Which Is A True Statement Regarding Air Pressure Variances
Onlines
Mar 03, 2025 · 6 min read
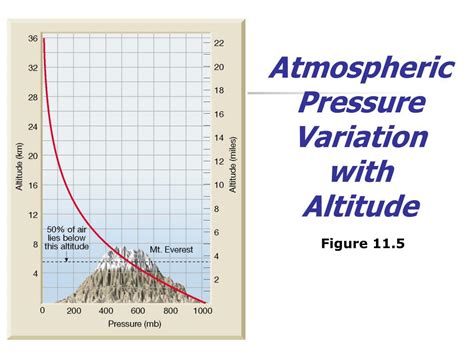
Table of Contents
Which is a True Statement Regarding Air Pressure Variances? Understanding Atmospheric Pressure Fluctuations
Air pressure, the force exerted by the weight of air molecules in the atmosphere, is a fundamental element influencing weather patterns, climate, and even our daily lives. Understanding its variances is crucial for comprehending various atmospheric phenomena. While seemingly constant, air pressure fluctuates significantly due to several interacting factors. This article delves into the complexities of air pressure variances, exploring the true statements surrounding this dynamic atmospheric variable and debunking common misconceptions.
Key Factors Influencing Air Pressure Variances
Several interconnected factors contribute to the constant fluctuation of atmospheric pressure. These include:
1. Altitude: The Height Factor
Perhaps the most straightforward influence on air pressure is altitude. As altitude increases, the density of air molecules decreases. This directly translates to a decrease in air pressure. At higher elevations, there are fewer air molecules above a given point, resulting in less weight pressing down. This is why mountaineers experience lower air pressure and why breathing becomes more challenging at higher altitudes. The relationship between altitude and air pressure is fundamentally inverse.
2. Temperature: Heat and Pressure's Dance
Temperature plays a crucial role in air pressure variations. Warmer air is less dense than cooler air because the air molecules move faster and spread out. This lower density results in lower air pressure. Conversely, cooler air is denser, leading to higher air pressure. This temperature-pressure relationship is a key driver of weather systems, as temperature differences create pressure gradients that drive wind.
3. Humidity: The Weight of Water Vapor
The amount of water vapor in the air, also known as humidity, also influences air pressure. Water vapor molecules are lighter than other atmospheric gases (like nitrogen and oxygen). Therefore, air with high humidity (more water vapor) will have slightly lower air pressure than drier air at the same temperature and altitude, because the lighter water vapor molecules displace heavier gas molecules. This effect is relatively small compared to temperature and altitude, but it's still a contributing factor in atmospheric pressure fluctuations.
4. Weather Systems: Cyclones and Anticyclones
Large-scale weather systems, such as cyclones (low-pressure systems) and anticyclones (high-pressure systems), directly cause significant air pressure variations. Cyclones are characterized by converging air, rising air, and relatively lower air pressure at their centers. The rising air cools and condenses, often leading to cloud formation and precipitation. Anticyclones, on the other hand, have descending air, diverging air, and higher air pressure at their centers. This descending air warms adiabatically, suppressing cloud formation and often resulting in clear, calm weather.
5. Geographic Location: Topography's Influence
Geographic location and topography also influence air pressure. Areas at higher elevations naturally experience lower air pressure than areas at sea level. Mountain ranges can create localized pressure differences due to their impact on air flow and temperature gradients. Coastal regions experience pressure variations influenced by the proximity to the sea and the differences in temperature between land and water.
Debunking Common Misconceptions about Air Pressure
Several misconceptions surrounding air pressure variations persist. Let's address some of the most prevalent ones:
Myth 1: Air pressure is constant.
Fact: Air pressure is not constant; it's constantly fluctuating due to the factors mentioned above. While these fluctuations may be subtle at times, they are always present and are crucial in driving weather systems and other atmospheric phenomena.
Myth 2: Higher altitude always means colder temperature.
