Which Choice Best Describes The Purpose Of Most Pharmacogenomic Research
Onlines
Mar 10, 2025 · 6 min read
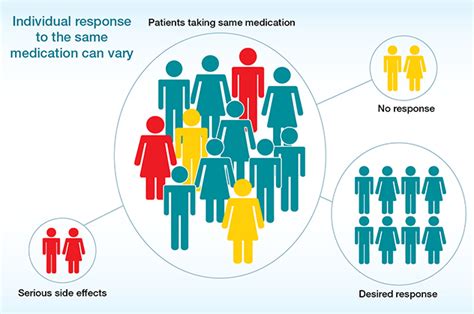
Table of Contents
Which Choice Best Describes the Purpose of Most Pharmacogenomic Research?
Pharmacogenomics, the study of how genes affect a person's response to drugs, is rapidly transforming the landscape of medicine. Understanding individual genetic variations and their impact on drug metabolism, efficacy, and toxicity is crucial for developing safer and more effective therapies. But what is the overarching purpose driving the vast majority of pharmacogenomic research? While various avenues are explored, the core aim boils down to personalizing medicine. This article delves deep into the multifaceted purposes of pharmacogenomic research, examining its impact on drug development, patient care, and the future of healthcare.
The Primary Goal: Personalized Medicine
The ultimate goal of most pharmacogenomic research is to tailor drug treatments to individual patients based on their unique genetic makeup. This approach, known as personalized medicine or precision medicine, aims to move beyond the "one-size-fits-all" approach of traditional medicine, where a single drug is prescribed for a wide range of patients with similar conditions. Instead, pharmacogenomics seeks to identify genetic markers that predict how a patient will respond to a specific drug.
Predicting Drug Response
A major focus is on predicting a patient's response to a drug before they even begin treatment. This involves identifying genes that influence drug metabolism, absorption, distribution, and excretion (ADME). Understanding these genetic variations allows clinicians to:
- Optimize drug dosage: For some individuals, their genetic makeup may lead to faster or slower metabolism of a drug. Pharmacogenomic testing can guide clinicians in selecting the appropriate dosage to ensure optimal therapeutic effect while minimizing the risk of adverse events.
- Predict drug efficacy: Some genetic variations can predict whether a patient is likely to respond well to a particular drug or not. This information can help clinicians avoid prescribing ineffective drugs, saving time, resources, and improving patient outcomes.
- Reduce adverse drug reactions (ADRs): A significant portion of pharmacogenomic research focuses on identifying genetic markers associated with increased risk of ADRs. This knowledge allows clinicians to choose alternative medications or adjust dosages to minimize the likelihood of harmful side effects.
Examples of Personalized Medicine in Practice
Several examples highlight the practical applications of pharmacogenomic research in personalized medicine:
- Warfarin Dosage: Warfarin, a blood thinner, is notoriously challenging to dose correctly. Genetic variations in genes like CYP2C9 and VKORC1 significantly affect how the body metabolizes warfarin. Pharmacogenomic testing can help determine the optimal starting dose, reducing the risk of bleeding or clotting complications.
- Chemotherapy Selection: In cancer treatment, pharmacogenomics is used to select the most effective chemotherapy regimen for individual patients. Genetic variations can influence the sensitivity or resistance of tumor cells to specific chemotherapy drugs, guiding clinicians in choosing the most appropriate treatment strategy.
- Mental Health Medications: Pharmacogenomics is increasingly being applied to mental health, helping to predict a patient's response to antidepressants, antipsychotics, and other psychotropic medications. This can lead to faster symptom relief and reduced trial-and-error in finding the right medication.
Secondary, but Equally Important, Purposes
While personalized medicine is the central theme, pharmacogenomic research pursues several other crucial objectives:
Drug Development and Design
Pharmacogenomics plays a pivotal role in the process of drug discovery and development. By identifying genetic factors influencing drug response, researchers can:
- Develop more effective drugs: Understanding the mechanisms of action and the genetic basis of drug efficacy can lead to the design of more potent and targeted therapies.
