When Stacking Materials Such As Bricks Ratio
Onlines
Apr 03, 2025 · 6 min read
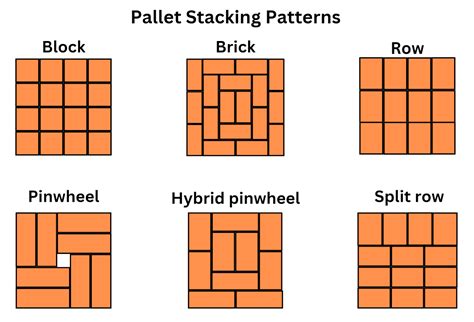
Table of Contents
When Stacking Materials Such as Bricks: Understanding Ratios for Strength and Stability
Stacking materials, particularly bricks, requires more than just haphazard piling. Understanding the ratios involved in creating stable and strong stacks is crucial for various applications, from construction projects to simple storage solutions. This article delves deep into the science and art of stacking, focusing on the critical role of ratios in achieving structural integrity and optimal material usage.
The Importance of Ratio in Material Stacking
The ratio in material stacking refers to the proportional relationship between different aspects of the stack, primarily:
- Height-to-Width Ratio: This determines the overall stability of the stack. A taller stack with a narrow base is inherently less stable than a shorter, wider one.
- Material-to-Material Ratio: This is especially relevant when stacking diverse materials with varying weights, densities, and shapes. Proper ratios prevent unequal stress distribution and potential collapse.
- Mortar-to-Brick Ratio (for bricklaying): In bricklaying, the ratio of mortar to bricks significantly impacts the strength and durability of the structure. Too little mortar leads to weak joints, while excessive mortar weakens the overall structure and adds unnecessary weight.
- Support Structure Ratio: This considers the relationship between the stack's weight and the strength of the underlying support structure (ground, pallet, shelf, etc.). An improperly supported stack will inevitably fail.
Ignoring these ratios can lead to:
- Stack Collapse: This is the most obvious consequence, potentially causing damage to materials, equipment, and even injury.
- Uneven Settling: Over time, uneven weight distribution can cause settling, leading to instability and potential structural failure.
- Material Damage: Crushing or damage to individual units due to excessive pressure or improper support.
- Wasted Materials: Inefficient stacking can lead to unnecessary material consumption and increased project costs.
Stacking Bricks: A Detailed Look at Ratios
Bricks, being a fundamental building material, demand a meticulous understanding of stacking ratios for robust structures. Let's explore the key ratios in bricklaying and stacking:
1. Height-to-Width Ratio in Brick Stacking:
The ideal height-to-width ratio for brick stacks depends heavily on several factors:
- Brick Type and Size: Larger, heavier bricks require a lower height-to-width ratio for stability. The dimensions and weight of the bricks directly influence the maximum achievable height.
- Mortar Strength: Stronger mortar allows for taller stacks, as it provides better bonding and support between bricks.
- Environmental Conditions: Wind, temperature fluctuations, and ground conditions can all affect the stability of a brick stack. In areas with strong winds or unstable ground, a lower height-to-width ratio is essential.
- Intended Purpose: A temporary stack for storage needs less stringent ratio requirements than a load-bearing wall in a building.
A general guideline is to maintain a height-to-width ratio that doesn’t exceed 1:2 or 1:3 for free-standing stacks. This ratio should be more conservative (closer to 1:4 or even lower) for taller stacks or those subjected to environmental stressors.
2. Mortar-to-Brick Ratio in Bricklaying:
The correct mortar-to-brick ratio is crucial for a durable and stable structure. The optimal ratio varies based on several factors:
- Type of Mortar: Different mortar mixes possess different strengths and workabilities. Stronger mortars allow for a slightly lower ratio.
- Brick Type: Porous bricks generally require more mortar to ensure complete filling of the joints.
- Joint Type: The type of joint (e.g., concave, convex, struck) affects the amount of mortar needed.
