Which Revision Of The Sentence Uses Parallel Structure 2.4.3
Onlines
Mar 09, 2025 · 5 min read
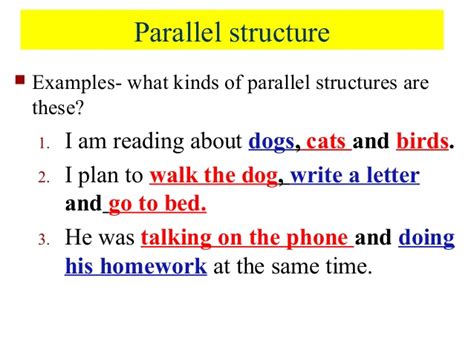
Table of Contents
Which Revision of the Sentence Uses Parallel Structure 2.4.3? Mastering Parallelism for Clarity and Impact
Parallel structure, also known as parallelism, is a fundamental principle of grammar that significantly enhances the clarity, readability, and impact of your writing. It involves expressing similar grammatical elements in a consistent and balanced way. Understanding and applying parallel structure is crucial for effective communication, particularly in academic writing, professional settings, and compelling storytelling. This article will delve into the concept of parallel structure, illustrating its importance through examples and exploring how to identify and correct instances where parallelism is lacking. We'll also specifically address the hypothetical "2.4.3" reference, examining potential scenarios where this might be used in a grading or editing context.
What is Parallel Structure?
Parallel structure is the use of similar grammatical forms to express related ideas within a sentence or series of sentences. This consistency creates a sense of rhythm and balance, making the writing easier to understand and more aesthetically pleasing. The most common forms of parallelism involve:
- Lists: Items in a list should all be in the same grammatical form (e.g., all nouns, all verbs in the same tense, all gerunds, etc.).
- Coordinating Conjunctions: When connecting clauses with coordinating conjunctions (for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so – FANBOYS), the clauses should be parallel.
- Correlative Conjunctions: Correlative conjunctions (e.g., either/or, neither/nor, both/and, not only/but also) also require parallel structure in the elements they connect.
- Comparisons: When comparing or contrasting ideas, maintain parallel structure to ensure clarity and balance.
Examples of Correct Parallel Structure:
- List: She enjoys swimming, hiking, and reading. (All gerunds)
- Coordinating Conjunction: He is intelligent and works diligently. (Both are verb phrases)
- Correlative Conjunction: She is not only beautiful but also kind and compassionate. (Both are adjective phrases)
- Comparison: Running is more beneficial than walking. (Both are adjective phrases)
Examples of Incorrect Parallel Structure:
- Incorrect List: He likes to play basketball, hiking, and to read. (Mixed gerund and infinitive)
- Incorrect Coordinating Conjunction: She is a talented writer and writes beautifully. (Mixed noun phrase and verb phrase)
- Incorrect Correlative Conjunction: He is both intelligent and works hard. (Mixed adjective phrase and verb phrase)
- Incorrect Comparison: Studying is better than to relax. (Mixed adjective and infinitive)
Identifying and Correcting Parallelism Errors
Recognizing and fixing parallelism errors requires careful attention to the grammatical structure of your sentences. Here's a step-by-step approach:
- Identify the core elements: Determine the key elements in your sentence that should be parallel. This often involves identifying lists, elements connected by conjunctions, or comparisons.
- Analyze the grammatical form: Examine the grammatical form of each element (noun, verb, adjective, adverb, phrase, clause).
- Check for consistency: Ensure all elements have the same grammatical form.
- Rewrite for parallelism: If inconsistencies exist, rewrite the sentence to create parallel structure.
The Hypothetical "2.4.3" Reference: Context is Key
The reference "2.4.3" likely points to a specific section within a style guide, grammar textbook, or assignment rubric related to parallelism. Without the specific context of what "2.4.3" refers to, we can only speculate on potential scenarios. It's crucial to consult the relevant document for the precise meaning and application.
Possible Interpretations of "2.4.3":
- A Style Guide Section: "2.4.3" could denote a section in a style guide (like the APA style guide, MLA style guide, Chicago style guide, etc.) dedicated to the rules and examples of parallel structure. This section might offer detailed explanations and examples, potentially categorizing types of parallelism or outlining common errors.
- A Textbook Chapter: Similarly, "2.4.3" could represent a chapter or subsection in a grammar or composition textbook that directly addresses parallelism. This section would likely cover the basics of parallel structure, provide examples of correct and incorrect usage, and offer exercises to solidify understanding.
- An Assignment Rubric: In an academic setting, "2.4.3" might be a code within an assignment rubric that specifically refers to the assessment criteria for parallel structure. This could mean that a portion of the grade is dedicated to the correct and consistent use of parallelism in the writing.
Scenario Examples Illustrating "2.4.3" Context:
Scenario 1: Multiple Choice Question
Let's say you encounter a multiple-choice question:
Question: Which of the following sentences uses parallel structure (referencing guideline 2.4.3)?
A. She likes to sing, dancing, and to paint. B. He is kind, helpful, and a good listener. C. They went to the store, bought groceries, and came home. D. The dog ran quickly, barked loudly, and wagged its tail happily.
Correct Answer: C and D. Options C and D use parallel structure: C employs gerunds, and D uses adverbial phrases consistently.
Scenario 2: Essay Feedback
Imagine receiving feedback on an essay: "Your essay contains several instances of non-parallel structure (referencing guideline 2.4.3). Please revise sentences 3, 7, and 12 to ensure parallelism." This feedback clearly indicates a specific expectation for using parallel structure based on the guideline mentioned.
The Importance of Parallel Structure in Different Contexts
Parallel structure is not merely a stylistic choice; it's a crucial element for clear and effective communication across various contexts.
Academic Writing:
In academic papers, maintaining parallel structure enhances clarity and professionalism. It avoids ambiguity and demonstrates a strong grasp of grammar. This is essential for conveying complex ideas accurately and achieving academic credibility.
Professional Writing:
In professional communication, parallel structure improves readability and conciseness. In emails, reports, presentations, and proposals, using parallelism ensures that your message is easily understood and avoids any confusion that might arise from inconsistent sentence structure.
Creative Writing:
While less rigid in creative writing, parallel structure can be used to create rhythm, emphasis, and a powerful effect. By strategically using parallel structures, writers can build suspense, create memorable imagery, or underscore specific ideas.
Conclusion: Mastering Parallelism for Effective Communication
Parallel structure is a vital grammatical tool that improves clarity, readability, and impact across all types of writing. Understanding its principles, learning to identify errors, and practicing its application is crucial for effective communication in academic, professional, and creative contexts. The hypothetical "2.4.3" reference emphasizes the importance of adhering to specific guidelines related to parallelism, highlighting its significance in achieving writing excellence. By mastering parallelism, you elevate your writing from simply conveying information to engaging and persuading your audience effectively. Remember to always refer to the specific style guide or resource indicated by the reference number (like 2.4.3) for detailed explanations and examples tailored to its context. Consistent and accurate parallel structure strengthens your writing and reflects a strong command of language.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Geometry Road Trip Project Answers Pdf
Mar 10, 2025
-
Name Cell B9 As Follows Cola
Mar 10, 2025
-
To Kill A Mockingbird Detailed Chapter Summary
Mar 10, 2025
-
A Customer Arrives At A Customer Service Desk
Mar 10, 2025
-
Part 2 Ch 8 15 Murder On The Orient Express Summary
Mar 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Revision Of The Sentence Uses Parallel Structure 2.4.3 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