Fact: While higher altitudes generally correlate with lower temperatures due to decreased air density and less absorption of solar radiation, this is not universally true. Certain weather phenomena, such as temperature inversions, can result in warmer temperatures at higher altitudes than at lower altitudes. These inversions can trap pollutants near the surface, creating smog and air quality issues.
Myth 3: Humidity only affects weather, not air pressure.
Fact: While the impact is less pronounced than temperature or altitude, humidity does affect air pressure. The lighter weight of water vapor molecules compared to other atmospheric gases results in slightly lower air pressure in humid conditions compared to dry conditions, all else being equal.
Myth 4: Air pressure is only significant for meteorologists.
Fact: Air pressure is essential for various aspects of our daily lives, extending far beyond meteorology. It affects aviation, where accurate pressure readings are crucial for safe flight operations. It influences human physiology, as variations in air pressure at high altitudes can impact breathing and health. It’s also vital in industrial processes that utilize pneumatic systems, which rely on compressed air.
Measuring and Predicting Air Pressure Variances
Accurate measurement and prediction of air pressure are vital for various applications, especially weather forecasting. Barometers are the primary instruments used to measure air pressure. These instruments come in various types, including aneroid barometers (using an evacuated metal cell) and mercury barometers (using the height of a mercury column).
Weather forecasting models utilize sophisticated computer simulations incorporating various atmospheric data, including air pressure measurements, to predict future pressure variations and their associated weather patterns. These models utilize complex algorithms to account for the interplay between temperature, humidity, altitude, and other factors.
The Significance of Understanding Air Pressure Variances
Understanding air pressure variances is not just a matter of academic interest; it has far-reaching implications:
-
Weather Forecasting: Accurate air pressure readings are fundamental to weather prediction. Changes in pressure gradients indicate the movement and intensity of weather systems.
-
Aviation: Pilots rely on air pressure data for altitude determination, flight planning, and safe navigation. Air pressure differences between altitudes affect aircraft performance.
-
Medicine: Understanding air pressure variations is crucial for understanding altitude sickness and its prevention. The lower pressure at higher altitudes can lead to reduced oxygen levels in the blood.
-
Industrial Applications: Numerous industrial processes rely on controlled air pressure, from pneumatic tools to hydraulic systems.
-
Climate Science: Monitoring long-term trends in air pressure contributes to understanding climate change and its impacts on various weather patterns.
True Statements Regarding Air Pressure Variances: Summary
Based on the discussion above, several true statements regarding air pressure variances can be confidently stated:
-
Air pressure decreases with increasing altitude. This is a fundamental principle directly related to the decrease in air density at higher elevations.
-
Air pressure is influenced by temperature. Warmer air has lower pressure, while cooler air has higher pressure, owing to the difference in air density.
-
Humidity affects air pressure, although less significantly than temperature or altitude. The lighter weight of water vapor compared to other gases causes slightly lower pressure in humid conditions.
-
Air pressure variations are crucial for weather forecasting and understanding weather patterns. Pressure gradients drive wind, influencing the development and movement of cyclones and anticyclones.
-
Air pressure is not constant; it's continually fluctuating. These fluctuations are caused by a complex interplay of interacting factors, including altitude, temperature, humidity, and weather systems.
Understanding the dynamics of air pressure and its various influences is crucial for comprehending atmospheric processes and their impact on our environment and daily lives. Continued research and advancements in atmospheric science will lead to more accurate predictions and a deeper understanding of this fundamental atmospheric variable.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Grasshopper And The Bell Cricket Summary
Mar 03, 2025
-
Summary Of The Promise By C Wright Mills
Mar 03, 2025
-
Great Expectations Summary Chapter By Chapter
Mar 03, 2025
-
Someone With Self And Social Awareness Is
Mar 03, 2025
-
Ready Mathematics Lesson 11 Quiz Answers
Mar 03, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Is A True Statement Regarding Air Pressure Variances . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