- Weather Conditions: In harsh weather conditions, slightly more mortar might be necessary to enhance the weather resistance of the structure.
A well-placed brick should have a fully filled joint with no gaps or voids. The mortar should be adequately compressed to ensure a strong bond. Too much mortar can lead to weak joints and increased susceptibility to damage; too little leads to insufficient bonding and structural weakness. Experienced bricklayers visually assess this ratio on the job and can effectively judge a good balance.
3. Stacking Multiple Layers of Bricks: Considering Weight Distribution
When stacking multiple layers, the weight distribution becomes even more critical. The weight of each layer adds pressure to the layers below. To mitigate this:
- Use a Strong Base: Ensure a sturdy and level base for the entire stack, capable of supporting the total weight. This could involve a solid foundation or a robust pallet.
- Stagger Bricks: Avoid stacking bricks directly on top of each other in every layer. This creates a more stable and evenly distributed weight pattern. Techniques like English bond and Flemish bond naturally incorporate this.
- Bonding: Proper bonding techniques are essential to ensure the bricks are interlocked and the load is distributed effectively throughout the stack.
- Periodic Inspection: Regular inspections of the stack are crucial, especially during and after construction, to detect any signs of instability or settling.
Stacking Other Materials: Adapting the Principles of Ratio
The principles of ratio in stacking are applicable to various materials beyond bricks. Consider these applications:
1. Stacking Lumber:
The height-to-width ratio is paramount. Tall stacks of lumber are prone to collapse due to the weight and potential bowing of the wood. Using cross-bracing or strategically placed support beams is vital to maintain stability. The stacking pattern—avoiding stacking the same cuts atop each other—is also important.
2. Stacking Metal Sheets:
Metal sheets are often stacked in pallets with specialized securing mechanisms to avoid slippage and damage. The weight distribution and the pallet's strength are crucial. The ratio of the sheet's size and the pallet's dimensions should be carefully considered.
3. Stacking Pallets:
The ratio of the pallet’s load capacity to the total weight of goods stacked on it is critically important. Overloading pallets leads to instability and potential damage. The height and evenness of the stack are key considerations, too.
4. Stacking Stones:
Natural stones vary considerably in size, weight, and shape, making stacking them more challenging. Smaller, lighter stones should be used towards the top of the stack, and careful consideration needs to be given to the shape of the stones and their interlocking properties to create stability.
Advanced Considerations: Factors Beyond Basic Ratios
Beyond the core ratios, several advanced factors impact the stability and strength of material stacks:
- Material Properties: Understanding the individual properties of the materials (strength, density, porosity, etc.) is crucial for determining safe stacking practices.
- Environmental Factors: Temperature, humidity, and wind loads affect the stability of any stack. Protective measures might be needed in extreme conditions.
- Dynamic Loads: Stacks subjected to vibrations or movements require additional support and consideration of dynamic loads.
- Safety Precautions: Appropriate safety measures, such as warning signs and personal protective equipment (PPE), should always be employed when stacking materials.
Conclusion: Mastering the Art of Ratio in Material Stacking
Mastering the art of material stacking involves a deep understanding of ratios and their influence on structural integrity. While basic principles remain constant, careful consideration of material properties, environmental factors, and intended use case must always be taken into account. Applying these principles will not only ensure safety but also optimize material usage, leading to significant cost savings and improved project efficiency. Remember that a well-planned and carefully executed stacking strategy is crucial for any successful project, big or small. Safe stacking practices are not just efficient, but they're crucial for preventing accidents and ensuring a safe working environment.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Pride And Prejudice Summary Chapter 13
Apr 04, 2025
-
Francis Has Designed A Picture Book
Apr 04, 2025
-
Summary Of Chapter 6 In Animal Farm
Apr 04, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is True Regarding Modular Wiring Systems
Apr 04, 2025
-
Is Ordnance And Accessories A Good Career Path
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about When Stacking Materials Such As Bricks Ratio . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
