What Three Environmental Conditions Have The Most Effect On Comfort
Onlines
Mar 18, 2025 · 6 min read
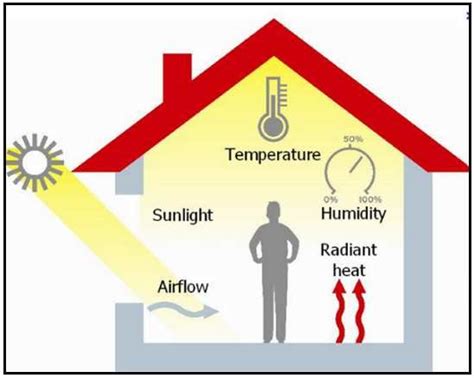
Table of Contents
- What Three Environmental Conditions Have The Most Effect On Comfort
- Table of Contents
- What Three Environmental Conditions Have the Most Effect on Comfort?
- 1. Temperature: The Foundation of Thermal Comfort
- The Impact of Temperature on Comfort
- Finding the Goldilocks Zone: The Role of Personal Preferences and Acclimatization
- 2. Humidity: The Invisible Influence
- The Effect of Humidity on Comfort
- Balancing Act: Finding the Optimal Humidity Range
- 3. Air Quality: The Often-Overlooked Factor
- The Impact of Poor Air Quality on Comfort
- Improving Indoor Air Quality for Enhanced Comfort
- The Interplay Between Temperature, Humidity, and Air Quality
- Conclusion: Creating a Comfortable Environment Through Holistic Approach
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
What Three Environmental Conditions Have the Most Effect on Comfort?
Creating a comfortable environment is crucial for our well-being, productivity, and overall quality of life. While many factors contribute to comfort, three environmental conditions stand out as having the most significant impact: temperature, humidity, and air quality. Understanding how these factors interact and influence our perception of comfort is key to designing and maintaining spaces that promote well-being. This article delves deep into each condition, exploring their individual effects and the interplay between them.
1. Temperature: The Foundation of Thermal Comfort
Temperature is arguably the most dominant factor influencing our perception of comfort. Our bodies are constantly striving to maintain a stable internal temperature of around 98.6°F (37°C). When the surrounding environment deviates significantly from this ideal, our bodies must work harder to compensate, leading to discomfort and potentially health issues.
The Impact of Temperature on Comfort
Too Hot: Excessive heat can lead to a range of negative effects. These include:
- Heat stress: This can manifest as fatigue, dizziness, nausea, and in severe cases, heatstroke.
- Reduced productivity: Studies have consistently shown a decline in cognitive function and physical performance in excessively hot environments.
- Sleep disturbances: High temperatures interfere with sleep quality, leading to daytime fatigue and reduced well-being.
- Increased irritability: Feeling too hot can negatively impact mood and increase irritability.
Too Cold: Similarly, exposure to excessively cold temperatures also presents significant challenges:
- Hypothermia: In extreme cases, prolonged exposure to cold can lead to hypothermia, a life-threatening condition.
- Reduced blood circulation: Cold temperatures cause blood vessels to constrict, reducing blood flow to extremities and leading to numbness and discomfort.
- Muscle stiffness: Cold muscles are less flexible and more prone to injury.
- Increased respiratory issues: Cold, dry air can irritate the respiratory system, exacerbating conditions like asthma.
Finding the Goldilocks Zone: The Role of Personal Preferences and Acclimatization
The ideal temperature for comfort is subjective and varies depending on several factors, including:
- Individual preferences: Some people naturally prefer warmer temperatures, while others prefer cooler ones. Age, activity level, and clothing choices also play a role.
- Acclimatization: Our bodies adapt to different temperature ranges over time. Someone accustomed to a hot climate will likely feel more comfortable at a higher temperature than someone from a cold climate.
- Activity level: Metabolic activity generates heat. Individuals engaged in physical activity will feel comfortable at a lower temperature than those at rest.
- Clothing: Appropriate clothing is crucial for maintaining thermal comfort. Layering allows for adjustments based on changing conditions.
2. Humidity: The Invisible Influence
Humidity, the amount of water vapor present in the air, significantly impacts our thermal comfort, often in a less obvious way than temperature. While temperature directly affects our body's heat exchange with the environment, humidity impacts how effectively our bodies can cool themselves through sweat evaporation.
The Effect of Humidity on Comfort
High Humidity: High humidity hinders the evaporation of sweat, reducing the body's ability to cool itself through perspiration. This can lead to:
- Increased perceived temperature: High humidity makes the air feel hotter than it actually is, exacerbating the effects of heat. This is often referred to as the "heat index."
