What Type Of Structure Is Shown In This Figure
Onlines
Mar 13, 2025 · 5 min read
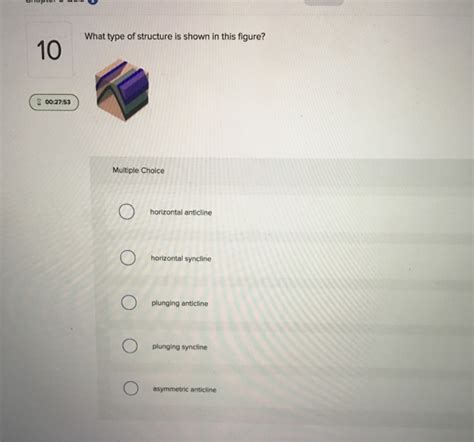
Table of Contents
Decoding Architectural Structures: A Comprehensive Guide to Identifying Building Types from Visuals
Identifying the type of structure depicted in a figure requires a keen eye for detail and a solid understanding of architectural styles and construction techniques. This guide delves into the process, examining various structural elements and their implications for classification. We'll move beyond simple labels like "house" or "building" and explore the nuances of architectural typology, focusing on how to accurately determine the structure's type from a visual representation.
The Importance of Visual Analysis in Structural Identification
Before we begin analyzing specific examples, let's emphasize the crucial role of visual observation. A picture, even a photograph, can reveal a wealth of information about a structure's characteristics. Careful examination allows us to identify key elements like:
-
Roofline: The shape and style of the roof are significant indicators. Gable, hip, gambrel, mansard, shed—each has distinct implications for the structure's type and purpose. The material (tiles, shingles, metal) also contributes to the overall impression.
-
Wall Systems: Are the walls load-bearing (supporting the roof directly)? Or is there a skeletal framework (like steel or timber) supporting the structure, allowing for more flexibility in design? The materials used (brick, stone, wood, concrete, etc.) also offer vital clues.
-
Window and Door Placement: The size, shape, and arrangement of windows and doors provide insights into the building's function and aesthetic style. Symmetrical facades often suggest formal designs, while asymmetrical designs hint at more informal or modern styles.
-
Overall Form and Proportion: The building's overall shape (rectangular, L-shaped, etc.) and the proportions of its elements (height, width, depth) contribute significantly to its visual identity and help determine its type.
-
Architectural Style: Recognizable architectural styles like Victorian, Georgian, Tudor, or Modernist possess distinctive features. Identifying these styles provides a strong starting point for classification.
Dissecting Architectural Styles: A Visual Approach
Let's explore some common architectural styles and their visual characteristics. Remember, these are general guidelines, and hybrid styles are frequent.
1. Victorian Architecture (1837-1901): Characterized by ornate detailing, asymmetrical facades, steeply pitched roofs (often with gables and towers), and a variety of decorative elements like gingerbread trim, bay windows, and elaborate porches.
2. Georgian Architecture (1714-1830): Known for its symmetry, rectangular form, evenly spaced windows, and a simple, elegant design. Usually features a classical facade with restrained ornamentation.
3. Tudor Architecture (15th-16th Century Revival): Defined by steep-pitched gables, prominent chimneys, half-timbering (exposed wooden framing), and decorative details inspired by medieval English architecture.
4. Colonial Architecture (Various): Encompasses a range of styles reflecting colonial influence, varying by region and time period. Common features include symmetrical facades, simple lines, and often the use of local materials. Examples include Spanish Colonial, Dutch Colonial, and Georgian Colonial.
5. Modern Architecture (Early 20th Century Onwards): Emphasizes functionality, clean lines, open floor plans, and the use of modern materials like steel and glass. Often characterized by a lack of ornamentation.
6. Post-Modern Architecture (Late 20th Century): A reaction against Modernism, characterized by playful use of form, color, and ornamentation. Often features a mix of historical and contemporary styles.
7. Contemporary Architecture (Present Day): A broad term encompassing current architectural trends, often characterized by sustainability, innovative materials, and unique designs. Can include a wide range of styles and aesthetics.
Analyzing Structural Elements for Classification
Beyond architectural styles, analyzing structural elements offers crucial clues. Let's examine specific elements:
1. Foundation: The type of foundation—slab-on-grade, basement, crawl space—reveals information about the building's age, location (soil conditions), and intended use.
2. Framing: Is the structure framed with wood, steel, or concrete? Wood framing is common in residential construction, while steel and concrete are more frequently used in larger commercial and industrial buildings.
3. Roofing System: The type of roofing system—trusses, rafters, arches—affects the building's structural strength and aesthetic appearance. Different roofing systems are suited to different spans and loads.
4. Load-Bearing Walls: Are the walls carrying the weight of the roof and floors? Load-bearing walls are thicker and less flexible than non-load-bearing walls.
Identifying Specific Structure Types
Let's look at how we can use these visual cues to identify specific structure types:
1. Residential Structures: Houses, apartments, townhouses, etc. These are usually smaller in scale, characterized by residential features like bedrooms, bathrooms, kitchens, and living spaces. Identifying the architectural style (Victorian, Colonial, Modern, etc.) further refines the classification.
2. Commercial Structures: Office buildings, retail spaces, restaurants, etc. These are often larger in scale, characterized by features suited to commercial activity. They might feature large open spaces, multiple entrances, and specialized facilities. They usually reflect more contemporary styles.
3. Industrial Structures: Warehouses, factories, power plants, etc. These structures emphasize functionality and durability. They often have large spans, heavy-duty construction, and specialized equipment. Their design is frequently utilitarian.
4. Institutional Structures: Schools, hospitals, government buildings, etc. These structures often have specific features required for their function, such as classrooms, operating rooms, or courtrooms. Their design reflects their function and often incorporates elements of grandeur or formality.
The Limitations of Visual Analysis
It's crucial to acknowledge the limitations of relying solely on visual analysis. A photograph may not capture all relevant details. Factors like the building's interior layout and construction techniques may not be visible. In some cases, additional information—like historical records or architectural drawings—might be needed for a complete understanding of the structure.
Conclusion: A Holistic Approach to Identification
Identifying the type of structure shown in a figure requires a multi-faceted approach. Combining visual analysis of architectural styles, structural elements, and the overall context provides a more accurate and comprehensive understanding. While a single image might offer clues, a holistic approach, considering all available information, is necessary for a definitive classification. Remember, practice sharpens your observational skills. The more images you analyze, the more adept you will become at recognizing subtle differences and accurately identifying the types of structures depicted.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Word Best Characterizes Yang Guizi
Mar 13, 2025
-
Unit 3 Homework 4 Graphing Quadratic Equations And Inequalities Answers
Mar 13, 2025
-
Q5 1 Which Of The Following Is False
Mar 13, 2025
-
Ap Lang Unit 8 Progress Check
Mar 13, 2025
-
Based On The Passage The Haida Had Values That
Mar 13, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Type Of Structure Is Shown In This Figure . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
