What Is The Instantaneous Rating Of A Fuse
Onlines
Mar 24, 2025 · 6 min read
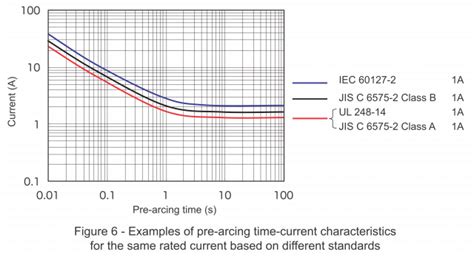
Table of Contents
What is the Instantaneous Rating of a Fuse? Understanding Fuse Characteristics for Optimal Circuit Protection
Fuses are unsung heroes of electrical systems, silently safeguarding our devices and preventing catastrophic failures. While their basic function—to interrupt current flow when it exceeds a safe level—is well-known, a deeper understanding of their characteristics, particularly the instantaneous rating, is crucial for selecting the right fuse for a specific application. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of instantaneous fuse ratings, exploring their significance, calculation methods, and practical implications.
Understanding Fuse Ratings: Beyond the Amperage
A fuse's rating, often expressed in amperes (A), represents its continuous current carrying capacity. This is the maximum current the fuse can withstand indefinitely without melting. However, this is only one aspect of a fuse's performance. Real-world scenarios involve transient current surges, short circuits, and fault conditions that far exceed the continuous rating. This is where the instantaneous rating, also known as the let-through energy, or sometimes described by pre-arcing current characteristics, becomes critically important.
The Significance of Instantaneous Rating
The instantaneous rating defines the fuse's ability to quickly interrupt excessively high currents. It's not a single numerical value but rather a complex relationship between:
- Current: The magnitude of the overcurrent.
- Time: The duration of the overcurrent.
- Energy: The total energy let through before the fuse blows.
A fuse with a high instantaneous rating can tolerate larger current surges for shorter durations before interrupting the circuit. Conversely, a fuse with a low instantaneous rating will quickly clear even relatively smaller surges. This characteristic is essential because some devices are susceptible to damage even from short-lived current spikes.
The Time-Current Characteristic Curve: Visualizing Fuse Behavior
The relationship between current and the time it takes a fuse to blow is depicted by the time-current characteristic (TCC) curve. This curve is crucial for understanding a fuse's instantaneous behavior. Different fuse types exhibit different TCC curves, reflecting their intended applications.
Deciphering the TCC Curve: Key Features
- Pre-arcing time: The time delay before the fuse starts to melt.
- Melting time: The time taken for the fuse element to completely melt and open the circuit.
- Total clearing time: The sum of pre-arcing and melting times.
- Interrupting rating: The maximum current the fuse can safely interrupt without damage to itself or the surrounding circuitry.
The TCC curve isn't simply a smooth line; it often includes distinct regions:
- Low current region: At currents slightly above the rated current, the fuse may take a relatively long time to blow. This characteristic is designed to accommodate temporary overloads.
- High current region: As the current increases significantly, the fuse's clearing time decreases drastically. This rapid response is essential to protect against short circuits and faults.
- Ultra-fast region (for specific fuse types): Some fuses, especially those designed for sensitive electronics, exhibit extremely fast clearing times even at moderately high currents.
How Instantaneous Rating is Determined and Expressed
Unfortunately, there isn't a single, universally accepted way to express a fuse's instantaneous rating. Manufacturers use various methods, often presenting data in different formats:
- Let-Through Energy: This is the total energy dissipated in the fuse before it clears the fault. It's often expressed in joules (J) or watt-seconds (Ws). Lower let-through energy indicates a faster response.
- Pre-arcing Current: This represents the current level at which the fuse begins to melt. This value, in conjunction with the TCC curve, helps to estimate the instantaneous response.
- Current Limiting: Some fuse datasheets specify the fuse's current-limiting capability. This refers to the peak current allowed before the fuse interrupts the flow.
- TCC Curves (Graphical Representation): The most complete representation of instantaneous characteristics is a detailed TCC curve provided by the manufacturer. This curve illustrates the fuse's behavior over a wide range of current levels.
Factors Affecting Instantaneous Fuse Behavior
Several factors influence a fuse's instantaneous response:
- Fuse Type: Different fuse types (e.g., fast-acting, slow-blow, ultra-fast) are designed with distinct TCC curves to meet specific needs.
- Ambient Temperature: Higher temperatures can affect the fuse element's melting point, potentially impacting its clearing time.
- Fuse Age: Over time, fuses can degrade, leading to changes in their TCC curve and potentially slower clearing times.
- Voltage: The voltage across the fuse influences the arcing behavior during the melting process, affecting the total clearing time.
Selecting the Right Fuse: Matching the Application to the Instantaneous Rating
Choosing the appropriate fuse requires a careful consideration of several factors:
- Load Characteristics: Analyze the load's current draw under normal operating conditions and during anticipated surges.
- Circuit Requirements: Determine the acceptable level of let-through energy for the protected equipment. Sensitive electronics require fuses with low let-through energy.
- Fuse Type: Select a fuse type whose TCC curve matches the anticipated current profiles.
- Environmental Conditions: Consider the impact of ambient temperature and other environmental factors on the fuse's performance.
- Manufacturer's Data Sheets: Always consult the manufacturer's datasheets, paying particular attention to the TCC curve and let-through energy specifications.
Consequences of Improper Fuse Selection: Safety and Reliability Risks
Using a fuse with an inadequate instantaneous rating can lead to several serious consequences:
- Equipment Damage: Current surges exceeding the fuse's capacity can damage sensitive components within the protected circuit.
- System Failure: Improper fuse selection can lead to complete system failure or malfunction.
- Fire Hazards: If the fuse fails to interrupt excessive current, it could generate excessive heat, posing a significant fire risk.
- Safety Risks: Failure to protect the circuit properly can result in electrical shocks or other safety hazards.
Advanced Fuse Technologies and Their Instantaneous Characteristics
Modern advancements in fuse technology have yielded more sophisticated solutions with enhanced instantaneous characteristics:
- High-Speed Fuses: These fuses exhibit extremely fast clearing times, even at high fault currents, making them ideal for protecting sensitive electronic equipment.
- Current-Limiting Fuses: These fuses not only interrupt the fault current but also significantly limit the peak current, reducing the energy let through and minimizing the impact on the circuit.
- Surface Mount Fuses: Small size and surface mount technology offer space-saving solutions for electronic devices with high-density circuits. These fuses also often boast improved performance in terms of instantaneous response.
Conclusion: Understanding Instantaneous Rating for Comprehensive Circuit Protection
The instantaneous rating of a fuse is a critical parameter for ensuring safe and reliable operation of electrical circuits. While the continuous current rating indicates a fuse's ability to handle steady-state currents, the instantaneous rating determines its response to transient events, short circuits, and other fault conditions. Understanding the time-current characteristic curve, let-through energy, and other related parameters is essential for selecting the right fuse for a given application. Failure to match the fuse's characteristics to the load and circuit requirements can lead to equipment damage, system failure, and even safety hazards. Therefore, always consult the manufacturer's datasheets and consider consulting with electrical professionals for complex applications to ensure optimal circuit protection.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
1 4 4 Practice Modeling The Rescue Ship Answer Key
Mar 26, 2025
-
Summary Of Contents Of The Dead Mans Pocket
Mar 26, 2025
-
Characters Of Their Eyes Were Watching God
Mar 26, 2025
-
Quotes From The Book And Then There Were None
Mar 26, 2025
-
Mrs Pierce Would Like To Enroll
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Instantaneous Rating Of A Fuse . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
