Which Of The Following Are Considered Voip Endpoints
Onlines
Mar 20, 2025 · 6 min read
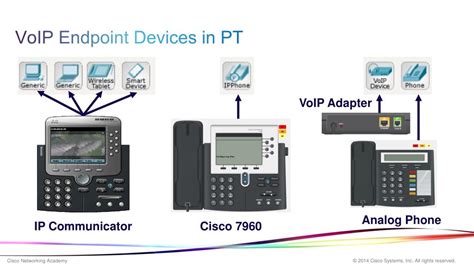
Table of Contents
Which of the Following are Considered VoIP Endpoints? A Comprehensive Guide
The world of Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) is constantly evolving, offering businesses and individuals increasingly sophisticated communication solutions. At the heart of any VoIP system lie its endpoints – the devices that allow users to make and receive calls. But what exactly constitutes a VoIP endpoint? This comprehensive guide dives deep into the various devices considered VoIP endpoints, exploring their functionalities, advantages, and disadvantages.
Understanding VoIP Endpoints
Before we delve into specific examples, let's establish a clear understanding of what defines a VoIP endpoint. Simply put, a VoIP endpoint is any device capable of converting analog voice signals into digital data packets for transmission over the internet and vice-versa. This process involves encoding and decoding audio signals, managing call setup and termination, and often providing additional features like call waiting, voicemail, and conferencing.
The crucial element is the device's ability to interface with a VoIP network. This network can be a public internet connection, a private network within a business, or a hybrid system combining both. The endpoint handles the technical complexities of converting voice into data and back again, allowing users a seamless communication experience.
Common Types of VoIP Endpoints
The landscape of VoIP endpoints is diverse, catering to various needs and preferences. Here's a breakdown of some of the most common types:
1. VoIP Phones
These are perhaps the most recognizable VoIP endpoints. VoIP phones are specifically designed for VoIP communication, often featuring advanced features not found in traditional analog phones. They come in various forms, including:
-
Software Phones (Softphones): These are applications installed on computers, smartphones, or tablets, transforming these devices into VoIP phones. Examples include apps like Zoiper, MicroSIP, and Linphone. They offer portability and flexibility, allowing users to make and receive calls from virtually anywhere with an internet connection. However, their reliance on the underlying device's processing power and network stability can be a limiting factor.
-
Hardware Phones: These are dedicated VoIP phones, similar in appearance to traditional desk phones, but with built-in VoIP capabilities. They often provide superior audio quality, advanced features, and more reliable performance compared to softphones. They range from basic models suitable for home use to sophisticated enterprise-grade devices with multiple lines and advanced call handling features. Hardware phones offer a dedicated and reliable solution, but they lack the portability of softphones.
2. IP Adapters (Analog Telephone Adapters - ATAs)
Analog Telephone Adapters (ATAs) bridge the gap between traditional analog phones and VoIP networks. They allow users to connect their existing analog phones to a VoIP service, providing a cost-effective way to transition to VoIP without replacing all their existing phone equipment. ATAs convert analog voice signals from the phone into digital data packets for transmission over the VoIP network and vice-versa. While functional, they often lack the advanced features found in dedicated VoIP phones.
3. IP Gateways
IP Gateways serve as a crucial connection point between VoIP networks and traditional Public Switched Telephone Networks (PSTNs). They enable communication between VoIP users and users on the traditional phone system, acting as a translator between the two. Larger organizations often utilize IP gateways to integrate their VoIP systems with their existing phone infrastructure. They offer advanced features like transcoding, allowing calls between different VoIP protocols to be connected seamlessly.
4. Mobile Devices (Smartphones and Tablets)
With the proliferation of mobile VoIP apps, smartphones and tablets have become increasingly popular VoIP endpoints. These devices, using dedicated VoIP applications or integrated VoIP capabilities, allow for flexible and mobile communication. They offer the convenience of making and receiving calls from virtually anywhere with an internet connection. However, reliance on mobile data and battery life can sometimes pose challenges.
5. Video Conferencing Systems
Video conferencing systems are sophisticated VoIP endpoints capable of handling both voice and video communication. They range from basic webcam systems to high-end enterprise solutions with advanced features like screen sharing, recording, and multi-point conferencing. These systems are often used for meetings, presentations, and collaboration. Their cost and complexity can vary widely, depending on the features and scale of the system.
6. Integrated Communication Platforms (UCaaS)
Unified Communications as a Service (UCaaS) platforms often incorporate multiple VoIP endpoints into a single integrated system. These platforms typically include VoIP calling, instant messaging, video conferencing, presence information, and other collaborative tools. They provide a comprehensive communication solution, streamlining communication across different channels and devices. UCaaS platforms offer a centralized management interface, simplifying administration and reducing the need for managing various individual endpoints.
Choosing the Right VoIP Endpoint
Selecting the appropriate VoIP endpoint depends heavily on several factors, including:
-
Budget: The cost of VoIP endpoints varies significantly, ranging from affordable softphones to high-end enterprise systems. Consider your budget constraints when making your selection.
-
Features: Determine the features you need. Do you require advanced call handling, voicemail, conferencing, or integration with other systems?
-
Scalability: If your needs are likely to grow, choose a solution that can easily scale to accommodate future expansion.
-
Ease of use: Select a solution that is easy to use and manage, particularly if you have limited technical expertise.
-
Reliability: Choose a reliable solution with minimal downtime and robust network connectivity.
-
Integration: Consider the endpoint's ability to integrate with your existing communication infrastructure and other business systems.
Advanced VoIP Endpoint Features
Many modern VoIP endpoints offer advanced features beyond basic call functionality. These include:
-
Call Recording: For compliance and training purposes, many endpoints offer the ability to record calls.
-
Voicemail to Email: Voicemail messages can be converted into email transcripts for easy access.
-
Call Queuing: Distributes calls to available agents, ensuring efficient call handling.
-
Automated Attendant: Provides automated greetings and call routing.
-
Integration with CRM systems: Provides seamless integration with Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems for enhanced customer service.
-
Presence Indicators: Shows the availability status of colleagues, improving communication efficiency.
Future Trends in VoIP Endpoints
The future of VoIP endpoints points towards greater integration, enhanced security, and improved user experience. We can anticipate:
-
Increased Integration with IoT Devices: VoIP endpoints will increasingly integrate with other IoT devices, creating a more connected and intelligent communication ecosystem.
-
Enhanced Security Features: With increasing cyber threats, security will become a paramount concern, leading to more robust security features in VoIP endpoints.
-
AI-Powered Features: Artificial intelligence will play an increasing role, enabling advanced features like real-time translation, intelligent call routing, and proactive support.
-
Improved User Experience: VoIP endpoints will become more user-friendly and intuitive, making them accessible to a wider range of users.
Conclusion
The diversity of VoIP endpoints available underscores the flexibility and adaptability of VoIP technology. Understanding the various types of endpoints and their functionalities is crucial for businesses and individuals seeking to leverage the power of VoIP communication. By carefully considering factors such as budget, features, and scalability, you can select the most appropriate endpoint to meet your specific communication needs and contribute to a more efficient and productive workflow. The ongoing evolution of VoIP technology ensures that even more innovative and sophisticated endpoints will emerge in the years to come.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Word Chapter 1 End Of Chapter Quiz
Mar 20, 2025
-
2 09 Unit Test Symbols And Imagery Part 1
Mar 20, 2025
-
Canciones De La Virgen De Guadalupe Letra
Mar 20, 2025
-
Factory Burden Is A Synonym For
Mar 20, 2025
-
The Wind Direction And Velocity At Kjfk Is From
Mar 20, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Are Considered Voip Endpoints . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
