Which Of The Following Best Describes The Graph Below
Onlines
Mar 19, 2025 · 5 min read
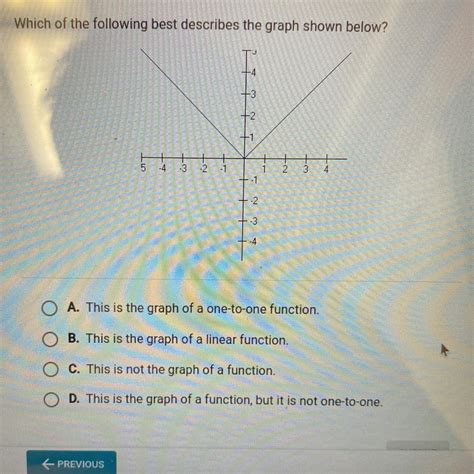
Table of Contents
Deciphering Data: A Comprehensive Guide to Graph Interpretation
Graphs are visual representations of data, providing a concise and easily understandable summary of complex information. Interpreting graphs correctly is crucial for informed decision-making across various fields, from scientific research to business analytics. This article delves into the process of graph interpretation, focusing on identifying key features and drawing meaningful conclusions. We'll explore different graph types, common pitfalls, and best practices for ensuring accurate analysis. Understanding the nuances of graph interpretation is a valuable skill that empowers you to extract actionable insights from data.
Types of Graphs and Their Interpretations
Before we delve into analyzing a specific graph (which will require the graph to be provided), let's familiarize ourselves with common graph types and their characteristics:
1. Line Graphs: These graphs are ideal for showcasing trends over time or illustrating the relationship between two continuous variables. The line connecting data points highlights the pattern, revealing increases, decreases, and periods of stability. Key features to observe include the slope (steepness) of the line, indicating the rate of change, and any significant peaks or troughs, representing extreme values. Example: Tracking stock prices over a month.
2. Bar Graphs (or Bar Charts): Bar graphs compare different categories or groups using the length of the bars to represent the magnitude of the data. They're effective for displaying discrete data and making comparisons between distinct entities. Pay attention to the height of each bar, the spacing between bars, and any labels or annotations providing additional context. Example: Comparing sales figures across different product lines.
3. Pie Charts: Pie charts visually represent proportions or percentages of a whole. Each slice of the pie corresponds to a category, with the size of the slice directly proportional to its share of the total. Pie charts are best suited when focusing on the relative contributions of different parts to a whole. Example: Showing the distribution of age groups in a population.
4. Scatter Plots: Scatter plots illustrate the relationship between two variables. Each point represents a data point, with its position determined by the values of the two variables. Scatter plots reveal patterns, trends, and correlations (positive, negative, or no correlation). The presence of clustering or outliers can provide valuable insights. Example: Investigating the correlation between hours studied and exam scores.
5. Histograms: Histograms display the distribution of a single continuous variable by dividing the data into intervals (bins) and showing the frequency or count of data points falling within each interval. Histograms reveal the shape of the data distribution (e.g., normal, skewed), identifying central tendencies and variability. Example: Representing the distribution of student heights in a class.
Analyzing a Graph: A Step-by-Step Approach
To accurately interpret any graph, follow these steps:
-
Identify the Graph Type: Determine the type of graph presented (line, bar, pie, scatter, histogram, etc.). Understanding the graph type informs the appropriate interpretation techniques.
-
Examine the Axes and Labels: Carefully examine the axes (x and y-axis) and their labels. This provides crucial context, revealing the variables being represented and the units of measurement. Inaccurate or missing labels can lead to misinterpretations.
-
Identify Key Features: Depending on the graph type, look for specific features: trends in line graphs, highest/lowest bars in bar graphs, largest/smallest slices in pie charts, clusters/outliers in scatter plots, shape of the distribution in histograms.
-
Look for Patterns and Trends: Observe if there are any discernible patterns or trends in the data. Are values increasing or decreasing? Are there any correlations between variables? Are there any significant peaks or valleys?
-
Consider the Context: Always consider the context in which the data was collected. Understanding the source of the data and any limitations of the data collection process is crucial for a balanced interpretation.
-
Identify Potential Biases or Limitations: Be mindful of potential biases in the data collection or presentation. Are there any missing data points? Is the scale of the axes manipulated to exaggerate or downplay certain trends?
-
Draw Conclusions: Based on your observations, formulate meaningful conclusions. Clearly articulate the insights derived from the graph. Avoid making assumptions or drawing conclusions that are not supported by the data.
-
Communicate Your Findings: Clearly and concisely communicate your findings to others. Use precise language, avoiding ambiguity. Support your conclusions with specific examples from the graph.
Common Pitfalls in Graph Interpretation
Several common pitfalls can lead to inaccurate interpretations:
- Ignoring Context: Failing to consider the context in which the data was collected.
- Misinterpreting Scale: Misunderstanding or misreading the scale of the axes.
- Overgeneralization: Drawing broad conclusions from limited data.
- Ignoring Outliers: Failing to account for outliers or unusual data points.
- Confusing Correlation with Causation: Assuming that a correlation between two variables implies a causal relationship.
- Cherry-Picking Data: Selecting only data that supports a pre-existing conclusion.
Improving Graph Interpretation Skills
Improving your graph interpretation skills requires practice and a keen eye for detail. Here are some tips:
- Practice Regularly: Regularly analyze graphs from various sources.
- Seek Feedback: Share your interpretations with others and seek their feedback.
- Use Multiple Resources: Consult different sources and perspectives.
- Develop Critical Thinking Skills: Cultivate your critical thinking skills to identify biases and limitations.
- Utilize Technology: Employ data visualization tools and software to enhance your understanding.
Conclusion: The Power of Data Visualization
Graph interpretation is a critical skill that empowers informed decision-making across many disciplines. By following a systematic approach, acknowledging potential pitfalls, and consistently practicing, you can unlock the power of data visualization to reveal meaningful insights and support data-driven decision-making. Remember, the graph is a tool – using it effectively requires careful observation, critical thinking, and a commitment to accuracy. The ability to correctly interpret graphs is not just a technical skill; it’s a crucial element of effective communication and problem-solving. By mastering this skill, you significantly enhance your ability to analyze information, draw sound conclusions, and effectively communicate your findings. This comprehensive approach ensures that your interpretation is not only accurate but also insightful and actionable. The more you practice, the more adept you’ll become at spotting patterns, identifying anomalies, and ultimately, making the most of the data presented visually.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
4 01 Immune Response Handout Answer Key
Mar 19, 2025
-
Springboard Math Algebra 1 Answer Key
Mar 19, 2025
-
Colorea Por Tiempo Preterito O Imperfecto
Mar 19, 2025
-
The State Fema Decision Cycle Includes Which Steps
Mar 19, 2025
-
A Financial Analyst Is Responsible For A Portfolio Hackerrank Solution
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Best Describes The Graph Below . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
