Which Of The Following Display Technologies Require Backlighting Select Two
Onlines
Mar 31, 2025 · 5 min read
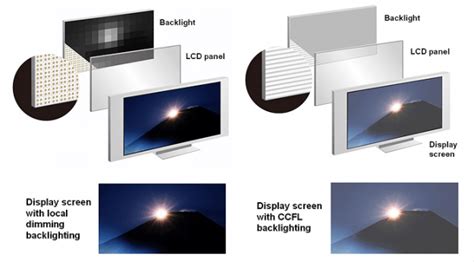
Table of Contents
Which of the Following Display Technologies Require Backlighting? (Select Two)
This article delves into the fascinating world of display technologies, specifically focusing on those that necessitate backlighting. We'll explore the inner workings of various display types, explaining why some require external light sources while others are self-illuminating. By the end, you'll not only be able to confidently select the two display technologies that require backlighting from a list but also possess a solid understanding of the underlying principles.
Let's first clarify what backlighting is and why it's crucial for certain display technologies.
Understanding Backlighting in Displays
Backlighting refers to the use of an external light source positioned behind the display panel to illuminate the pixels. This light shines through the pixels, enabling them to produce a visible image. Without backlighting, the pixels would remain dark and invisible. The quality of the backlight, including its type, brightness, and uniformity, significantly impacts the overall visual experience, affecting aspects like color accuracy, contrast, and viewing angles.
Now, let's examine several prominent display technologies and determine whether they need backlighting:
Display Technologies Requiring Backlighting:
-
Liquid Crystal Display (LCD): This is arguably the most prevalent display technology requiring backlighting. LCDs use liquid crystals sandwiched between two polarized filters. These crystals themselves don't emit light; instead, they twist to control the amount of light passing through them. The backlight illuminates the liquid crystals, and the twisting action determines the color and intensity of each pixel, creating the image we see. Different types of backlights are used with LCDs, including Cold Cathode Fluorescent Lamps (CCFL) and Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs). LED backlights are increasingly popular due to their superior energy efficiency, longer lifespan, and better control over brightness and uniformity. Therefore, LCDs definitively require backlighting.
-
Passive-Matrix LCD (PM-LCD): This is a simpler and less expensive variant of LCD technology. PM-LCDs use a single transistor to control a row or column of pixels, leading to slower response times and lower image quality compared to their active-matrix counterparts. However, even these displays rely on backlighting to function. The backlight illuminates the liquid crystals, and the transistors control the transmission of light, producing the image. Consequently, PM-LCDs also necessitate backlighting.
-
Transflective LCD: A specialized type of LCD designed for use in both bright and low-light conditions. This technology utilizes a reflective layer alongside the backlight. In bright environments, the display reflects ambient light, reducing reliance on the backlight and extending battery life. In low-light conditions, the backlight takes over. Although it uses ambient light, the backlight is still a necessary component of the display. So, even transflective LCDs require backlighting.
Display Technologies That Don't Require Backlighting:
-
Organic Light-Emitting Diode (OLED): Unlike LCDs, OLED displays are self-emissive. Each pixel contains its own light source made up of organic compounds that emit light when an electric current is passed through them. This eliminates the need for a separate backlight, resulting in superior contrast ratios, deeper blacks, and wider viewing angles. The absence of a backlight also contributes to the slimmer profile of OLED displays. OLEDs do not require backlighting.
-
MicroLED: A newer display technology that builds upon LED technology but at a smaller, micrometer scale. Each pixel is an individual tiny LED, making it self-emissive, similar to OLED. This allows for incredible brightness, higher resolution, and superior efficiency. Because of the self-emissive nature, MicroLED displays also don't require backlighting.
-
Quantum Dot (QD)-LED: This hybrid technology combines the advantages of quantum dots with LED backlighting. Quantum dots are nanocrystals that emit specific colors of light when excited by light from an LED backlight. The backlight shines through the quantum dots, which then enhance color saturation and brightness. While quantum dots improve the quality of the image produced by the backlight, the backlight itself remains a necessary component. Therefore, QD-LEDs require backlighting.
Deep Dive into Backlight Types:
The performance and characteristics of a backlit display are heavily influenced by the type of backlight used. Here's a breakdown of common backlight types:
-
Cold Cathode Fluorescent Lamps (CCFL): These were prevalent in older LCD displays but are now largely replaced by LEDs. CCFLs are bulky, less energy-efficient, and have shorter lifespans compared to LEDs.
-
Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs): LED backlights are now the industry standard for LCDs. They offer numerous advantages, including improved energy efficiency, longer lifespan, thinner profiles, better color accuracy, and enhanced brightness control. Several variations exist, including edge-lit and full-array local dimming (FALD) LED backlights.
-
Edge-lit LED backlights: LEDs are placed along the edges of the LCD panel and diffuse the light across the screen. This approach is cost-effective but can result in less uniform brightness and potentially poorer contrast.
-
Full-Array Local Dimming (FALD) LED backlights: LEDs are positioned directly behind the LCD panel in a matrix arrangement. This allows for precise control of individual LED zones, enabling better contrast, deeper blacks, and enhanced HDR performance.
-
Choosing the Right Display Technology:
The selection of a display technology hinges on several factors, including cost, performance requirements, power consumption, and desired aesthetics. For applications where superior image quality, deeper blacks, and wide viewing angles are crucial, OLED and MicroLED technologies are excellent choices. However, they come at a higher cost. LCDs, with their diverse variations and improvements through LED backlighting, remain a cost-effective and reliable option for many applications.
Conclusion:
In summary, the two display technologies from a given list that require backlighting would be LCD and Passive-Matrix LCD (PM-LCD). While other display technologies might incorporate backlights in their design, such as QD-LED, these two are intrinsically dependent on an external light source to function correctly. Understanding the characteristics of different display technologies and their reliance (or not) on backlighting is crucial for making informed decisions when choosing displays for various applications. The ongoing evolution of display technologies promises even more advanced and efficient options in the years to come.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Warrior Toughness Encompasses Mind Body And What Other Attribute
Apr 02, 2025
-
A Peoples History Of The United States Chapter 1 Summary
Apr 02, 2025
-
Pedigrees And The Inheritance Of Lactose Intolerance Answer Key
Apr 02, 2025
-
Unit 1 Rhetorical Situation Reading Quiz
Apr 02, 2025
-
Adolescence Is A Time When Existential Issues
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Display Technologies Require Backlighting Select Two . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
