When Turning To The Right The Contact Patches Of The
Onlines
Mar 14, 2025 · 6 min read
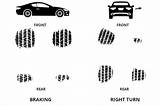
Table of Contents
When Turning Right: Understanding Contact Patch Behavior
Turning a vehicle, especially at speed, involves complex interactions between tires, the road surface, and the vehicle's dynamics. While seemingly simple, the behavior of the contact patches – the small area where the tire meets the road – is crucial for understanding traction, stability, and overall vehicle control. This article delves into the specifics of how contact patches behave when turning right, examining the forces at play and the implications for safe driving.
The Contact Patch: A Tiny But Crucial Interface
The contact patch is the only connection between your vehicle and the road. It's surprisingly small, typically only a few inches wide and long, and its size and shape change constantly depending on factors like tire inflation pressure, vehicle load, and driving maneuvers. Understanding how this small area functions is vital for safe and efficient driving.
When turning right, several factors influence the contact patch's behavior on each tire:
Front Tires: The Steering Force
The front tires are responsible for initiating and guiding the turn. As the steering wheel is turned to the right, the inner front tire (the tire closer to the center of the turn) experiences several changes:
- Increased Camber Angle: The inner front tire leans inward, increasing its camber angle. This affects the contact patch shape, potentially reducing the effective contact area. A more negative camber angle can increase grip during cornering, especially in racing scenarios. However, excessive negative camber can reduce stability and tire wear.
- Increased Slip Angle: The slip angle is the angle between the tire's direction of travel and the direction it's pointing. During a right turn, the inner front tire experiences a larger slip angle than the outer front tire, generating more lateral force to assist in turning.
- Higher Load Transfer: During a turn, weight shifts to the outside of the vehicle. This leads to higher vertical load on the outer front tire and lower load on the inner front tire. Reduced load on the inner tire can decrease its grip.
- Steering Forces and Torque: The inner front tire experiences the highest steering forces and torque. This is vital for initiating and maintaining the turning trajectory.
The outer front tire (the tire farther from the center of the turn) also experiences changes, although less dramatic than the inner tire:
- Reduced Camber Angle: The outer front tire leans slightly outward, decreasing its camber angle.
- Smaller Slip Angle: Its slip angle is smaller than the inner tire.
- Higher Vertical Load: Due to weight transfer, it carries a significantly greater vertical load, improving its grip and traction. However, excessive load can cause overheating and premature tire wear.
Rear Tires: Maintaining Stability
The rear tires are responsible for maintaining stability and providing driving force during the turn. Similar to the front tires, their contact patches are affected by several forces:
- Increased Slip Angle (Inner Rear Tire): The inner rear tire experiences an increased slip angle, but typically less than the inner front tire.
- Smaller Slip Angle (Outer Rear Tire): The outer rear tire has a smaller slip angle.
- Weight Transfer and Load Distribution: Weight transfer affects the rear tires as well, with the outer rear tire carrying more load than the inner rear tire. This affects traction and grip.
- Over- or Under-steer: The interaction between front and rear tire contact patches determines the vehicle's tendency to oversteer (rear wheels lose traction and the car spins) or understeer (front wheels lose traction, and the car continues straight). Proper weight distribution and tire pressure are key factors in preventing oversteer and understeer.
Factors Affecting Contact Patch Behavior
Several factors beyond steering input influence contact patch behavior during a right turn:
- Tire Pressure: Incorrect tire pressure can dramatically alter the contact patch shape and size, affecting traction and handling. Under-inflation reduces the contact patch's width, while over-inflation reduces its length.
- Tire Tread Depth and Condition: Worn tires have reduced grip, affecting stability and control, particularly during cornering.
- Road Surface: Dry, smooth surfaces offer better grip than wet, uneven surfaces. The type of road surface significantly impacts traction.
- Vehicle Speed: Higher speeds lead to greater forces acting on the contact patches, requiring increased grip.
- Vehicle Load: A heavier vehicle increases the load on the tires, affecting their grip. Proper load distribution is crucial for safe handling.
- Suspension System: The suspension's ability to manage weight transfer during cornering and maintain tire contact with the road significantly impacts handling.
Implications for Safe Driving
Understanding how contact patches behave during a right turn is essential for safe and controlled driving. Here are some implications:
- Smooth Steering Inputs: Sudden, jerky steering inputs can disrupt the contact patch's grip, potentially leading to loss of control. Smooth, gradual steering is crucial for maintaining traction.
- Appropriate Speed: Driving too fast into a turn reduces the available grip, increasing the risk of skidding or losing control. Adjusting speed before entering the turn is essential.
- Proper Tire Maintenance: Ensuring proper tire inflation, tread depth, and overall condition is critical for optimal grip and safe handling.
- Awareness of Road Conditions: Adapting driving style to changing road conditions is crucial for maintaining control. Reduce speed on slippery surfaces and adjust driving technique accordingly.
- Vehicle Maintenance: Regular vehicle maintenance, including checking the suspension and braking systems, ensures optimal handling and stability.
Advanced Considerations: Tire Slip Angle and Lateral Forces
The slip angle, as mentioned earlier, plays a significant role in generating the lateral forces needed for cornering. The relationship between slip angle and lateral force is not linear. At small slip angles, the lateral force increases proportionally. However, beyond a certain point, the tire reaches its limit of adhesion, and the lateral force plateaus or even decreases, leading to a loss of traction. This is the point where the tire starts to skid.
Understanding this relationship is crucial for advanced driving techniques, such as racing. Drivers learn to control the slip angles of their tires to maximize traction and cornering speed without losing control.
Conclusion: Mastering the Contact Patch for Safer Driving
The contact patches on your tires are the silent heroes of every driving maneuver. Understanding their behavior, especially during turns, is essential for safe and efficient driving. By considering the factors that affect contact patch behavior – tire pressure, road conditions, speed, and vehicle dynamics – drivers can improve their skills and enhance their safety on the road. Remember that maintaining proper vehicle maintenance and employing smooth, controlled driving techniques are crucial for maximizing tire grip and ensuring a safe and enjoyable driving experience. Continuously learning and refining driving skills based on a fundamental understanding of tire dynamics will enhance road safety and overall driving proficiency.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Examples Of Questions That Focus On Process Include
Mar 15, 2025
-
All Quiet On The Western Front Themes
Mar 15, 2025
-
Murder And A Meal Lab Answer Key
Mar 15, 2025
-
Marina Querer Yo Traer La Compra A Casa
Mar 15, 2025
-
Summary Of Chapter 4 Of Animal Farm
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about When Turning To The Right The Contact Patches Of The . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
