Which Of The Following Statements About Cellulitis Is True
Onlines
Apr 05, 2025 · 6 min read
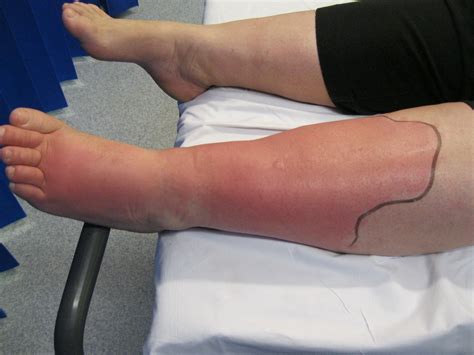
Table of Contents
Which of the following statements about cellulitis is true?
Cellulitis is a common and potentially serious bacterial skin infection. Understanding its characteristics, causes, treatment, and prevention is crucial for effective management and minimizing complications. This article will explore various statements about cellulitis, determining their accuracy and providing a comprehensive overview of this infection.
Understanding Cellulitis: A Deep Dive
Before evaluating specific statements, let's establish a solid understanding of cellulitis itself. Cellulitis is characterized by a localized infection of the skin and underlying connective tissues, primarily caused by bacteria such as Streptococcus and Staphylococcus. These bacteria typically enter the body through a break in the skin, even a tiny, unnoticed one. The infection spreads rapidly, leading to inflammation and redness.
Key Characteristics of Cellulitis:
- Rapid Spread: One of the hallmark features is its rapid progression. The affected area can expand significantly within hours or days.
- Inflammation and Redness: The skin becomes red, swollen, and tender to the touch. The redness often has a poorly defined border, unlike other skin infections.
- Pain and Warmth: The affected area is usually painful and feels warmer than the surrounding skin.
- Fever and Chills: Systemic symptoms like fever, chills, and malaise can accompany the infection, especially in more severe cases.
- Lymphangitis: In some instances, red streaks (lymphangitis) may be visible, indicating the spread of infection along the lymphatic vessels.
- Blisters or Ulcers: Severe cellulitis can lead to the formation of blisters or ulcers.
Evaluating Statements About Cellulitis
Now, let's analyze some common statements regarding cellulitis and determine their veracity:
Statement 1: Cellulitis is always caused by a Staphylococcus aureus infection.
FALSE. While Staphylococcus aureus is a frequent culprit, cellulitis can be caused by various bacteria, including Streptococcus pyogenes (group A Streptococcus), Haemophilus influenzae, and others. The specific bacteria involved can influence treatment choices. Therefore, this statement is an oversimplification.
Statement 2: Cellulitis only affects the legs.
FALSE. Although cellulitis commonly affects the lower extremities (legs and feet), it can occur anywhere on the body, including the face, arms, and torso. The location of the infection depends on where the bacteria enter the skin. This statement is inaccurate due to its limited scope.
Statement 3: Cellulitis is easily treated with over-the-counter antibiotics.
FALSE. Cellulitis requires treatment with prescription antibiotics, typically oral or intravenous, depending on the severity of the infection. Over-the-counter medications might alleviate symptoms like pain and fever, but they cannot effectively combat the bacterial infection itself. Ignoring this and relying solely on over-the-counter remedies can lead to serious complications.
Statement 4: Cellulitis is a contagious infection.
FALSE. Cellulitis itself is not contagious in the traditional sense. It's not spread directly from person to person like the flu or a cold. However, the bacteria that cause cellulitis can be contagious. For instance, Staphylococcus aureus can spread through direct contact with infected wounds or shared personal items. The bacteria cause the cellulitis, not the cellulitis itself. It's a crucial distinction to understand.
Statement 5: A warm compress is an effective treatment for cellulitis.
FALSE. While warm compresses might provide temporary relief from pain and discomfort, they are not a treatment for the underlying bacterial infection. Heat can even potentially worsen the infection by promoting bacterial growth. Appropriate antibiotic treatment is essential.
Statement 6: Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for preventing serious complications.
