Which Of The Following Is True Of Internal Reprogramming
Onlines
Mar 17, 2025 · 6 min read
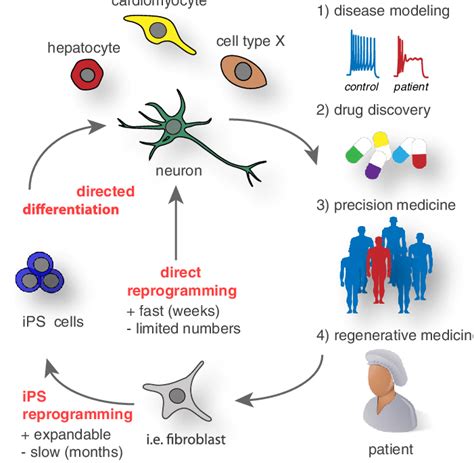
Table of Contents
Which of the following is true of internal reprogramming? Unraveling the Mysteries of Cellular Transformation
Internal reprogramming, a term often associated with cellular rejuvenation and regenerative medicine, holds immense promise for treating age-related diseases and injuries. However, understanding its intricacies requires delving into its mechanisms, potential benefits, and limitations. This comprehensive article will explore the complexities of internal reprogramming, clarifying common misconceptions and highlighting its significance in various fields of research. We will examine what is true about internal reprogramming, addressing key aspects including its processes, applications, and future directions.
What is Internal Reprogramming?
Internal reprogramming, in the context of cellular biology, refers to the process of reverting differentiated cells (cells with specialized functions) back to a pluripotent state. This means transforming specialized cells, such as skin cells or heart cells, into cells that have the potential to become any type of cell in the body. This is achieved by manipulating the expression of specific genes, essentially "rewriting" the cell's genetic program. This reprogramming is distinct from external reprogramming, which involves the introduction of exogenous factors like transcription factors. Instead, internal reprogramming focuses on leveraging the cell's inherent mechanisms to achieve this transformation.
Mechanisms of Internal Reprogramming:
Several mechanisms are implicated in internal reprogramming, each involving a complex interplay of signaling pathways and gene regulatory networks. Some key elements include:
-
Epigenetic Modifications: Internal reprogramming heavily relies on epigenetic modifications – changes in gene expression that don't involve alterations to the DNA sequence itself. These modifications include DNA methylation, histone modification, and non-coding RNA regulation. By altering these epigenetic marks, the cell's gene expression profile can be reset, leading to a shift towards a pluripotent state.
-
Metabolic Reprogramming: The metabolic state of a cell plays a crucial role in its capacity for reprogramming. Studies have shown that manipulating cellular metabolism, for instance, by altering glucose or fatty acid utilization, can influence the efficiency of reprogramming. This metabolic shift often involves the activation of pathways that promote cell growth and survival, essential for the successful reversion to a pluripotent state.
-
Signal Transduction Pathways: Various signaling pathways, including the Wnt, TGF-β, and Notch pathways, are involved in regulating the cellular processes during internal reprogramming. These pathways influence the expression of genes crucial for maintaining cellular identity and pluripotency. Modulation of these pathways can steer the cell towards a more malleable state, facilitating the reprogramming process.
-
Microenvironment: The cellular microenvironment, including the extracellular matrix and neighboring cells, significantly influences the success of internal reprogramming. The composition of the extracellular matrix and the presence of specific growth factors or cytokines can promote or hinder the reprogramming process. Optimizing the microenvironment is thus crucial for achieving efficient internal reprogramming.
Potential Benefits of Internal Reprogramming:
The potential applications of internal reprogramming are vast, spanning across numerous medical fields. Its ability to rejuvenate cells and tissues holds immense potential for:
-
Tissue Regeneration: Reprogramming somatic cells into specific cell types offers a promising avenue for repairing damaged tissues and organs. This could revolutionize treatments for conditions such as heart failure, spinal cord injury, and neurodegenerative diseases. By generating new, healthy cells from the patient's own cells, the risk of rejection is minimized.
