Unit 6 Similar Triangles Homework 2 Similar Figures Answer Key
Onlines
Mar 09, 2025 · 5 min read
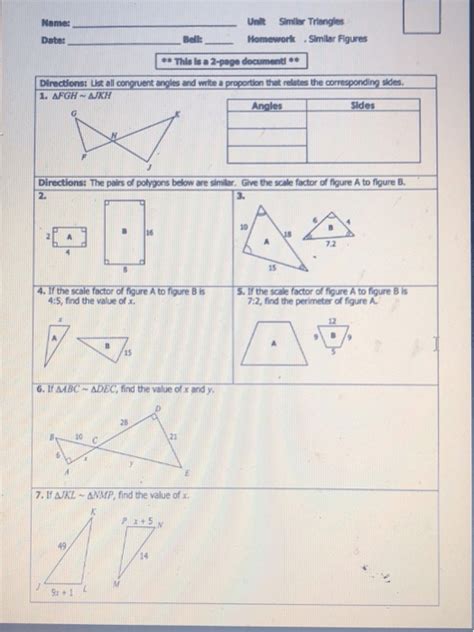
Table of Contents
Unit 6 Similar Triangles Homework 2: Similar Figures – A Comprehensive Guide
This comprehensive guide will help you master the concepts of similar figures, focusing on the problems typically found in Unit 6, Homework 2 of many geometry courses. We will explore the core principles of similarity, delve into problem-solving strategies, and provide detailed examples to solidify your understanding. This guide aims to be your complete resource for conquering similar figures and achieving success in your geometry studies.
Understanding Similar Figures
Similar figures are figures that have the same shape but not necessarily the same size. This means their corresponding angles are congruent (equal in measure), and their corresponding sides are proportional. This proportionality is key to solving problems involving similar figures. The ratio of corresponding sides is called the scale factor.
Key Properties of Similar Figures:
- Congruent Angles: Corresponding angles in similar figures are equal.
- Proportional Sides: Corresponding sides in similar figures are proportional; their ratios are equal.
- Scale Factor: The ratio of corresponding sides is the scale factor. If the scale factor is greater than 1, the similar figure is an enlargement; if it's less than 1, it's a reduction.
Solving Problems Involving Similar Figures
Let's break down common problem types found in Unit 6, Homework 2, using step-by-step strategies:
1. Determining Similarity
Problem Type: Given two figures, determine if they are similar.
Strategy:
- Compare Corresponding Angles: Check if all corresponding angles are congruent.
- Check Proportional Sides: Calculate the ratios of corresponding sides. If the ratios are equal (or very close, accounting for rounding errors), the figures are similar.
Example:
Two triangles, ΔABC and ΔDEF, have the following measurements:
- ΔABC: ∠A = 60°, ∠B = 80°, ∠C = 40°, AB = 6, BC = 8, AC = 10
- ΔDEF: ∠D = 60°, ∠E = 80°, ∠F = 40°, DE = 3, EF = 4, DF = 5
Solution:
- Angles: Corresponding angles are congruent (60° = 60°, 80° = 80°, 40° = 40°).
- Sides:
- DE/AB = 3/6 = 0.5
- EF/BC = 4/8 = 0.5
- DF/AC = 5/10 = 0.5
Since all corresponding angles are congruent and the ratios of corresponding sides are equal (0.5), ΔABC and ΔDEF are similar. The scale factor is 0.5, indicating ΔDEF is a reduction of ΔABC.
2. Finding Missing Side Lengths
Problem Type: Given similar figures with some side lengths known, find the missing side lengths.
Strategy:
- Identify Corresponding Sides: Determine which sides correspond to each other in the similar figures.
- Set up a Proportion: Create a proportion using the known side lengths and the unknown side length.
- Solve the Proportion: Use cross-multiplication or other algebraic methods to solve for the unknown side length.
Example:
Two similar rectangles, ABCD and EFGH, have the following measurements:
- Rectangle ABCD: AB = 12, BC = 8
- Rectangle EFGH: EF = 6, FG = x
Solution:
- Corresponding Sides: AB corresponds to EF, and BC corresponds to FG.
