which diagnoses are considered most likely. For example, a history of asthma and the presence of wheezing would make asthma exacerbation a higher probability.
The Importance of Communication and Critical Thinking
Effective communication is paramount in gathering accurate subjective data. Using open-ended questions, active listening, and empathetic communication techniques creates a safe space for Tina Jones to share her experience fully. Critical thinking is equally important in analyzing the data collected, identifying inconsistencies, recognizing patterns, and developing a sound differential diagnosis. The Shadow Health platform allows students to practice these skills in a safe and controlled environment.
Using Tina Jones to Master Subjective Data Collection: Tips for Success
- Practice active listening: Pay close attention to both verbal and nonverbal cues.
- Ask clarifying questions: Don't hesitate to ask follow-up questions to gain a deeper understanding.
- Use OLDCARTS consistently: This mnemonic ensures comprehensive HPI documentation.
- Document thoroughly: Record all relevant subjective data meticulously.
- Analyze critically: Reflect on the data collected and consider potential connections between findings.
- Develop a differential diagnosis: Create a list of possible diagnoses based on the evidence.
- Utilize the Shadow Health feedback: Learn from the feedback provided by the platform to improve your assessment skills.
Conclusion: The Value of Tina Jones in Nursing Education
Tina Jones in Shadow Health provides an invaluable opportunity to practice comprehensive assessment skills, particularly in gathering and analyzing subjective data. By mastering the art of subjective data collection and integrating it with objective findings, nursing students develop the crucial skills needed to provide safe and effective patient care. The realistic scenarios and immediate feedback offered by the Shadow Health platform significantly enhances learning and prepares students for real-world clinical practice. Through diligent practice and critical analysis of the subjective data provided by Tina Jones, students can build a strong foundation for future success in their nursing careers. Remember, the subjective data represents the patient’s lived experience and is a vital piece of the puzzle in delivering holistic and effective care.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Did You Get To The Top Of Sao Carlos
Mar 06, 2025
-
Find The Trigonometric Ratio Maze Answer Key
Mar 06, 2025
-
How Did Postwar Authors Show Disillusionment With Prewar Institutions
Mar 06, 2025
-
A Wrinkle In Time Chapter Summary
Mar 06, 2025
-
John Proctor Is The Villain Script Pdf
Mar 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Tina Jones Comprehensive Assessment Shadow Health Subjective . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
