Unit 10 Circles Homework 1 Answer Key
Onlines
Mar 09, 2025 · 5 min read
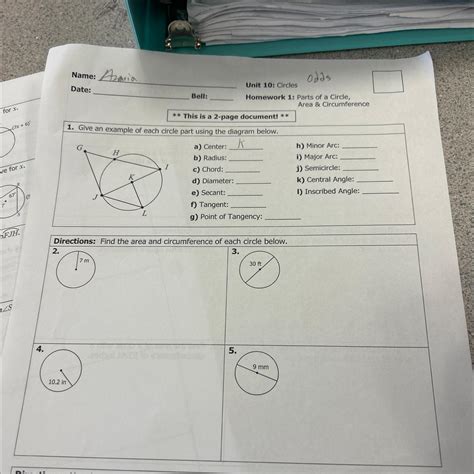
Table of Contents
Unit 10 Circles Homework 1 Answer Key: A Comprehensive Guide
Are you struggling with your Unit 10 Circles Homework 1? Don't worry, you're not alone! Many students find circles challenging, but with the right approach and resources, mastering this unit is entirely achievable. This comprehensive guide will provide you with a detailed walkthrough of common problems found in Unit 10 Circles Homework 1, along with explanations and strategies to help you succeed. We'll cover key concepts, formulas, and problem-solving techniques, ensuring you understand the underlying principles rather than just memorizing answers.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Circles
Before diving into the homework problems, let's refresh our understanding of fundamental circle concepts. This solid foundation is crucial for tackling even the most complex problems.
Key Definitions and Terminology
- Circle: A set of all points in a plane that are equidistant from a given point, called the center.
- Radius (r): The distance from the center of the circle to any point on the circle.
- Diameter (d): The distance across the circle through the center; it's twice the radius (d = 2r).
- Circumference (C): The distance around the circle; calculated using the formula C = 2πr or C = πd.
- Area (A): The space enclosed within the circle; calculated using the formula A = πr².
- Chord: A line segment whose endpoints lie on the circle.
- Secant: A line that intersects a circle at two points.
- Tangent: A line that intersects a circle at exactly one point (the point of tangency).
- Arc: A portion of the circle's circumference.
- Sector: A region bounded by two radii and an arc.
- Segment: A region bounded by a chord and an arc.
- Central Angle: An angle whose vertex is the center of the circle.
- Inscribed Angle: An angle whose vertex lies on the circle and whose sides are chords.
Essential Formulas and Relationships
Remembering these formulas is vital for solving problems involving circles:
- Circumference: C = 2πr = πd
- Area: A = πr²
- Relationship between radius and diameter: d = 2r or r = d/2
- Arc Length: (θ/360°) * 2πr (where θ is the central angle in degrees)
- Area of a Sector: (θ/360°) * πr² (where θ is the central angle in degrees)
Tackling Common Problem Types in Unit 10 Circles Homework 1
Now, let's address some common problem types encountered in Unit 10 Circles Homework 1. We'll illustrate with examples and step-by-step solutions.
Problem Type 1: Finding Circumference and Area
Example: A circle has a radius of 5 cm. Find its circumference and area.
Solution:
- Circumference: C = 2πr = 2π(5 cm) = 10π cm ≈ 31.42 cm
- Area: A = πr² = π(5 cm)² = 25π cm² ≈ 78.54 cm²
Problem Type 2: Finding Radius and Diameter from Circumference or Area
Example: The circumference of a circle is 24π inches. Find its radius and diameter.
Solution:
- Radius: We know C = 2πr, so 24π inches = 2πr. Dividing both sides by 2π gives r = 12 inches.
- Diameter: d = 2r = 2(12 inches) = 24 inches.
Problem Type 3: Working with Arcs and Sectors
Example: A circle has a radius of 8 cm. Find the length of an arc with a central angle of 60°. Find the area of the sector formed by this arc and the two radii.
Solution:
- Arc Length: Arc length = (θ/360°) * 2πr = (60°/360°) * 2π(8 cm) = (1/6) * 16π cm = (8π/3) cm ≈ 8.38 cm
- Area of Sector: Area of sector = (θ/360°) * πr² = (60°/360°) * π(8 cm)² = (1/6) * 64π cm² = (32π/3) cm² ≈ 33.51 cm²
Problem Type 4: Problems Involving Tangents and Chords
Example: A tangent line touches a circle with a radius of 7 cm at a point. The distance from the center of the circle to a point on the tangent line is 10 cm. Find the length of the segment of the tangent line from the point of tangency to the point on the line.
Solution: This problem utilizes the Pythagorean theorem. The radius, the segment of the tangent line, and the distance from the center to the point on the tangent line form a right-angled triangle.
- Let x be the length of the tangent segment.
- By the Pythagorean theorem: x² + 7² = 10²
- x² + 49 = 100
- x² = 51
- x = √51 cm ≈ 7.14 cm
Problem Type 5: Inscribed Angles and Central Angles
Example: An inscribed angle in a circle subtends an arc of 80°. Find the measure of the inscribed angle.
Solution: The measure of an inscribed angle is half the measure of its intercepted arc. Therefore, the inscribed angle measures 80°/2 = 40°.
Problem Type 6: Circles and Coordinate Geometry
Example: Find the equation of a circle with center (3, -2) and radius 4.
Solution: The equation of a circle with center (h, k) and radius r is given by (x - h)² + (y - k)² = r². Therefore, the equation is (x - 3)² + (y + 2)² = 16.
Advanced Problem Solving Strategies for Unit 10 Circles Homework 1
For more challenging problems in Unit 10 Circles Homework 1, consider these advanced techniques:
- Drawing diagrams: Always start by drawing a clear diagram to visualize the problem. This helps identify relevant relationships and formulas.
- Breaking down complex problems: Divide complex problems into smaller, more manageable parts. Solve each part individually and then combine the results.
- Using properties of circles: Familiarize yourself with various theorems and properties related to circles (e.g., the Inscribed Angle Theorem, the Tangent-Secant Theorem).
- Applying trigonometry: For problems involving angles and arc lengths, trigonometry can be a powerful tool.
- Utilizing algebraic manipulation: Practice algebraic manipulation to solve equations involving circles' properties.
Tips for Success in Mastering Unit 10 Circles
- Practice consistently: Regular practice is key to mastering any mathematical concept, including circles. Work through as many problems as possible.
- Seek help when needed: Don't hesitate to ask your teacher, classmates, or tutors for help if you're stuck on a particular problem.
- Review your notes: Regularly review your class notes and textbook to reinforce your understanding of the concepts.
- Use online resources: Many online resources (Khan Academy, for example) provide additional explanations and practice problems. Use these judiciously to supplement your learning.
- Focus on understanding, not memorization: While memorizing formulas is important, understanding the underlying principles is crucial for applying them effectively to diverse problems.
By following these steps and utilizing the strategies outlined above, you'll be well-equipped to conquer your Unit 10 Circles Homework 1 and develop a strong understanding of circles. Remember, consistent effort and a focused approach will lead to success! Good luck!
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Role Of Media Answer Key
Mar 10, 2025
-
Pharmacology Made Easy 4 0 The Hematologic System
Mar 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Unit 10 Circles Homework 1 Answer Key . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
