Where In The Body Is Hyaluronic Acid Found Milady
Onlines
Mar 06, 2025 · 6 min read
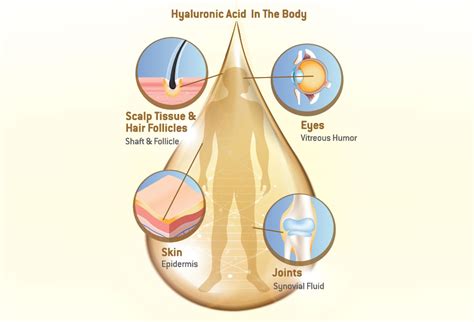
Table of Contents
Where in the Body is Hyaluronic Acid Found? A Milady Perspective
Hyaluronic acid (HA), a naturally occurring glycosaminoglycan (GAG), plays a pivotal role in maintaining the health and function of various tissues throughout the body. Understanding its precise locations and functions is crucial for appreciating its importance in skincare, wound healing, and overall bodily health. This comprehensive article delves into the diverse locations of hyaluronic acid within the human body, exploring its significant contributions to each area from a Milady-informed perspective – a perspective that blends scientific understanding with practical application in the beauty and wellness industries.
Hyaluronic Acid: A Deep Dive into its Molecular Structure and Functions
Before we explore the specific locations of HA in the body, let's briefly revisit its molecular structure and primary functions. Hyaluronic acid is a large, unbranched polysaccharide composed of repeating disaccharide units of glucuronic acid and N-acetylglucosamine. This unique structure allows HA to bind an immense amount of water, giving it its exceptional hydrating properties.
Key Functions of Hyaluronic Acid:
- Lubrication: HA acts as a lubricant in joints, reducing friction and facilitating smooth movement. This is especially crucial in weight-bearing joints like knees and hips.
- Hydration: Its remarkable water-binding capacity makes HA a potent humectant, drawing and retaining moisture in the skin and other tissues. This keeps tissues hydrated, plump, and resilient.
- Wound Healing: HA plays a vital role in the wound healing process, promoting cell proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis (formation of new blood vessels).
- Tissue Structure and Integrity: HA contributes to the structural integrity of various tissues by providing a supportive matrix for cells. It helps maintain the shape and firmness of tissues.
- Inflammation Regulation: Emerging research suggests HA can modulate the inflammatory response, potentially aiding in reducing inflammation in various conditions.
The Ubiquitous Presence of Hyaluronic Acid in the Human Body
Hyaluronic acid is not confined to a single location; it's distributed throughout the body, exhibiting varying concentrations and playing distinct roles in different tissues and organs. Let's examine its presence in key areas:
1. Skin: The Hyaluronic Acid Hotspot
The skin is arguably the most well-known location for hyaluronic acid. It's abundant in the dermis, the skin's middle layer, where it contributes significantly to skin hydration, elasticity, and firmness. As we age, the natural production of HA decreases, leading to drier, less elastic skin and the appearance of wrinkles. This is a major focus area for many skincare products incorporating HA as a key ingredient.
Specific Roles in Skin:
- Moisture Retention: HA's ability to bind water keeps the skin hydrated, plump, and smooth.
- Skin Barrier Function: HA contributes to the integrity of the skin barrier, protecting against environmental damage and water loss.
- Wound Healing: HA stimulates the healing process in skin injuries, aiding in tissue regeneration.
2. Joints: The Lubricant and Shock Absorber
Synovial fluid, the viscous fluid that lubricates joints, contains a high concentration of hyaluronic acid. This HA acts as a crucial lubricant, reducing friction between the articular cartilage of bones and ensuring smooth joint movement. It also provides cushioning and shock absorption, protecting joints from damage during physical activity. In conditions like osteoarthritis, the level of HA in synovial fluid can decrease, contributing to joint pain and stiffness.
HA's Significance in Joint Health:
- Joint Lubrication: Reduces friction between joint surfaces, promoting smooth movement.
- Shock Absorption: Protects joints from impact and wear and tear.
- Cartilage Health: Supports the health and integrity of articular cartilage.
