Which Point Represents The Vertex Of The Marked Angle
Onlines
Apr 06, 2025 · 5 min read
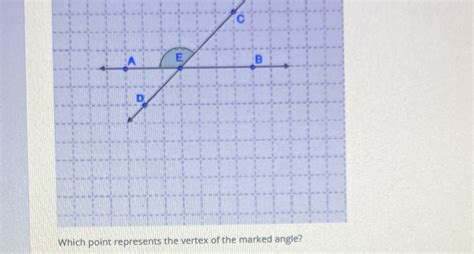
Table of Contents
Which Point Represents the Vertex of the Marked Angle? A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding angles is fundamental in geometry and numerous other fields. A crucial aspect of working with angles is identifying the vertex – the point where two rays or line segments meet to form the angle. This article will delve into the concept of the vertex of an angle, providing a comprehensive explanation, illustrative examples, and practical applications. We'll also explore different types of angles and how to identify their vertices in various contexts.
Understanding Angles and Their Components
Before pinpointing the vertex, let's solidify our understanding of angles. An angle is formed by two rays that share a common endpoint. These rays are called the sides of the angle, and the common endpoint is the vertex. Imagine two arms extending from your shoulder – your shoulder is the vertex, and your arms are the sides of the angle they form.
The size of an angle is measured in degrees (°) or radians. A full rotation around a point is 360°, while a straight line represents an angle of 180°. Angles can be classified based on their size:
- Acute Angle: An angle measuring less than 90°.
- Right Angle: An angle measuring exactly 90°.
- Obtuse Angle: An angle measuring more than 90° but less than 180°.
- Straight Angle: An angle measuring exactly 180°.
- Reflex Angle: An angle measuring more than 180° but less than 360°.
Identifying the Vertex: A Step-by-Step Approach
Identifying the vertex of a marked angle is straightforward. Look for the point where the two rays or line segments intersect. This point of intersection is always the vertex. Here’s a step-by-step approach:
- Locate the Rays or Line Segments: Identify the two lines or line segments that form the angle.
- Find the Intersection: Look for the point where these two lines or line segments meet.
- Verify the Intersection: Ensure that the point of intersection is the common endpoint of both lines or line segments.
Let's illustrate this with an example. Consider an angle denoted as ∠ABC. In this notation:
- A and C represent points on the two rays forming the angle.
- B represents the point where the two rays meet, thus making B the vertex.
The angle is named using the vertex letter in the middle. This convention ensures clarity and avoids ambiguity.
Visual Examples and Different Representations
Let's examine various scenarios and visualize the vertex identification process:
Scenario 1: Simple Angle
Imagine a simple acute angle drawn on a piece of paper. The two lines will clearly intersect at one point. This point of intersection is the vertex.
Scenario 2: Angle in a Triangle
In a triangle, each angle has its vertex at one of the triangle's corners. The vertices of the triangle are also the vertices of its internal angles. For instance, in triangle XYZ, the vertex of angle X is point X.
Scenario 3: Overlapping Angles
Sometimes, you might encounter overlapping angles, meaning multiple angles share a common vertex. In such cases, carefully identify the specific rays or line segments that define the angle in question before determining its vertex. The vertex remains the point of intersection of those specific rays.
Scenario 4: Angles in Geometric Shapes
In various geometric shapes such as squares, rectangles, and polygons, the corners represent the vertices of the internal angles. Identifying the vertices is crucial for calculating the interior angles, understanding the shape's properties, and solving geometric problems.
Scenario 5: Angles in Coordinate Geometry
When working in coordinate geometry, angles can be formed by lines represented by equations. The vertex is the point of intersection of these lines, which can be determined by solving the system of equations representing the lines.
Practical Applications: Why Vertex Identification Matters
The ability to correctly identify the vertex of an angle is crucial in various applications across multiple disciplines:
-
Engineering and Architecture: Precise angle measurements are essential in construction, bridge building, and designing buildings. The vertex represents the point of convergence for different structural elements.
-
Computer Graphics and Game Development: Vertex identification is fundamental in creating and manipulating 3D models and animations. The position of vertices determines the shape and form of objects.
-
Cartography and Geography: Angles are used to determine directions, distances, and locations on maps and in geographic information systems (GIS). The understanding of vertex positions is crucial for accurate mapmaking.
-
Robotics and Automation: Robots use angle measurements to navigate and perform tasks. The vertex point becomes the reference for robotic arm movements and orientation.
-
Trigonometry and Calculus: The concept of an angle and its vertex is fundamental in trigonometric functions and various calculus applications.
Advanced Concepts and Challenges
While identifying the vertex of a simple angle is usually straightforward, more complex situations can present challenges. These include:
-
Angles Formed by Curved Lines: When dealing with angles formed by curves, the concept of a vertex becomes more nuanced and might require the use of tangents and calculus.
-
Angles in Three-Dimensional Space: Identifying vertices in three-dimensional space adds complexity, demanding a deeper understanding of spatial geometry and coordinate systems.
-
Ambiguous Angle Representations: In some diagrams, the angle might be implicitly defined without explicit markings, requiring careful interpretation of the figure to correctly identify the vertex.
Conclusion: Mastering the Vertex
Identifying the vertex of a marked angle is a fundamental skill in geometry and related fields. Through a systematic approach and careful observation, one can accurately determine the vertex and utilize this knowledge in various applications. Understanding the properties of different types of angles and their vertices empowers you to solve geometric problems, interpret diagrams, and apply this knowledge to practical scenarios across various disciplines. The seemingly simple task of finding a vertex plays a vital role in more advanced mathematical concepts and practical real-world applications. By mastering this basic concept, you lay a solid foundation for success in further geometrical studies and applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Pain In The Gut Case Study Answers
Apr 08, 2025
-
Art Labeling Activity Figure 12 4 B
Apr 08, 2025
-
Suppose That The Video Game Company Ultravision
Apr 08, 2025
-
A Tax Imposed On The Sellers Of A Good Will
Apr 08, 2025
-
Signing Naturally Units 1 6 Pdf Answers
Apr 08, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Point Represents The Vertex Of The Marked Angle . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.