What Is A Resource Market In Economics
Onlines
Apr 06, 2025 · 7 min read
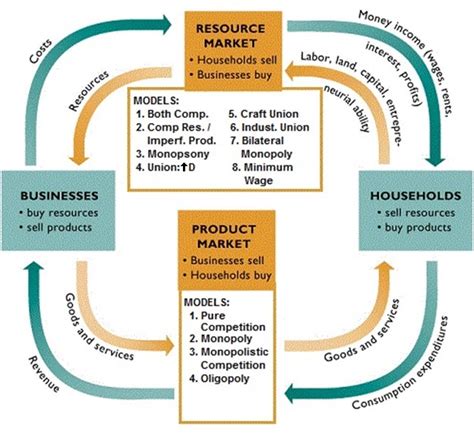
Table of Contents
What is a Resource Market in Economics? A Deep Dive
The resource market, also known as the factor market, forms a crucial cornerstone of economic activity. It's where the factors of production – land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurship – are bought and sold. Understanding how this market functions is essential to grasping the broader dynamics of any economy, from the microeconomic choices of individual firms to the macroeconomic trends influencing national output and employment. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of resource markets, exploring their key components, characteristics, and influence on the overall economy.
The Four Factors of Production: The Building Blocks of the Resource Market
The resource market revolves around the exchange of the four fundamental factors of production:
1. Land: More Than Just Dirt
In economics, "land" encompasses far more than just physical terrain. It includes all natural resources: minerals, forests, water bodies, and even the geographical location itself. The value of land is determined by its inherent productivity and its accessibility. A prime location for a business, for instance, will command a higher price than a remote, less accessible plot. Land rent, the payment for the use of land, is a significant component of resource market transactions.
2. Labor: The Human Capital
Labor represents the human effort exerted in the production process. This encompasses a wide spectrum of skills and abilities, from unskilled manual labor to highly specialized technical expertise. The price of labor is the wage rate, influenced by factors such as supply and demand, worker productivity, education levels, and market conditions. The labor market, a significant subset of the resource market, is highly complex and influenced by numerous social and economic factors. Labor unions and minimum wage laws play a crucial role in shaping the dynamics of the labor market.
3. Capital: Tools and Technology
Capital refers to the man-made goods used in the production of other goods and services. This includes machinery, equipment, factories, and technology. Unlike land, capital is a produced factor of production; it’s created through human effort and investment. The return on capital is typically in the form of interest or profit, reflecting the risk and opportunity cost associated with its deployment. Investment decisions play a pivotal role in shaping the demand for capital in the resource market.
4. Entrepreneurship: The Driving Force
Entrepreneurship is often considered the most crucial factor of production. It involves the ability to identify opportunities, organize resources effectively, and take the risks associated with starting and running a business. Entrepreneurs are the innovators and risk-takers who drive economic growth and create new jobs. Their reward is profit, which is the driving force behind entrepreneurial activity in the resource market. The level of entrepreneurial activity is heavily influenced by factors such as government regulations, access to capital, and the overall economic climate.
Supply and Demand in the Resource Market: A Dynamic Interaction
The resource market operates under the fundamental principles of supply and demand, mirroring the dynamics seen in the goods and services market.
Supply of Resources: Factors Influencing Availability
The supply of each factor of production is determined by a range of factors. Land supply is generally considered inelastic, as the quantity of land is fixed. However, the effective supply can be increased through technological advancements (e.g., better irrigation techniques), or through the discovery of new resources.
Labor supply is more elastic, responding to changes in wage rates and other factors such as education levels, population growth, and immigration policies. Capital supply depends on saving and investment rates, influenced by interest rates, technological advancements, and investor confidence. Entrepreneurial supply is difficult to quantify, but factors such as education, risk tolerance, and the overall economic environment play significant roles.
Demand for Resources: Derived Demand
The demand for resources in the resource market is a derived demand. This means it's derived from the demand for the goods and services that those resources produce. For example, the demand for labor in the construction industry is derived from the demand for new buildings. If the demand for new buildings increases, the demand for construction workers will also increase, leading to higher wages.
Several factors influence the demand for resources, including:
- Consumer demand: Higher consumer demand for goods and services will increase the demand for the resources used to produce them.
