Unit 10 Homework 1 Parts Of Circles Area And Circumference
Onlines
Mar 17, 2025 · 5 min read
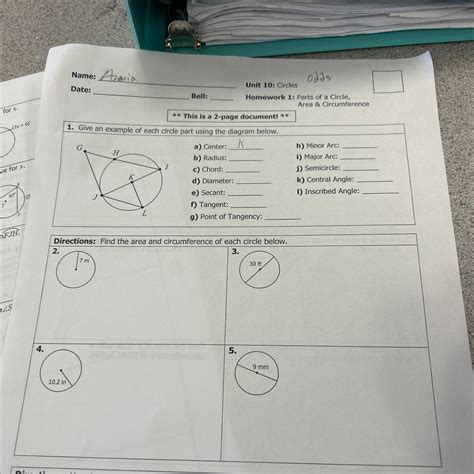
Table of Contents
Unit 10 Homework 1: Mastering Circles – Area and Circumference
This comprehensive guide dives deep into the concepts of area and circumference of circles, providing a thorough understanding to conquer Unit 10 Homework 1 and beyond. We'll cover definitions, formulas, problem-solving strategies, and real-world applications, ensuring you master this crucial geometrical topic.
Understanding Circles: A Foundation
Before tackling area and circumference calculations, let's establish a solid understanding of the fundamental components of a circle.
Key Terminology
- Radius (r): The distance from the center of the circle to any point on the circle. Think of it as the circle's "arm."
- Diameter (d): The distance across the circle passing through the center. It's simply twice the radius (d = 2r).
- Circumference (C): The distance around the circle. Imagine walking around the entire circle; that distance is the circumference.
- Area (A): The space enclosed within the circle. It's the amount of surface the circle covers.
- Pi (π): A mathematical constant, approximately equal to 3.14159. It represents the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter (C/d = π). For calculations, you might use a rounded version like 3.14 or the value stored in your calculator.
Calculating Circumference: The Distance Around
The circumference of a circle is calculated using the following formula:
C = 2πr or C = πd
Where:
- C = Circumference
- r = Radius
- d = Diameter
- π = Pi (approximately 3.14 or use your calculator's π value for greater accuracy)
Example 1: Find the circumference of a circle with a radius of 5 cm.
Using the formula C = 2πr:
C = 2 * 3.14 * 5 cm = 31.4 cm
Example 2: Find the circumference of a circle with a diameter of 12 inches.
Using the formula C = πd:
C = 3.14 * 12 inches = 37.68 inches
Calculating Area: The Space Inside
The area of a circle is calculated using the following formula:
A = πr²
Where:
- A = Area
- r = Radius
- π = Pi (approximately 3.14 or use your calculator's π value for greater accuracy)
Example 3: Find the area of a circle with a radius of 7 meters.
Using the formula A = πr²:
A = 3.14 * 7² m² = 3.14 * 49 m² = 153.86 m²
Example 4: Find the area of a circle with a diameter of 10 feet. Remember, you'll need the radius to use the area formula. Since the diameter is 10 feet, the radius is half of that, or 5 feet.
Using the formula A = πr²:
A = 3.14 * 5² ft² = 3.14 * 25 ft² = 78.5 ft²
Solving Complex Problems: A Step-by-Step Approach
Many problems involving circles require a combination of understanding the formulas and applying logical reasoning. Let's explore some more challenging scenarios.
Problem 1: Finding the Radius Given the Circumference
A circular garden has a circumference of 25.12 meters. What is the radius of the garden?
- Identify the known: We know the circumference (C = 25.12 meters).
- Choose the appropriate formula: Use the circumference formula: C = 2πr
- Substitute and solve: 25.12 = 2 * 3.14 * r
- 25.12 = 6.28r
- r = 25.12 / 6.28
- r = 4 meters
Therefore, the radius of the garden is 4 meters.
Problem 2: Finding the Diameter Given the Area
A circular pizza has an area of 78.5 square inches. What is the diameter of the pizza?
- Identify the known: We know the area (A = 78.5 square inches).
- Choose the appropriate formula: Use the area formula: A = πr²
- Substitute and solve: 78.5 = 3.14 * r²
- r² = 78.5 / 3.14
- r² = 25
- r = √25
- r = 5 inches
- Find the diameter: Since the radius is 5 inches, the diameter is 2 * r = 10 inches.
Therefore, the diameter of the pizza is 10 inches.
Problem 3: Combining Area and Circumference
A circular pool has an area of 1256 square feet. What is its circumference?
- Find the radius: Use the area formula (A = πr²) to find the radius:
- 1256 = 3.14 * r²
- r² = 1256 / 3.14
- r² = 400
- r = √400 = 20 feet
- Find the circumference: Use the circumference formula (C = 2πr):
- C = 2 * 3.14 * 20 feet
- C = 125.6 feet
Therefore, the circumference of the pool is 125.6 feet.
Real-World Applications: Beyond the Textbook
Understanding area and circumference isn't just for academic exercises; it has numerous practical applications in various fields:
- Engineering: Designing circular structures like pipes, wheels, and gears requires precise calculations of area and circumference to ensure functionality and efficiency.
- Architecture: Architects use these concepts to design circular spaces, calculate material needs, and ensure structural integrity.
- Agriculture: Determining the area of circular fields helps farmers calculate the amount of fertilizer, seeds, or irrigation needed.
- Landscaping: Landscaping projects often involve circular features, requiring accurate area calculations for planting or paving.
- Manufacturing: Manufacturing processes frequently involve circular components, and understanding their dimensions is crucial for production.
Tips for Success on Unit 10 Homework 1
- Memorize the formulas: Knowing the formulas for area (A = πr²) and circumference (C = 2πr or C = πd) is essential.
- Practice regularly: Solve numerous problems to build your proficiency and identify areas needing improvement.
- Use a calculator: Employ a calculator to ensure accuracy, especially when dealing with decimals and larger numbers.
- Understand the units: Always pay attention to the units used (cm, inches, meters, etc.) and maintain consistency throughout your calculations.
- Draw diagrams: Sketching a diagram of the circle can help visualize the problem and clarify your understanding.
- Break down complex problems: If a problem seems overwhelming, break it down into smaller, manageable steps.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Advanced Concepts
While this guide focuses on the fundamental concepts of area and circumference, exploring advanced topics can further enhance your understanding:
- Sectors and Segments: Learn how to calculate the area of a sector (a portion of a circle) and a segment (the area between a chord and an arc).
- Annulus: Understanding the area of an annulus (the region between two concentric circles) involves subtracting the area of the smaller circle from the area of the larger circle.
- Inscribed and Circumscribed Circles: Explore the relationship between circles and polygons, learning how to calculate the radius and area of circles inscribed within or circumscribed around polygons.
By mastering the fundamentals presented in this guide and exploring these advanced concepts, you'll not only ace Unit 10 Homework 1 but also build a strong foundation in geometry that will serve you well in future studies and real-world applications. Remember, consistent practice and a clear understanding of the core principles are key to success. Good luck!
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How To Read Like A Professor Summary
Mar 17, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is True About Temporary Stair Treads
Mar 17, 2025
-
Ati Growth And Development Template Preschool
Mar 17, 2025
-
You Have Just Been Hired As The Assistant Manager
Mar 17, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Linux File Systems Support Journaling
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Unit 10 Homework 1 Parts Of Circles Area And Circumference . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
