Wave Interference Phet Lab Answer Key Pdf
Onlines
Mar 04, 2025 · 6 min read
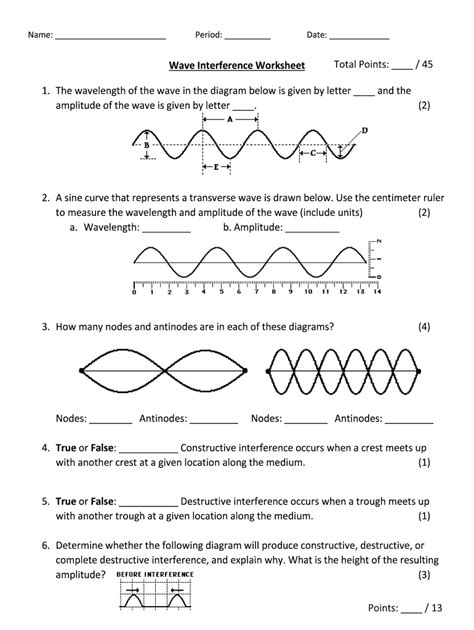
Table of Contents
Decoding Wave Interference: A Comprehensive Guide to the PhET Lab
The PhET Interactive Simulations website offers a fantastic resource for learning physics, including their Wave Interference simulation. This simulation allows users to explore the principles of wave superposition, constructive and destructive interference, and diffraction in a dynamic and engaging way. While there isn't an official "answer key" PDF for the PhET Wave Interference lab, this comprehensive guide will dissect the key concepts, potential experimental setups, and expected observations, essentially providing a detailed walkthrough to help you fully understand and interpret your results.
Understanding Wave Interference: The Fundamentals
Before diving into the lab, let's solidify our understanding of wave interference. Wave interference is the phenomenon that occurs when two or more waves overlap in space. The resulting wave is the superposition of the individual waves. This superposition can lead to either constructive interference or destructive interference.
Constructive Interference: Waves in Sync
Constructive interference occurs when two waves meet with their crests (peaks) aligned. The amplitudes of the individual waves add up, resulting in a wave with a larger amplitude than either of the original waves. Think of it like pushing a swing in time with its motion – each push adds to the swing's height. In the PhET simulation, you'll observe this as a taller, more intense wave.
Destructive Interference: Waves Out of Sync
Destructive interference occurs when two waves meet with a crest of one wave aligned with a trough (valley) of the other. The amplitudes of the waves subtract, potentially resulting in a wave with a smaller amplitude or even cancellation. Imagine pushing a swing just as it's moving towards you – your push counteracts its motion. In the PhET simulation, you'll see this as a smaller or completely canceled wave.
Key Parameters Affecting Interference
Several factors influence the outcome of wave interference:
- Wavelength (λ): The distance between two consecutive crests or troughs. Waves with similar wavelengths will interfere more predictably.
- Amplitude: The height of the wave from its equilibrium position. Larger amplitudes generally lead to more noticeable interference effects.
- Frequency (f): The number of waves passing a point per unit of time. While not directly influencing the interference pattern itself, frequency is linked to wavelength through the wave speed (v = fλ).
- Phase difference: The difference in position between two corresponding points on the waves. A zero phase difference leads to constructive interference, while a 180-degree phase difference leads to destructive interference.
Exploring the PhET Wave Interference Simulation: A Step-by-Step Guide
The PhET Wave Interference simulation provides various tools to manipulate wave parameters and observe their impact on interference patterns. Let's break down potential experiments and the expected results:
Experiment 1: Two Sources, Identical Waves
- Setup: Begin with two point sources emitting identical waves (same wavelength, amplitude, and frequency).
- Observation: As you adjust the distance between the sources, observe the interference pattern. You'll see alternating regions of constructive and destructive interference creating a pattern of bright and dark bands (or loud and quiet regions if you are using sound waves). The spacing between these bands is related to the wavelength and distance between the sources. This demonstrates the principle of double-slit interference.
- Analysis: Measure the distance between the bright (constructive interference) bands and calculate the wavelength based on the known distance between the sources. Compare your calculated wavelength with the value set in the simulation. This allows for verifying the relationship between wavelength, source separation, and interference pattern.