- Technological advancements: New technologies can increase productivity, altering the demand for certain resources. For example, automation might reduce the demand for unskilled labor while increasing the demand for skilled technicians.
- Government policies: Taxes, subsidies, and regulations can significantly impact the demand for resources.
- Prices of other resources: The relative prices of different factors of production influence the demand for each. If the price of labor increases, businesses might substitute capital for labor.
Market Equilibrium and Resource Allocation: Finding the Balance
The interaction of supply and demand determines the equilibrium price and quantity of each factor of production in the resource market. This equilibrium point reflects the efficient allocation of resources within the economy. However, market imperfections can lead to deviations from this ideal allocation.
Market Imperfections in the Resource Market: Challenges and Consequences
The resource market, despite its theoretical efficiency, is frequently affected by various market imperfections:
1. Monopsony: Single Buyer Dominance
In a monopsony, a single buyer dominates the market for a particular resource. This allows the buyer to exert significant influence on the price, often suppressing wages or resource prices below their competitive levels. A classic example could be a large mining company in a small town – the company might be the sole employer, giving it significant leverage in wage negotiations.
2. Monopoly: Single Seller Dominance
A monopoly in the resource market occurs when a single seller controls the supply of a crucial resource. This allows the seller to charge artificially high prices, potentially leading to inefficient resource allocation and reduced economic output. A company owning a unique mineral deposit might exert such monopolistic control.
3. Imperfect Information: Uncertainty and Risk
Asymmetric information, where one party has more information than the other, can significantly distort resource market outcomes. For example, employers might have more information about job opportunities than job seekers, impacting wage negotiations. Similarly, landowners might have better knowledge of land quality than potential buyers, leading to inefficient pricing.
4. Externalities: Unaccounted Costs and Benefits
Externalities occur when the production or consumption of a good or service imposes costs or benefits on third parties not directly involved in the transaction. For instance, pollution from a factory affects the surrounding environment and community, representing a negative externality. These unaccounted costs or benefits can lead to inefficient resource allocation.
5. Government Intervention: Regulations and Policies
Government intervention, through regulations, taxes, subsidies, and minimum wage laws, can significantly impact resource market outcomes. While aiming to improve equity or address market failures, these interventions can also lead to unintended consequences, such as distortions in resource allocation or reduced efficiency.
The Resource Market's Impact on the Macroeconomy: A Broader Perspective
The resource market plays a pivotal role in influencing macroeconomic outcomes:
- Economic Growth: The efficient allocation of resources is crucial for economic growth. A well-functioning resource market ensures that resources are channeled to their most productive uses, maximizing output and creating new opportunities.
- Inflation: Changes in resource prices, particularly wages and raw material costs, can significantly impact the overall inflation rate. Rapid increases in resource prices can contribute to cost-push inflation.
- Employment: The labor market, a critical component of the resource market, determines employment levels and unemployment rates. Changes in labor demand and supply directly affect the number of people employed in the economy.
- Income Distribution: The resource market significantly influences the distribution of income among different factors of production. Changes in wage rates, land rents, interest rates, and profits affect the income received by workers, landowners, capitalists, and entrepreneurs.
Conclusion: Understanding the Resource Market for a Holistic Economic View
The resource market is far more than just a theoretical construct; it's the engine that drives economic activity. Understanding its dynamics, from the supply and demand interactions of its four key components to the market imperfections that often hinder its efficiency, is essential for any thorough comprehension of how economies function. By analyzing the interplay of supply, demand, and various market influences, we can gain valuable insights into broader macroeconomic trends, fostering more informed economic policies and decisions. Furthermore, grasping the role of the resource market helps in understanding how resources are allocated, income is distributed, and ultimately, how societies strive for sustainable and equitable economic growth.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Graceful Dancer Moved Across The Stage
Apr 08, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Statements Are True Regarding Political Independents
Apr 08, 2025
-
Electron Configuration Worksheet Pogil Answer Key
Apr 08, 2025
-
Which Statement Describes The Valve Control On Pressurized Vessels
Apr 08, 2025
-
The Scarlet Letter Summary Chapter 3
Apr 08, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is A Resource Market In Economics . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.