- Increased discomfort: The sticky, clammy feeling associated with high humidity is inherently uncomfortable.
- Exacerbation of health conditions: High humidity can worsen respiratory conditions and trigger allergic reactions.
- Mold and mildew growth: High humidity creates a favorable environment for the growth of mold and mildew, potentially impacting indoor air quality and health.
Low Humidity: Conversely, low humidity can also create discomfort:
- Dry skin and mucous membranes: Dry air can lead to dry skin, chapped lips, and irritated respiratory passages.
- Static electricity: Low humidity increases static electricity, which can be annoying and even cause minor shocks.
- Increased susceptibility to respiratory infections: Dry air can make the respiratory system more vulnerable to infections.
Balancing Act: Finding the Optimal Humidity Range
The ideal humidity range for comfort typically falls between 30% and 60%. Levels outside this range can negatively impact comfort and health. Humidifiers and dehumidifiers can be used to adjust humidity levels in indoor spaces to achieve optimal comfort.
3. Air Quality: The Often-Overlooked Factor
Air quality encompasses a wide range of factors, all of which can significantly affect comfort and well-being. These factors include:
- Temperature: As discussed earlier, temperature is a crucial aspect of air quality and impacts our comfort levels significantly.
- Humidity: Humidity also plays a critical role in air quality, influencing the growth of mold and other allergens.
- Particulate matter (PM): These tiny particles, originating from sources such as vehicle exhaust, industrial emissions, and dust, can irritate the respiratory system and cause discomfort.
- Volatile organic compounds (VOCs): VOCs are emitted from various sources, including paints, cleaning products, and building materials. Exposure to high levels of VOCs can cause headaches, eye irritation, and other health problems.
- Carbon dioxide (CO2): High levels of CO2 can lead to drowsiness, headaches, and reduced cognitive function.
- Allergens: Pollens, dust mites, pet dander, and mold spores are common allergens that can trigger allergic reactions and respiratory problems.
- Odors: Unpleasant odors from various sources can also impact comfort and well-being.
The Impact of Poor Air Quality on Comfort
Poor air quality can lead to:
- Respiratory problems: Irritated airways, coughing, wheezing, and other respiratory symptoms are common consequences of poor air quality.
- Headaches and fatigue: Exposure to pollutants and allergens can lead to headaches, fatigue, and reduced cognitive function.
- Allergies and asthma attacks: Poor air quality can trigger allergic reactions and exacerbate asthma symptoms.
- Reduced productivity: Poor air quality can negatively impact concentration and productivity.
Improving Indoor Air Quality for Enhanced Comfort
Improving indoor air quality involves addressing various factors, including:
- Ventilation: Adequate ventilation is essential for diluting pollutants and bringing in fresh air.
- Air filtration: High-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters can remove airborne particles and allergens.
- Source control: Reducing the sources of pollutants, such as using low-VOC paints and cleaning products, is crucial.
- Regular cleaning: Regular cleaning and dusting can remove allergens and other contaminants.
- Plant usage: Certain plants can help filter the air and improve air quality.
The Interplay Between Temperature, Humidity, and Air Quality
It's crucial to understand that these three environmental conditions don't act in isolation. They interact in complex ways, and optimizing one without considering the others can lead to suboptimal results. For instance:
- High temperature and high humidity: This combination creates a particularly uncomfortable environment, as the body's ability to cool itself through sweat evaporation is significantly reduced.
- Low temperature and low humidity: This can lead to dry, uncomfortable air that exacerbates respiratory issues.
- Good air quality with poor temperature control: Even with clean air, an excessively hot or cold environment will be uncomfortable.
Conclusion: Creating a Comfortable Environment Through Holistic Approach
Creating a comfortable environment requires a holistic approach that considers the interplay between temperature, humidity, and air quality. By understanding the individual effects of these factors and their interactions, we can design and maintain spaces that promote well-being, productivity, and overall quality of life. This might involve investing in HVAC systems with advanced controls, implementing air purification strategies, and educating occupants about the importance of maintaining optimal environmental conditions. Ultimately, prioritizing comfort through a thoughtful and comprehensive approach leads to significant improvements in health, happiness, and overall well-being.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Chapter 10 Dihybrid Cross Worksheet Answer Key
Mar 18, 2025
-
7 7 Scale Drawings And Models Answer Key
Mar 18, 2025
-
Ap Physics Unit 6 Progress Check Mcq
Mar 18, 2025
-
Summary For Chapter 8 Lord Of The Flies
Mar 18, 2025
-
A User Is Unable To Reach Google Com
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Three Environmental Conditions Have The Most Effect On Comfort . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