Experiment 2: Two Sources, Different Wavelengths
- Setup: Now, adjust the wavelength of one source while keeping the other constant.
- Observation: Notice that the interference pattern becomes less clear and regular. The spacing between constructive and destructive interference regions changes, and the overall pattern is more complex.
- Analysis: This illustrates that waves with different wavelengths don't produce a consistent interference pattern. The overlapping waves have varying phase relationships which lead to a less predictable superposition.
Experiment 3: Two Sources, Different Amplitudes
- Setup: Maintain identical wavelengths but change the amplitudes of the two sources.
- Observation: The intensity of the bright bands (constructive interference) will change; higher amplitudes will result in brighter bands. The dark bands (destructive interference), however, might not be completely dark as the waves don't completely cancel each other out if their amplitudes are different.
- Analysis: This highlights the role of amplitude in the intensity of the resultant wave. Even with destructive interference, the residual wave amplitude reflects the difference in the initial amplitudes.
Experiment 4: Exploring Diffraction
- Setup: Use a single point source and introduce a barrier with a slit or multiple slits.
- Observation: You'll observe diffraction, the bending of waves as they pass through the opening. A single slit will produce a diffraction pattern with a central bright region and weaker, dimmer bands on either side. Multiple slits create a more complex interference pattern combining diffraction and interference effects (similar to a diffraction grating).
- Analysis: The width of the central bright region in single-slit diffraction is related to the wavelength and the slit width. Multiple slits create a more complex pattern with sharp interference maxima (bright bands) whose spacing depends on the slit separation and wavelength.
Experiment 5: Investigating Phase Shifts
- Setup: Use the simulation's tools to introduce a phase shift between the two sources. This manipulates the starting position of one wave relative to the other.
- Observation: As you change the phase shift, you'll see the interference pattern shift. A 180-degree phase shift will transform regions of constructive interference into destructive interference and vice-versa.
- Analysis: This experiment directly shows the role of phase difference in wave superposition. It demonstrates that the relative positions of wave crests and troughs at the point of overlap critically determines the type of interference observed.
Beyond the Simulation: Real-World Applications of Wave Interference
Wave interference isn't just a theoretical concept; it has significant real-world implications:
- Noise-canceling headphones: These devices use destructive interference to reduce unwanted sounds. A microphone detects incoming noise and produces an "anti-noise" wave with opposite phase, effectively canceling it out.
- Optical instruments: Interference plays a vital role in the functioning of interferometers, tools used for precise measurements of distances, refractive indices, and surface irregularities.
- Holography: This technique uses interference of light waves to create three-dimensional images.
- Thin-film interference: The iridescent colors in soap bubbles and oil slicks are a result of interference between light waves reflected from the top and bottom surfaces of a thin film.
- Radio and television broadcasting: The design of antennas uses the principle of constructive interference to maximize signal strength and minimize unwanted signals.
Conclusion: Mastering Wave Interference
The PhET Wave Interference simulation is an excellent tool for understanding a fundamental concept in physics. By systematically exploring different wave parameters and observing their impact on interference patterns, you gain a deeper, intuitive understanding of wave superposition. This knowledge isn't just confined to the lab; its applications extend to various fields, highlighting the practical significance of wave interference in our daily lives and technological advancements. Remember, the key to mastering this topic lies in experimentation, observation, and careful analysis of the results. While there isn't a single "answer key," this detailed guide serves as a roadmap to navigate the simulation and derive a comprehensive understanding of wave interference. Conduct your experiments meticulously, record your observations precisely, and analyze the data thoroughly. Your understanding will emerge through the process of actively engaging with the simulation's interactive features.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
We Have Always Lived In The Castle Sparknotes
Mar 04, 2025
-
How Long Has William Morningstar Been Missing
Mar 04, 2025
-
Symbols In The Novel Lord Of The Flies
Mar 04, 2025
-
Records Are Considered Lost When The Following Conditions Are True
Mar 04, 2025
-
Catcher In The Rye List Of Characters
Mar 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Wave Interference Phet Lab Answer Key Pdf . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