3. Eyes: Maintaining Transparency and Function
The vitreous humor, the gel-like substance that fills the eye's posterior cavity, contains a significant amount of hyaluronic acid. This HA contributes to the vitreous humor's structural integrity and transparency, maintaining the eye's shape and optical clarity. Furthermore, HA is also found in the cornea, where it plays a role in maintaining its hydration and transparency.
HA in Ocular Tissues:
- Vitreous Humor Structure: Maintains the shape and clarity of the vitreous humor.
- Corneal Hydration: Contributes to the hydration and transparency of the cornea.
4. Connective Tissue: Providing Structural Support
Hyaluronic acid is present in various connective tissues throughout the body, including cartilage, tendons, and ligaments. It contributes to their structural integrity and mechanical properties, providing support and resilience. Its presence in these tissues highlights its importance in maintaining the overall musculoskeletal system's health and function.
HA's Role in Connective Tissues:
- Structural Support: Provides a supportive matrix for cells in connective tissues.
- Tissue Resilience: Contributes to the elasticity and strength of connective tissues.
5. Nervous System: Supporting Neural Function
Recent research has revealed a significant role for hyaluronic acid in the central and peripheral nervous systems. HA is found in the extracellular matrix of the brain and spinal cord, where it may influence neural cell function, neuronal migration, and axon regeneration. Its role in the nervous system is an area of ongoing research, with potential implications for neurodegenerative diseases and traumatic brain injuries.
Emerging Roles in the Nervous System:
- Neural Cell Function: May influence the function and survival of neurons.
- Axon Regeneration: Potentially involved in the repair of damaged nerve fibers.
6. Cardiovascular System: Influence on Vascular Health
While less extensively studied than its roles in other tissues, HA's presence in the cardiovascular system is becoming increasingly recognized. Some studies suggest it may influence vascular permeability, blood vessel formation, and even blood pressure regulation. Further research is needed to fully elucidate its impact on cardiovascular health.
Potential Roles in the Cardiovascular System:
- Vascular Permeability: May influence the permeability of blood vessels.
- Angiogenesis: Potential involvement in blood vessel formation.
Hyaluronic Acid and Aging: The Decline and its Implications
As we age, the body's natural production of hyaluronic acid gradually declines. This decrease contributes to several age-related changes, particularly in the skin and joints:
- Skin Aging: Reduced HA levels lead to decreased skin hydration, elasticity, and firmness, resulting in wrinkles, dryness, and sagging.
- Joint Degradation: Lower HA concentrations in synovial fluid contribute to joint pain, stiffness, and osteoarthritis.
- Eye Changes: Decreased HA in the vitreous humor can contribute to age-related changes in the eye.
Utilizing Hyaluronic Acid in Skincare and Wellness
The understanding of hyaluronic acid's importance has led to its widespread use in various skincare products and therapeutic applications. Topical application of HA provides immediate hydration and plumpness to the skin. Injections of HA are used to fill wrinkles and restore volume to the face, while oral supplements may offer some benefits, though their absorption and efficacy remain debated.
Considerations for using HA:
- Formulation: The molecular weight of HA used in products can impact its penetration and effectiveness.
- Product Quality: Choosing high-quality products with appropriate concentrations of HA is vital.
- Individual Needs: The most suitable HA product or treatment will depend on individual needs and skin type.
Conclusion: Hyaluronic Acid – A Vital Component of Bodily Health
Hyaluronic acid is a ubiquitous molecule with diverse and crucial functions throughout the human body. From lubricating our joints and hydrating our skin to supporting the structural integrity of connective tissues and potentially influencing the nervous system, its presence and functions are far-reaching. Understanding HA's roles across different tissues is paramount, not only for appreciating its contribution to overall bodily health but also for harnessing its potential in skincare, therapeutic interventions, and ongoing research into its myriad roles. The widespread presence of HA and its multifaceted effects continue to fascinate and inspire further investigation, promising future advancements in health and wellness.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Used The Tactic Of Ethnic Cleansing To Eliminate Muslims
Mar 06, 2025
-
Stations Activity Build A Phylogenetic Tree Answer Key
Mar 06, 2025
-
Rocio Esta Muy Tranquila Cuando Espera A Marcela
Mar 06, 2025
-
For Esme With Love And Squalor Summary
Mar 06, 2025
-
A Goodman Is Hard To Find Symbols
Mar 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Where In The Body Is Hyaluronic Acid Found Milady . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
