Which Of The Following Accurately Describes Metadata
Onlines
Mar 04, 2025 · 6 min read
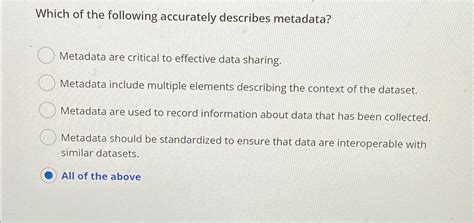
Table of Contents
Which of the Following Accurately Describes Metadata? Unpacking the Essence of Data About Data
Metadata. The term itself sounds somewhat technical, even intimidating. But in reality, metadata is a fundamental concept underpinning how we organize, access, and understand information in the digital age. It's the "data about data," providing context and structure to the raw information we work with every day. Understanding metadata is crucial, not just for technical professionals, but for anyone who interacts with digital files, databases, and online content. This comprehensive guide will delve deep into the nature of metadata, exploring its various types, uses, and implications.
What Exactly is Metadata?
At its core, metadata describes data. It's the information that provides context and meaning to the data itself. Think of it as the descriptive label on a file, a database entry, or even a photograph. While the file might contain a document, a picture, or a spreadsheet, the metadata describes what that data is, when it was created, who created it, and where it's stored. This information isn't part of the primary data itself, but it's essential for managing and interpreting it effectively.
Examples of Metadata:
- File Name: A seemingly simple file name like "Project Report Q3 2024.docx" already contains metadata. It tells us the content (project report), the time period (Q3 2024), and the file type (Word document).
- Image EXIF Data: Digital photos contain extensive metadata, including camera settings (aperture, ISO, shutter speed), GPS coordinates (location where the photo was taken), and date and time stamps.
- Database Field Descriptions: Databases use metadata to define the structure of data, including field names, data types (text, number, date), and relationships between different tables.
- Web Page Metadata: Websites utilize metadata such as title tags, meta descriptions, and keywords to help search engines understand the content of a page, ultimately influencing its search engine ranking.
Types of Metadata: A Deeper Dive
Metadata is typically categorized into several types, depending on its purpose and how it relates to the data it describes:
1. Descriptive Metadata: Telling Us What the Data Is
Descriptive metadata focuses on identifying the data and its characteristics. It’s the most common type of metadata and is readily understandable by humans. Examples include:
- Title: The name given to the data.
- Author: The creator of the data.
- Subject: Keywords or topics that describe the data's content.
- Abstract: A brief summary of the data's content.
- Date: The date the data was created or modified.
Descriptive metadata is crucial for searchability and discoverability. It allows users to easily find and identify the specific data they need.
2. Structural Metadata: Organizing and Presenting the Data
Structural metadata describes how the data is organized and structured. It's essential for defining the relationships between different elements within a dataset. This is particularly important in complex data structures such as databases or multimedia files.
- Table of Contents: For documents, a table of contents defines the hierarchical structure of chapters and sections.
- XML Tags: In XML documents, tags are used to define the structure and relationships between different data elements.
- Hyperlinks: In web pages, hyperlinks organize information and link different parts of the content together.
- Page Numbers: Simple yet effective in organizing the flow of information within a document.
3. Administrative Metadata: Managing and Tracking the Data
Administrative metadata focuses on managing the data's lifecycle, from creation to deletion. It often includes information about ownership, access rights, and data quality.
- Copyright Information: Specifies the ownership and usage rights of the data.
- Creation Date: Indicates when the data was first created.
- Modification Date: Shows when the data was last modified.
- File Size: Provides information about the data's size.
- Version History: Tracks different versions of the data over time.
- Security Access Levels: Specifies who can access and modify the data.
The Importance of Metadata: Why It Matters
The importance of metadata cannot be overstated. It plays a vital role in various aspects of data management and utilization:
- Discoverability: Metadata makes it easier to find specific information within large datasets. Think of using search engines to find web pages – the metadata associated with those pages (keywords, descriptions) guides the search results.
- Organization: Metadata provides structure and organization to datasets, allowing for efficient management and retrieval of information.
- Interoperability: Metadata facilitates the exchange and integration of data from different sources. This is crucial in collaborative projects and data sharing environments.
- Preservation: Metadata helps to preserve the meaning and context of data over time. This is especially important for long-term archiving of digital assets.
- Data Quality: Well-structured metadata enhances data quality by providing accurate descriptions and improving the reliability of the information.
- Data Analysis: Metadata can be used to improve data analysis by providing valuable context and insights into the dataset.
Metadata and Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
In the context of web development and digital marketing, metadata is a cornerstone of Search Engine Optimization (SEO). Websites use metadata to communicate important information about their pages to search engines. This includes:
- Title Tags: A crucial element, accurately describing the page's content and targeting relevant keywords.
- Meta Descriptions: A concise summary of the page's content that appears in search engine results.
- Header Tags (H1-H6): These tags structure the content and indicate headings and subheadings, providing context and hierarchy to the information.
- Image Alt Text: Descriptive text for images that helps search engines understand the image's content, improving accessibility for visually impaired users and enhancing SEO.
- Schema Markup: Structured data markup that provides additional context and information to search engines, improving the richness of search results and potentially increasing click-through rates.
Metadata and Data Security
Metadata can also play a significant role in data security. Administrative metadata, in particular, helps in managing access control, tracking changes, and ensuring data integrity. This is essential for protecting sensitive information and complying with relevant regulations.
Choosing the Right Metadata Schema
Depending on the type of data and its intended use, different metadata schemas may be more suitable. A metadata schema is a formal structure that defines the elements and attributes of metadata. Popular schemas include Dublin Core, MODS, and schema.org. The choice of schema depends on the specific needs and requirements of the project.
The Future of Metadata
As the amount of data continues to grow exponentially, the importance of metadata will only continue to increase. The development of new technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), is leading to more sophisticated methods for generating, managing, and utilizing metadata. AI can automate metadata creation, improving efficiency and accuracy. ML algorithms can learn from existing metadata to improve data organization and retrieval.
Conclusion: Metadata – The Unsung Hero of Data Management
In conclusion, metadata is not just a technical detail; it's a crucial component of efficient data management, accessibility, and utilization. Understanding the different types of metadata, their importance, and how they are used is essential for anyone working with digital information. By effectively managing and utilizing metadata, individuals and organizations can enhance data discoverability, improve data quality, and ensure the long-term preservation of valuable information. From simple file names to complex database schemas, metadata provides the essential context and structure that unlocks the full potential of our increasingly data-driven world. Therefore, appreciating and leveraging the power of metadata is critical for success in today’s digital landscape.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Systems Analysis Is Required When
Mar 04, 2025
-
3 2 Study Guide Key Medical Interventions Answer Key
Mar 04, 2025
-
My Fathers Eyes My Mothers Rage Pdf
Mar 04, 2025
-
Which Term Best Describes The Statement Given Below
Mar 04, 2025
-
They Say I Say 6th Edition Pdf
Mar 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Accurately Describes Metadata . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
