Unit 9 Transformations Homework 3 Rotations
Onlines
Mar 24, 2025 · 5 min read
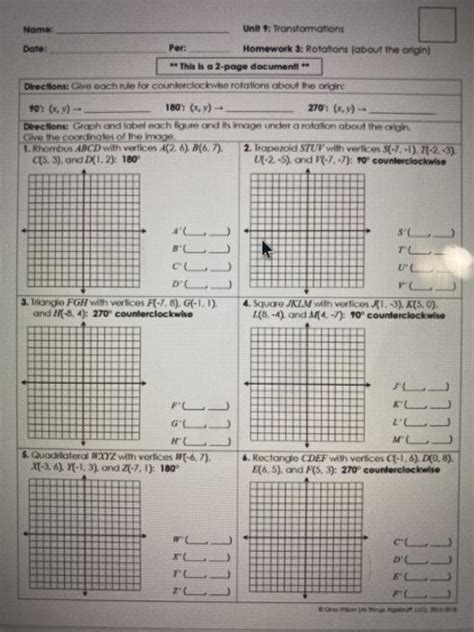
Table of Contents
Unit 9 Transformations Homework 3: Mastering Rotations
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of Unit 9 Transformations Homework 3, focusing specifically on rotations. We'll break down the core concepts, provide step-by-step solutions to common problem types, and offer strategies for mastering this crucial geometry topic. Whether you're struggling with the basics or aiming for mastery, this guide will equip you with the tools and understanding you need to succeed.
Understanding Rotations: The Foundation
A rotation, in the context of geometric transformations, is a rigid transformation that moves a shape around a fixed point called the center of rotation. This movement is characterized by an angle of rotation, specifying the amount of turn. Imagine spinning a shape around a pin – that pin is the center of rotation, and the amount you spin it is the angle of rotation.
Key Components of a Rotation:
- Pre-image: The original shape before the transformation.
- Image: The shape after the transformation (rotation).
- Center of Rotation: The fixed point around which the shape rotates.
- Angle of Rotation: The amount of rotation, measured in degrees (clockwise or counterclockwise).
- Direction of Rotation: Clockwise (right) or counterclockwise (left).
Types of Rotations:
While all rotations share the fundamental principles, they can be categorized based on their angle:
- 90° Rotation: A quarter-turn.
- 180° Rotation: A half-turn.
- 270° Rotation: Three-quarter turn.
- 360° Rotation: A full turn, resulting in the image coinciding with the pre-image.
Applying Rotation Rules: Step-by-Step Solutions
Let's explore how to perform rotations using different methods, starting with the coordinate plane.
Rotating Points on a Coordinate Plane:
Rotating points on a coordinate plane involves applying specific rules depending on the center of rotation and the angle of rotation. The most common scenario involves rotating around the origin (0,0).
Rules for Rotating Points Around the Origin (0,0):
- 90° Counterclockwise Rotation:
(x, y) → (-y, x) - 180° Rotation:
(x, y) → (-x, -y) - 270° Counterclockwise Rotation:
(x, y) → (y, -x) - 90° Clockwise Rotation:
(x, y) → (y, -x) - 270° Clockwise Rotation:
(x, y) → (-y, x)
Example:
Let's rotate point A (2, 3) 90° counterclockwise around the origin.
Using the rule (x, y) → (-y, x), we substitute:
(2, 3) → (-3, 2)
The rotated point A' is (-3, 2).
Rotating Shapes on a Coordinate Plane:
Rotating a shape involves rotating each of its vertices and then connecting the rotated vertices to form the rotated shape.
Example:
Let's rotate a triangle with vertices A(1,1), B(3,1), and C(2,3) 180° around the origin.
- A(1,1): Using the rule
(x, y) → (-x, -y), A' becomes (-1, -1). - B(3,1): B' becomes (-3, -1).
- C(2,3): C' becomes (-2, -3).
Connect A', B', and C' to form the rotated triangle.
Rotations with a Different Center of Rotation:
When the center of rotation isn't the origin, the process becomes slightly more complex. You'll need to:
- Translate: Shift the shape so the center of rotation is at the origin.
- Rotate: Apply the appropriate rotation rule.
- Translate Back: Shift the shape back to its original position.
Tackling Different Rotation Problems:
Unit 9 Transformations Homework 3 likely presents a variety of problems. Here's how to approach some common types:
Problem Type 1: Identifying Rotations
These problems require you to analyze a pair of shapes and determine if a rotation has occurred, identifying the center of rotation and the angle of rotation. Look for patterns in the movement of corresponding points. Using tracing paper can be incredibly helpful for visually identifying the center and angle.
Problem Type 2: Performing Rotations
These problems directly ask you to rotate a shape or point given the center of rotation and the angle of rotation. Follow the steps outlined above, utilizing the appropriate rules and careful attention to detail.
Problem Type 3: Describing Rotations
You might be given a rotated shape and asked to describe the rotation, specifying the center of rotation, angle of rotation, and direction. Careful observation and potentially using geometric tools are key here.
Problem Type 4: Rotational Symmetry
Some problems may delve into rotational symmetry. A shape possesses rotational symmetry if it can be rotated less than 360° and still look identical to the original. The order of rotational symmetry is the number of times the shape can be rotated to look identical.
Advanced Rotation Concepts:
- Composition of Rotations: This involves performing multiple rotations consecutively. The final image is the result of the combined effect of all rotations.
- Matrices and Rotations: Linear algebra provides a powerful way to represent and perform rotations using matrices. This method is particularly useful for complex rotations and computer graphics.
- Isometries and Rotations: Rotations are a type of isometry, meaning they preserve distances and angles.
Strategies for Mastering Rotations:
- Practice Regularly: Consistent practice is key to solidifying your understanding of rotation concepts. Work through numerous problems, starting with easier ones and gradually increasing the difficulty.
- Visual Aids: Use tracing paper, graph paper, and geometry software to visualize rotations. This can significantly improve your understanding and problem-solving abilities.
- Understand the Rules: Memorize the rotation rules for common angles around the origin. Understanding the underlying logic behind these rules will help you tackle more complex problems.
- Break Down Complex Problems: If a problem seems overwhelming, break it down into smaller, manageable steps. For example, when rotating around a point other than the origin, separate the translation, rotation, and reverse translation steps.
- Seek Help When Needed: Don't hesitate to ask your teacher, classmates, or tutor for help if you're struggling with specific concepts or problems.
Conclusion:
Mastering rotations in Unit 9 Transformations Homework 3 requires a solid understanding of the fundamental concepts, a systematic approach to problem-solving, and consistent practice. By following the strategies outlined in this guide and dedicating sufficient time and effort, you can confidently tackle any rotation-related problem and achieve success in your geometry studies. Remember to utilize visual aids, break down complex problems, and seek help when needed. With diligent effort and a focused approach, mastering rotations will become a rewarding accomplishment.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Summary Of Chapter 5 Scarlet Letter
Mar 27, 2025
-
Unit 8 Test Right Triangles And Trigonometry Answer Key Pdf
Mar 27, 2025
-
Unit 5 Relationships In Triangles Homework 1 Triangle Midsegments
Mar 27, 2025
-
Match The Physical Characteristics Of The Organisms To Their Purpose
Mar 27, 2025
-
You Are Designing An Ecommerce Web Application
Mar 27, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Unit 9 Transformations Homework 3 Rotations . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