- Proportion: AB/EF = BC/FG => 12/6 = 8/x
- Solve: Cross-multiply: 12x = 48 => x = 4
Therefore, FG = 4.
3. Applications of Similar Triangles
Problem Type: Using similar triangles to solve real-world problems (e.g., shadow problems, height problems).
Strategy:
- Identify Similar Triangles: Look for similar triangles formed by the objects and their shadows or other relevant measurements.
- Set up a Proportion: Create a proportion using the known and unknown measurements.
- Solve the Proportion: Solve for the unknown quantity.
Example: Shadow Problem
A tree casts a shadow of 20 feet. At the same time, a 6-foot-tall person casts a shadow of 4 feet. How tall is the tree?
Solution:
- Similar Triangles: The tree and its shadow form a right-angled triangle, similar to the triangle formed by the person and their shadow.
- Proportion: Let h be the height of the tree. Then: h/20 = 6/4
- Solve: Cross-multiply: 4h = 120 => h = 30
Therefore, the tree is 30 feet tall.
4. Scale Factor and Area/Volume Ratios
Problem Type: Finding the ratio of areas or volumes of similar figures given their scale factor.
Strategy:
- Area Ratio: If the scale factor of similar figures is k, the ratio of their areas is k².
- Volume Ratio: If the scale factor of similar figures is k, the ratio of their volumes is k³.
Example:
Two similar cubes have a scale factor of 3. If the smaller cube has a volume of 8 cubic units, what is the volume of the larger cube?
Solution:
The scale factor is 3, so the ratio of their volumes is 3³ = 27. Therefore, the volume of the larger cube is 27 * 8 = 216 cubic units.
Advanced Problem-Solving Techniques
As you progress through Unit 6, Homework 2, you might encounter more complex problems. Here are some advanced techniques:
- Using Multiple Proportions: Sometimes you'll need to set up and solve multiple proportions simultaneously to find unknown values.
- Geometric Mean: The geometric mean is useful in problems involving similar triangles where altitudes or medians are involved.
- Trigonometric Ratios: In some problems, trigonometric ratios (sine, cosine, tangent) may be necessary to find unknown side lengths or angles.
Practice Problems
To truly solidify your understanding, practice is essential. Here are some practice problems similar to those you'd find in Unit 6, Homework 2:
-
Two triangles are similar. The sides of the first triangle are 5, 12, and 13. The shortest side of the second triangle is 10. Find the lengths of the other two sides.
-
A flagpole casts a shadow of 15 meters. At the same time, a meter stick casts a shadow of 2.5 meters. How tall is the flagpole?
-
Two similar cylinders have radii of 3 and 9. If the volume of the smaller cylinder is 27π cubic units, what is the volume of the larger cylinder?
-
Two similar cones have heights of 4 and 12. If the surface area of the smaller cone is 16π square units, find the surface area of the larger cone.
-
In similar triangles ABC and DEF, AB = 6, BC = 8, AC = 10, and DE = 9. Find the lengths of EF and DF.
Conclusion
Mastering similar figures is crucial for success in geometry. By understanding the fundamental principles of similarity, employing effective problem-solving strategies, and practicing regularly, you can confidently tackle the challenges presented in Unit 6, Homework 2, and beyond. Remember to break down complex problems into smaller, manageable steps, and don't hesitate to review the core concepts and examples provided in this guide. Good luck!
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Application Of Low Grade Metamorphic Forces To A Rock Causes
Mar 09, 2025
-
2 4 2 Student Response Sheet Activity 11 Answers
Mar 09, 2025
-
Place The Following Terms Or Examples With The Correct Category
Mar 09, 2025
-
Trish Wishes Her Job Were More Interesting
Mar 09, 2025
-
Y Ahora Que Queria Anselmo Que Hiciera La Chona
Mar 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Unit 6 Similar Triangles Homework 2 Similar Figures Answer Key . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
