What Is One Component Of Proactive Procedures
Onlines
Mar 05, 2025 · 6 min read
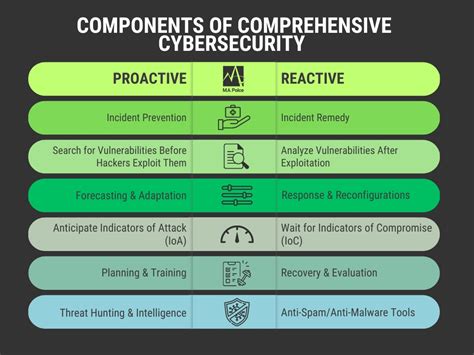
Table of Contents
What is One Component of Proactive Procedures? Risk Assessment
Proactive procedures are the cornerstone of effective risk management, enabling organizations to anticipate and mitigate potential problems before they escalate into crises. While numerous components contribute to a robust proactive approach, risk assessment stands out as a fundamental and crucial element. This article delves into the critical role of risk assessment within proactive procedures, exploring its methodologies, benefits, and essential considerations for implementation.
Understanding Risk Assessment as a Proactive Procedure
Risk assessment, at its core, is a systematic process of identifying potential hazards, analyzing their likelihood and potential impact, and determining appropriate control measures. It's not merely about identifying problems; it's about proactively understanding the potential for problems and developing strategies to prevent them. This proactive approach differentiates it from reactive measures, which address problems only after they occur.
Within the broader framework of proactive procedures, risk assessment provides the foundational information needed for strategic decision-making. It allows organizations to:
- Prioritize resources: By understanding the relative risks, organizations can allocate resources effectively, focusing on the most critical threats.
- Develop mitigation strategies: Risk assessment informs the development of targeted strategies to reduce or eliminate identified risks.
- Improve operational efficiency: Proactive identification and mitigation of risks can prevent costly disruptions and downtime.
- Enhance compliance: Many industries have regulatory requirements for risk assessment, ensuring compliance and avoiding penalties.
- Strengthen organizational resilience: By anticipating potential threats, organizations build resilience and increase their capacity to withstand unexpected challenges.
The Five Key Steps of a Comprehensive Risk Assessment
A comprehensive risk assessment typically involves five crucial steps:
-
Hazard Identification: This initial step involves identifying all potential hazards, both internal and external, that could affect the organization. This includes reviewing past incidents, conducting site inspections, analyzing operational processes, and considering external factors like economic downturns or natural disasters. Thoroughness is paramount at this stage; overlooked hazards can have significant consequences.
- Techniques for Hazard Identification: Brainstorming sessions, checklists, fault tree analysis, and hazard and operability studies (HAZOP) are common techniques used for effective hazard identification.
-
Risk Analysis: Once hazards are identified, the next step involves analyzing the likelihood and potential impact of each hazard. This often involves a qualitative or quantitative assessment. Qualitative assessments use descriptive terms (e.g., low, medium, high) to characterize likelihood and impact, while quantitative assessments utilize numerical data to express probabilities and consequences.
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative Analysis: The choice between qualitative and quantitative analysis depends on factors such as the complexity of the hazard, the availability of data, and the resources available. Often, a combination of both methods is employed for a more comprehensive assessment.
-
Risk Evaluation: This step involves combining the likelihood and impact assessments to determine the overall level of risk associated with each hazard. This often uses a risk matrix, which visually represents the relationship between likelihood and impact, allowing for prioritization of risks.
- Prioritization and Risk Matrix: A risk matrix helps to prioritize risks based on their severity. High-risk hazards require immediate attention, while lower-risk hazards might be addressed later or with less intensive mitigation strategies.
-
Risk Control: This crucial step involves determining appropriate control measures to reduce or eliminate the identified risks. Control measures can range from simple administrative changes (e.g., improved training) to more complex engineering controls (e.g., safety equipment). The goal is to implement cost-effective measures that reduce risk to an acceptable level.
- Hierarchy of Controls: A common approach is to follow a hierarchy of controls, prioritizing elimination, substitution, engineering controls, administrative controls, and finally, personal protective equipment (PPE).
