Which Of The Following Statements Regarding Abdominal Eviscerations Is Correct
Onlines
Mar 20, 2025 · 6 min read
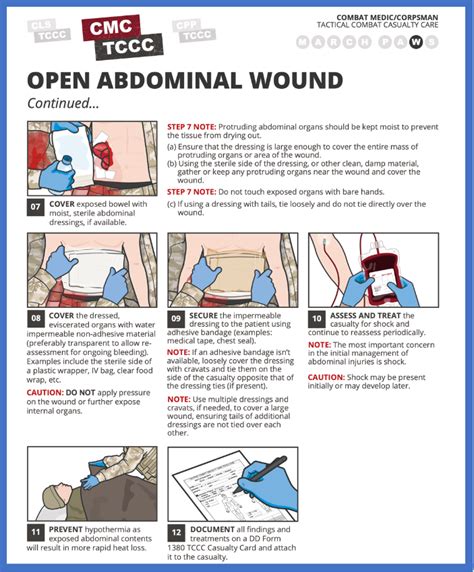
Table of Contents
Which of the Following Statements Regarding Abdominal Eviscerations is Correct? A Comprehensive Guide
Abdominal evisceration, the protrusion of abdominal organs through a wound in the abdominal wall, is a critical surgical emergency. Understanding the correct management is paramount to patient survival. This article will delve into various statements regarding abdominal eviscerations, analyzing their accuracy and providing a comprehensive overview of this life-threatening condition. We will explore the pathophysiology, assessment, immediate and definitive management, and crucial considerations for optimal patient outcomes.
Understanding Abdominal Evisceration: A Pathophysiological Overview
Before evaluating statements about abdominal eviscerations, it's crucial to grasp the underlying pathophysiology. Evisceration results from a disruption of the integrity of the abdominal wall, typically caused by penetrating trauma (stab wounds, gunshot wounds) or blunt force trauma (motor vehicle accidents, falls from height). The severity depends on the size and location of the wound, the organs involved, and the presence of associated injuries.
The initial injury causes damage to the abdominal wall musculature, peritoneum, and potentially underlying organs. The intra-abdominal pressure, normally maintained by the abdominal muscles and fascia, is compromised, leading to the expulsion of organs through the defect. This exposes the vulnerable viscera to the external environment, increasing the risk of infection, hypothermia, desiccation, and further trauma. The extent of organ damage varies widely, from superficial abrasions to complete lacerations and perforation.
Assessing the Severity: A Multifaceted Approach
Accurate assessment is critical in managing abdominal eviscerations effectively. This involves a systematic approach encompassing primary and secondary surveys.
Primary Survey (ABCDEs):
- Airway: Ensure a patent airway, managing any airway obstruction caused by bleeding or trauma.
- Breathing: Assess respiratory effort and oxygen saturation, addressing pneumothorax or hemothorax if present.
- Circulation: Control bleeding, assess vital signs (heart rate, blood pressure), and manage hypovolemic shock through fluid resuscitation.
- Disability: Briefly assess neurological status, checking for level of consciousness and pupillary responses.
- Exposure: Completely expose the abdomen to fully assess the extent of the evisceration and associated injuries.
Secondary Survey:
Following the primary survey, a detailed secondary survey is performed. This includes:
- Detailed Examination of the Wound: Determine the size, location, and depth of the wound. Note the type and extent of evisceration.
- Assessment of Eviscerated Organs: Identify the specific organs protruding and assess their viability. Look for signs of ischemia (pale, dusky color), perforation, or damage.
- Assessment of Associated Injuries: Examine for other injuries, including head injuries, chest injuries, pelvic fractures, and extremity fractures. This is crucial as evisceration is frequently associated with other life-threatening conditions.
- Imaging Studies: Abdominal X-rays, CT scans, and FAST (focused assessment with sonography for trauma) exams are often used to identify intra-abdominal injuries and guide management.
Managing Abdominal Eviscerations: Immediate and Definitive Care
Management of abdominal eviscerations is a multi-step process demanding swift and decisive action.
Immediate Management:
- Call for Help: Immediately call for emergency medical services (EMS). This is crucial for timely transport to a trauma center with appropriate surgical expertise.
- Control Bleeding: If significant bleeding is present, apply direct pressure to control the hemorrhage. Avoid directly manipulating the eviscerated organs.
- Cover the Eviscerated Organs: Cover the exposed organs with a sterile, moist dressing. This helps prevent desiccation, contamination, and further injury. Ideally, a saline-soaked sterile dressing is used. Never attempt to push the organs back into the abdominal cavity.