-
Age-Related Disease Treatment: The accumulation of cellular damage and dysfunction is a hallmark of aging. Internal reprogramming could potentially reverse or mitigate these age-related changes, potentially leading to the development of therapies for diseases like Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and cardiovascular disease. By rejuvenating aged cells, the body's natural repair mechanisms could be reactivated.
-
Cancer Treatment: While reprogramming can potentially lead to uncontrolled cell growth if not carefully managed, it also holds promise in cancer treatment. Understanding the mechanisms of internal reprogramming could help researchers develop strategies to selectively reprogram cancer cells, making them more susceptible to therapies or reverting them to a less malignant state.
Challenges and Limitations:
Despite its potential, internal reprogramming faces several challenges:
-
Efficiency: Achieving efficient and complete reprogramming remains a significant hurdle. The process is often inefficient, with only a small percentage of cells successfully reprogrammed. Improving the efficiency of reprogramming is critical for its wider application.
-
Safety: The uncontrolled proliferation of reprogrammed cells poses a safety concern. Robust safety measures and strategies for controlling cell growth are necessary to prevent tumorigenesis.
-
Ethical Considerations: The use of human cells for research and therapeutic purposes raises ethical considerations that need to be carefully addressed. These concerns necessitate strict ethical guidelines and regulations to ensure responsible research practices.
-
Complexity: The intricate interplay of signaling pathways and gene regulatory networks involved in internal reprogramming makes it a highly complex process to understand and manipulate. Further research is needed to fully elucidate the molecular mechanisms governing this process.
Future Directions of Research:
Future research in internal reprogramming will likely focus on:
-
Improving Reprogramming Efficiency: Scientists are actively exploring new methods and strategies to enhance the efficiency of internal reprogramming. This involves investigating novel factors, optimizing the cellular microenvironment, and developing more effective reprogramming protocols.
-
Enhancing Safety: Research is aimed at developing strategies to prevent the uncontrolled growth of reprogrammed cells. This includes identifying and targeting specific pathways involved in cell proliferation and developing methods to monitor and control the behavior of reprogrammed cells.
-
Developing Clinical Applications: Translating the findings from preclinical studies into clinical applications is a crucial next step. Rigorous clinical trials are needed to assess the safety and efficacy of internal reprogramming therapies in humans.
-
Understanding the Mechanisms: Further research is crucial to fully elucidate the complex molecular mechanisms that govern internal reprogramming. This will allow for more precise manipulation of the reprogramming process and the development of more targeted therapies.
Distinguishing Internal Reprogramming from Other Techniques:
It's essential to differentiate internal reprogramming from other techniques like somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT) and induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) technology. While all three aim to generate pluripotent cells, their approaches differ significantly. SCNT involves transferring the nucleus of a somatic cell into an enucleated egg cell, while iPSC technology uses the introduction of exogenous transcription factors to reprogram somatic cells. Internal reprogramming, however, aims to harness the cell's own mechanisms to achieve this transformation, without the need for external factors or egg cells.
Conclusion:
Internal reprogramming represents a significant advancement in cellular biology and regenerative medicine. Its potential to rejuvenate cells and regenerate tissues holds immense promise for treating a wide range of diseases and injuries. However, considerable challenges remain, requiring further research to improve efficiency, enhance safety, and address ethical considerations. Despite these challenges, the ongoing progress in this field suggests a promising future for internal reprogramming therapies, potentially revolutionizing healthcare and extending human lifespan and healthspan. Continued investment in research and development is crucial to unlocking the full potential of internal reprogramming for the benefit of humankind. The ongoing unraveling of the intricate processes involved promises to lead to innovative treatments and breakthroughs in the years to come, further enhancing our understanding of cellular rejuvenation and its potential impact on human health. The future of internal reprogramming is bright, carrying the potential to reshape the landscape of medicine and extend healthy human lifespans.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Mrs Duarte Is Enrolled In Original Medicare
Mar 18, 2025
-
Choose The Function Whose Graph Is Given Below
Mar 18, 2025
-
National Geographic Secrets Of The Body Farm Answers
Mar 18, 2025
-
6 11 Unit Test Injury Prevention And Safety Part 1
Mar 18, 2025
-
Identify A Guideline Associated With Anti Dandruff Treatments
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Is True Of Internal Reprogramming . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
