Triangle Congruence Review Maze Answer Key
Onlines
Mar 15, 2025 · 6 min read
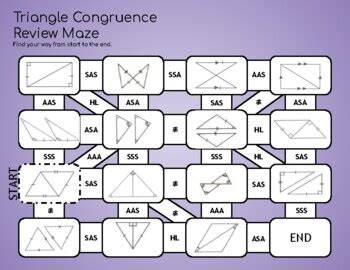
Table of Contents
Triangle Congruence Review Maze: Answer Key and Comprehensive Guide
This comprehensive guide provides the answer key to a triangle congruence review maze, along with detailed explanations of each triangle congruence postulate and theorem. Understanding triangle congruence is crucial in geometry, serving as a foundational concept for many advanced topics. This guide aims to solidify your understanding and help you navigate similar exercises with confidence.
Understanding Triangle Congruence
Before diving into the maze answer key, let's refresh our understanding of triangle congruence. Two triangles are considered congruent if their corresponding sides and angles are equal. This means that if you were to superimpose one triangle onto the other, they would perfectly overlap. We don't need to prove all six parts are equal, however. Several postulates and theorems provide shortcuts for proving congruence.
Key Postulates and Theorems
-
SSS (Side-Side-Side): If three sides of one triangle are congruent to three sides of another triangle, then the triangles are congruent. This is arguably the most intuitive postulate. If all the sides match, the triangles must be the same shape and size.
-
SAS (Side-Angle-Side): If two sides and the included angle of one triangle are congruent to two sides and the included angle of another triangle, then the triangles are congruent. The "included" angle is the angle between the two sides. This is a critical postulate as it highlights the importance of the angle's position.
-
ASA (Angle-Side-Angle): If two angles and the included side of one triangle are congruent to two angles and the included side of another triangle, then the triangles are congruent. Similar to SAS, the position of the side matters.
-
AAS (Angle-Angle-Side): If two angles and a non-included side of one triangle are congruent to two angles and the corresponding non-included side of another triangle, then the triangles are congruent. Note the subtle difference between ASA and AAS.
-
HL (Hypotenuse-Leg): This theorem applies only to right-angled triangles. If the hypotenuse and a leg of one right-angled triangle are congruent to the hypotenuse and a leg of another right-angled triangle, then the triangles are congruent. This is a specific case and should only be used for right triangles.
Navigating the Triangle Congruence Maze
A triangle congruence maze typically presents a series of triangles with marked sides and angles. The goal is to navigate the maze by selecting the path that leads to congruent triangles based on the applicable postulate or theorem. The maze's complexity varies, often incorporating multiple pathways and challenges to test your understanding.
Sample Maze and Answer Key (Illustrative Example)
(Note: Since I cannot create visual mazes here, I will describe a hypothetical maze and its solution. You can apply this methodology to your specific maze.)
Let's imagine a maze with five possible paths. Each path presents two triangles with some information about their sides and angles. We will represent the triangles with letter notations (e.g., triangle ABC and triangle DEF).
Path 1: Triangle ABC: AB = 5, BC = 7, AC = 9; Triangle DEF: DE = 5, EF = 7, DF = 9. Solution: SSS
Path 2: Triangle ABC: AB = 6, angle B = 50°, BC = 8; Triangle DEF: DE = 8, angle E = 50°, EF = 6. Solution: SAS (Note the order is important here)
Path 3: Triangle ABC: angle A = 40°, AB = 4, angle B = 70°; Triangle DEF: angle D = 40°, DE = 4, angle E = 70°. Solution: ASA
Path 4: Triangle ABC: angle A = 35°, angle C = 90°, AC = 10; Triangle DEF: angle D = 35°, angle F = 90°, DF = 10. Solution: AAS
Path 5: Triangle ABC: AB = 12, angle A = 30°, angle B = 60°; Triangle DEF: DE = 12, angle D = 30°, angle E = 60°. Solution: AAS (or ASA if you consider angle C and angle F which are deduced)
Incorrect Paths and Common Mistakes:
Many mazes include deliberately misleading paths to test your understanding. These paths might:
- Present incomplete information: You might have only two sides, but no included angle.
- Incorrectly order the information: This is crucial with SAS and ASA.
- Include information irrelevant to any congruence postulate: Extra information that doesn't fit into any postulate shouldn't mislead you.
- Use SSA (Side-Side-Angle): This is not a valid congruence postulate. Remember that SSA does not guarantee congruence.
Strategies for Solving Triangle Congruence Mazes:
- Carefully examine each triangle: Note all given information about sides and angles.
- Identify the type of information given: Do you have side lengths, angles, or a mix?
- Match the information to the postulates and theorems: Does the information fit SSS, SAS, ASA, AAS, or HL?
- Check the order of information: If using SAS or ASA, ensure the sides and angles are in the correct order.
- Eliminate incorrect paths: If a path doesn't fit any postulate or theorem, it is not a correct path.
- Double-check your work: Before selecting a path, review your reasoning.
Beyond the Maze: Applying Triangle Congruence
The skills you develop while solving triangle congruence mazes have far-reaching applications in geometry and related fields. Understanding triangle congruence is essential for:
- Proving geometric theorems: Many geometric theorems rely on showing that triangles are congruent.
- Solving geometric problems: Congruence allows us to find missing lengths and angles.
- Constructing geometric figures: Understanding congruences guides the precise construction of shapes.
- Trigonometry: The foundations of trigonometry hinge upon understanding relationships between angles and sides in triangles.
- Engineering and Architecture: Congruence principles are fundamental in designing stable and symmetrical structures.
Advanced Applications and Extensions
While mazes offer a focused way to practice, understanding triangle congruence extends into more complex geometric problems. Consider these advanced aspects:
- Indirect Proofs: Sometimes, you may need to use indirect proof techniques to establish congruence by showing the impossibility of the opposite conclusion.
- Coordinate Geometry: You can apply congruence theorems to triangles defined by coordinates in a Cartesian plane.
- Three-Dimensional Geometry: The principles of congruence extend to three-dimensional figures, requiring you to consider congruence between faces and volumes.
- Transformations: Congruent triangles are related by various transformations like reflections, rotations, and translations.
Conclusion
Mastering triangle congruence is a cornerstone of geometric understanding. This guide, along with practice using mazes and other exercises, will equip you with the necessary skills to navigate complex geometric problems confidently. Remember to focus on understanding the postulates and theorems, practice regularly, and always double-check your work. By mastering these concepts, you'll open doors to a deeper understanding of geometry and its applications in various fields. The seemingly simple act of solving a maze can unlock a profound understanding of mathematical principles.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Theme The Masque Of Red Death
Mar 15, 2025
-
Ap Physics 1 Unit 6 Progress Check Mcq
Mar 15, 2025
-
Worksheet A Topic 1 8 Rational Functions And Zeros
Mar 15, 2025
-
How To Win Friends And Influence People Chapter 1 Summary
Mar 15, 2025
-
Discovering Psychology Sensation And Perception Episode 4 Worksheet Answers
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Triangle Congruence Review Maze Answer Key . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