- Maintain Body Temperature: Hypothermia is a significant concern. Maintain the patient's body temperature with blankets, warming lights, or other appropriate measures.
- Oxygen Supplementation: Administer supplemental oxygen to maintain adequate tissue perfusion.
- Fluid Resuscitation: Initiate fluid resuscitation to correct hypovolemia and maintain hemodynamic stability. Blood products may be necessary to replace blood loss.
- Pain Management: Administer analgesia as needed to alleviate pain and anxiety.
Definitive Management:
Definitive management of abdominal eviscerations involves surgical intervention. The goals of surgery are:
- Wound Closure: Repair the abdominal wall defect using appropriate surgical techniques. This may involve layered closure of the fascia, muscle, and subcutaneous tissues, followed by skin closure.
- Organ Repair/Resection: Repair any damaged organs or perform resection if necessary. This may involve suturing lacerations, removing devitalized tissue, or performing bowel resection and anastomosis.
- Debridement: Remove any devitalized or contaminated tissue to reduce the risk of infection.
- Exploration of the Abdomen: Thoroughly explore the abdominal cavity to identify and manage other injuries, such as bleeding, organ damage, or bowel perforations. This may involve the placement of drains to evacuate fluid and prevent abscess formation.
- Post-operative Care: Post-operative care includes pain management, nutritional support, and close monitoring for signs of infection or complications. This may also involve antibiotic therapy to prevent or treat infection.
Evaluating Statements Regarding Abdominal Eviscerations
Now, let's analyze some common statements related to abdominal eviscerations and determine their accuracy:
Statement 1: The primary goal of initial management is to immediately push the eviscerated organs back into the abdominal cavity.
FALSE. This is absolutely incorrect and potentially fatal. Pushing the organs back in can cause further damage to the organs, introduce infection, and make surgical repair significantly more difficult. The priority is to control bleeding, cover the organs with a sterile, moist dressing, and transport the patient to a surgical facility for definitive care.
Statement 2: A sterile, dry dressing should be used to cover eviscerated organs.
FALSE. A dry dressing will allow the exposed organs to dry out and become damaged. A moist, sterile dressing helps to keep the organs hydrated and reduces the risk of contamination. Saline is the preferred solution.
Statement 3: Abdominal eviscerations are always accompanied by significant internal bleeding.
FALSE. While significant hemorrhage is a possibility, the amount of bleeding varies depending on the extent and location of the injury. Some cases may involve minimal bleeding, while others can lead to life-threatening hypovolemic shock.
Statement 4: Immediate surgical intervention is always necessary in abdominal eviscerations.
TRUE (with qualifications). While surgical repair is usually required, the timing of surgery depends on several factors including the overall condition of the patient, associated injuries, and the viability of eviscerated organs. Immediate surgery is critical when there is uncontrolled bleeding or severe organ damage. However, other injuries might need to be addressed first, making the surgery a staged procedure.
Statement 5: The prognosis for patients with abdominal eviscerations is always poor.
FALSE. The prognosis depends on several factors, including the timing and effectiveness of treatment, the severity of associated injuries, the presence of complications (such as infection or sepsis), and the patient's overall health. With prompt and effective management, many patients can survive and make a full recovery.
Conclusion: A Collaborative Approach to Optimal Outcomes
Abdominal evisceration is a severe surgical emergency requiring a rapid, organized, and collaborative approach. Accurate assessment, appropriate initial management, and timely surgical intervention are crucial for optimizing patient outcomes. Understanding the correct management principles, outlined above, is essential for healthcare professionals involved in the care of trauma patients. Remember, never attempt to replace the eviscerated organs yourself; instead focus on preserving organ viability, preventing further injury and contamination, and ensuring rapid transport to a facility equipped for definitive surgical management. The statements analyzed in this article highlight the importance of accurate knowledge and adherence to established guidelines in this high-stakes scenario. This careful approach will help to significantly improve survival rates and long-term functional outcomes for individuals suffering from abdominal eviscerations.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Value Chain Describes Blank Of A Firm
Mar 20, 2025
-
What Evasion Aid Is Tailored To Cover An Individual
Mar 20, 2025
-
The Milky Way Documentary Guided Notes
Mar 20, 2025
-
The Love Suicides At Amijima Summary
Mar 20, 2025
-
Tends To Supervise Employees Very Closely
Mar 20, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Statements Regarding Abdominal Eviscerations Is Correct . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