- Reduce the risk of ADRs during clinical trials: By incorporating pharmacogenomic information into clinical trial design, researchers can better identify individuals at high risk of adverse events, potentially leading to safer drug development.
- Improve drug safety and efficacy profiles: Genetic biomarkers can help stratify patients in clinical trials, allowing researchers to obtain a clearer picture of the drug's efficacy and safety profile in different subpopulations.
Understanding Disease Mechanisms
Pharmacogenomic research often uncovers fundamental insights into the genetic basis of diseases. By studying how genetic variations influence drug response, researchers can gain a deeper understanding of:
- Disease pathogenesis: Studying how genes influence drug metabolism can shed light on the underlying mechanisms of various diseases.
- Disease susceptibility: Genetic markers associated with altered drug response can help identify individuals at increased risk of developing specific diseases.
- Potential therapeutic targets: The identification of genes affecting drug response can lead to the discovery of novel therapeutic targets for drug development.
Improving Healthcare Outcomes and Reducing Costs
The ultimate aim of pharmacogenomic research is to improve patient outcomes and reduce healthcare costs. By tailoring treatments to individual patients, we can:
- Improve treatment efficacy: Personalized medicine reduces the use of ineffective drugs, leading to faster symptom relief and improved overall health outcomes.
- Reduce ADRs: Preventing adverse drug reactions decreases the need for hospitalizations, emergency room visits, and other costly interventions.
- Reduce healthcare costs: Optimized drug selection and dosage reduces the overall cost of healthcare by minimizing the use of ineffective treatments and preventing costly complications.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite its immense potential, pharmacogenomic research faces several challenges:
- Cost and accessibility: Pharmacogenomic testing can be expensive, limiting its accessibility to some patients. Further research is needed to develop more cost-effective testing methods.
- Data interpretation and integration: Analyzing large datasets of genomic and clinical information requires sophisticated computational tools and expertise.
- Ethical considerations: Ensuring privacy and security of genetic information is crucial. Addressing ethical concerns related to genetic testing and personalized medicine is essential.
The future of pharmacogenomic research lies in:
- Developing more comprehensive genomic databases: Larger and more diverse genomic datasets are needed to enhance our understanding of individual variation in drug response.
- Improving data analysis methods: Advanced bioinformatics tools and machine learning algorithms are needed to analyze complex genomic datasets and identify novel genetic markers.
- Integrating pharmacogenomics into clinical practice: Pharmacogenomic testing needs to be more seamlessly integrated into routine clinical care, so that clinicians can make informed prescribing decisions.
- Developing new therapeutic strategies: Pharmacogenomic research is paving the way for the development of innovative therapeutic strategies, such as gene therapy and personalized vaccines.
Conclusion
The purpose of most pharmacogenomic research is to realize the potential of personalized medicine. By understanding how individual genetic variations influence drug response, we can create a healthcare system that is safer, more effective, and more cost-efficient. While challenges remain, the continued advancement of pharmacogenomic research promises to revolutionize how we treat and prevent disease, creating a future where every patient receives the best possible treatment tailored to their unique genetic profile. The pursuit of personalized medicine isn't just a scientific endeavor; it's a fundamental shift towards a more patient-centric approach to healthcare, ensuring the best possible health outcomes for all.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Moles And Chemical Formulas Report Sheet Answers
Mar 10, 2025
-
Spanish 1b Unit 6 Review Of Unit 1
Mar 10, 2025
-
Is It In My Blood Worksheet
Mar 10, 2025
-
Hartmans Nursing Assistant Care Workbook Sixth Edition Answer Key Pdf
Mar 10, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Accurate Concerning Patient Rights
Mar 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Choice Best Describes The Purpose Of Most Pharmacogenomic Research . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