-
Risk Monitoring and Review: The risk assessment process is not a one-time event. Risks change over time, and the effectiveness of control measures needs to be regularly reviewed and updated. This ongoing monitoring allows for prompt adaptation to new risks and ensures that the proactive approach remains effective.
- Regular Review and Updates: Regular reviews should be scheduled, considering factors such as changes in legislation, operational procedures, or external factors.
The Benefits of a Proactive Risk Assessment Approach
The benefits of incorporating risk assessment as a core component of proactive procedures are significant and far-reaching:
- Reduced Accidents and Incidents: Proactive identification and mitigation of hazards significantly reduce the likelihood of accidents and incidents, protecting employees, assets, and the organization's reputation.
- Improved Safety Culture: A robust risk assessment process fosters a positive safety culture, encouraging employees to identify and report hazards, promoting a proactive and responsible approach to safety.
- Cost Savings: Preventing incidents is far more cost-effective than dealing with the consequences of an accident or incident. This includes reduced costs associated with medical expenses, repairs, legal fees, and lost productivity.
- Enhanced Operational Efficiency: By anticipating and mitigating potential disruptions, organizations can maintain operational efficiency and minimize downtime.
- Increased Competitiveness: Organizations that prioritize safety and risk management often gain a competitive advantage, attracting and retaining talent, and building stronger relationships with clients and stakeholders.
- Improved Compliance: Risk assessment is often a mandatory requirement for regulatory compliance in many industries, helping organizations avoid fines and penalties.
- Stronger Reputation: Demonstrating a commitment to safety and risk management enhances the organization's reputation and builds trust with stakeholders.
- Better Decision-Making: Risk assessment provides the data and insights needed for informed and effective decision-making at all levels of the organization.
Key Considerations for Implementing Effective Risk Assessments
Successful implementation of risk assessment requires careful consideration of several factors:
- Scope and Objectives: Clearly define the scope of the risk assessment, specifying the areas, processes, or activities to be included. Establishing clear objectives helps to focus the assessment and ensure that it addresses the most relevant risks.
- Team Composition: Assemble a multidisciplinary team with expertise in relevant areas, ensuring diverse perspectives are considered. This team should include individuals with experience in safety, operations, and legal compliance.
- Data Collection Methods: Select appropriate data collection methods to gather relevant information, considering the nature of the hazards and the available resources. This might involve interviews, surveys, inspections, and data analysis.
- Documentation: Maintain meticulous documentation throughout the process, recording all identified hazards, risk assessments, control measures, and review schedules. This documentation is crucial for demonstrating compliance and facilitating future assessments.
- Communication and Training: Effective communication and training are essential to ensure that all employees understand the importance of risk assessment and their role in the process. This fosters a culture of proactive safety and risk management.
- Regular Review and Updates: Risk assessments are not static documents. They must be reviewed and updated regularly to reflect changes in operations, technology, legislation, and external factors. This ensures that the risk assessment remains relevant and effective over time.
Conclusion: Risk Assessment – The Proactive Cornerstone
Risk assessment is undoubtedly a critical component of proactive procedures. It’s more than just a checklist; it's a continuous process that empowers organizations to anticipate, mitigate, and manage potential hazards. By systematically identifying, analyzing, evaluating, controlling, and monitoring risks, organizations can build a culture of safety, enhance operational efficiency, and achieve sustainable success. The investment in a robust risk assessment program is an investment in the organization's future, safeguarding its assets, protecting its people, and ensuring its long-term viability. Through a well-planned and consistently implemented risk assessment process, organizations can transform potential threats into opportunities for growth and resilience.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
By Any Other Name Questions And Answers Pdf
Mar 05, 2025
-
We Have Always Lived In A Castle Sparknotes
Mar 05, 2025
-
El Capitan Era El Mas Feliz Correct Incorrect
Mar 05, 2025
-
Which Of These Statements Accurately Describes A Dts Role
Mar 05, 2025
-
Julius Caesar Act 2 Character Map
Mar 05, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is One Component Of Proactive Procedures . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