TRUE. This statement accurately reflects the importance of prompt medical attention. Early diagnosis and treatment with appropriate antibiotics significantly reduce the risk of serious complications, such as:
- Sepsis: A life-threatening condition caused by the body's overwhelming response to an infection.
- Abscess formation: A localized collection of pus.
- Lymphangitis: Inflammation of the lymphatic vessels.
- Necrotizing fasciitis: A severe and rapidly spreading infection of the fascia (the tissue layer beneath the skin). This is a medical emergency.
Statement 7: People with weakened immune systems are at higher risk of developing cellulitis.
TRUE. Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with diabetes, HIV/AIDS, or undergoing chemotherapy, are more susceptible to bacterial infections like cellulitis. Their compromised immune response makes them less able to fight off the infection effectively.
Statement 8: Proper wound care is essential in preventing cellulitis.
TRUE. Maintaining good hygiene and properly caring for any wounds, even minor ones, is crucial in preventing cellulitis. Cleaning and dressing wounds promptly minimizes the risk of bacterial entry and infection. Prompt attention to any wound is essential.
Statement 9: Cellulitis can be easily diagnosed through a visual examination.
PARTIALLY TRUE. While the characteristic signs and symptoms of cellulitis, such as redness, swelling, and pain, often suggest a diagnosis, a definitive diagnosis may require additional testing, such as blood tests to identify the causative bacteria or imaging studies (e.g., ultrasound) to rule out deeper infections. Visual examination is the starting point, not the endpoint, of diagnosis.
Statement 10: Cellulitis always leaves scarring.
FALSE. Whether or not cellulitis leaves a scar depends on the severity and depth of the infection. Mild cases often resolve without scarring, while more severe infections may result in some scarring. This is not a guaranteed outcome, however.
Risk Factors for Cellulitis
Several factors can increase the risk of developing cellulitis:
- Pre-existing skin conditions: Eczema, psoriasis, and other skin conditions can compromise the skin barrier, increasing susceptibility to infection.
- Chronic medical conditions: Diabetes, heart failure, and other conditions can weaken the immune system.
- Obesity: Obesity can reduce blood flow to the skin, impairing the body's ability to fight infection.
- Lymphedema: Fluid buildup in the tissues, often in the arms or legs, can create an environment conducive to bacterial growth.
- Recent surgery or trauma: Surgery or injuries that break the skin create entry points for bacteria.
- Impaired immune function: Conditions like HIV/AIDS or use of immunosuppressant medications.
Prevention Strategies
Several steps can significantly reduce the risk of developing cellulitis:
- Maintain good hygiene: Wash your hands frequently and thoroughly, especially after touching wounds or potentially contaminated surfaces.
- Proper wound care: Clean and dress any wounds promptly and appropriately.
- Control chronic conditions: Manage diabetes, heart failure, and other chronic conditions effectively.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Maintaining a healthy weight can improve blood flow and immune function.
- Protect your skin: Avoid injuries to the skin, and use protective measures when engaging in activities that could lead to skin trauma.
- Prompt treatment of skin infections: Addressing minor skin infections promptly can prevent them from progressing to cellulitis.
Conclusion
Cellulitis is a serious bacterial skin infection requiring prompt medical attention. While visual examination plays a role in diagnosis, further testing may be needed to confirm the diagnosis and identify the causative bacteria. Misconceptions about cellulitis's causes, treatment, and contagiousness are prevalent, emphasizing the need for accurate information. Understanding the true nature of cellulitis, its risk factors, and effective prevention strategies is crucial for minimizing the risk and managing this condition effectively. Always consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment of cellulitis.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Choose The Sentence That Uses Parallel Structure Correctly
Apr 06, 2025
-
Hartmans Nursing Assistant Care The Basics Workbook Answers
Apr 06, 2025
-
Escaped Convict Selden Hound Of The Baskervilles
Apr 06, 2025
-
In Time Of The Butterflies Sparknotes
Apr 06, 2025
-
Match Each Vector Field With Its Graph
Apr 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Statements About Cellulitis Is True . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
