Which Role Does Product Management Work With To Prioritize Enablers
Onlines
Apr 04, 2025 · 6 min read
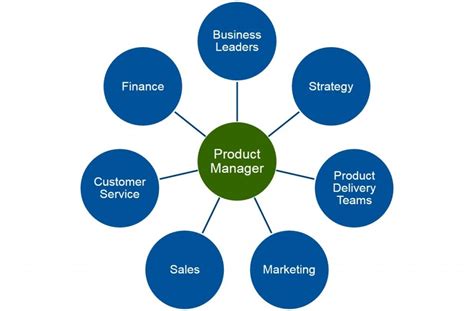
Table of Contents
Which Roles Does Product Management Work With to Prioritize Enablers?
Product management is a multifaceted discipline requiring collaboration across various teams to achieve product success. One crucial aspect of this collaboration involves prioritizing enablers – the underlying infrastructure, tools, processes, and capabilities that empower the product team to build, launch, and scale their product effectively. Understanding which roles are key to this prioritization process is critical for efficient product development and achieving business objectives.
The Core Team: Defining the Enabler Prioritization Process
The initial stage of prioritizing enablers involves a core team comprising the product manager, engineering lead, and design lead. This team sets the overall strategy and establishes criteria for evaluating enablers.
The Product Manager's Role:
The product manager (PM) owns the product vision and strategy. Their role in enabler prioritization is pivotal:
- Strategic Alignment: The PM ensures that all prioritized enablers directly support the product roadmap and long-term goals. They identify bottlenecks and areas where improved infrastructure or processes would significantly accelerate product development.
- Business Value Assessment: PMs assess the potential business impact of each enabler, considering factors like increased efficiency, reduced costs, improved user experience, and faster time to market. This is crucial for justifying investment and prioritization.
- Stakeholder Management: PMs communicate the importance of enablers to various stakeholders, building consensus and securing necessary resources. They translate technical details into business-friendly language to foster understanding and support.
- Prioritization Framework: The PM often leads the development and application of a prioritization framework (e.g., MoSCoW method, RICE scoring, value vs. effort matrix) to objectively rank enablers based on their impact and feasibility.
The Engineering Lead's Role:
The engineering lead plays a crucial role in assessing the technical feasibility and impact of enablers:
- Technical Feasibility Analysis: Engineers assess the technical complexity, resource requirements, and potential risks associated with each enabler. They provide realistic timelines and estimates for implementation.
- Architectural Impact: Engineers evaluate the impact of enablers on the existing system architecture, identifying potential integration challenges and dependencies.
- Resource Allocation: Engineering leads help determine the resources (personnel, budget, tools) required for implementing each enabler. This information is crucial for effective resource allocation and project planning.
- Technology Stack Evaluation: The engineering lead can identify opportunities to upgrade or change the technology stack to improve efficiency, scalability, and maintainability, which are often considered as enablers.
The Design Lead's Role:
The design lead contributes to enabler prioritization by focusing on the user experience and workflow improvements:
- User Experience Impact: Designers assess how each enabler will impact the user experience, identifying opportunities to improve workflows, reduce friction, and enhance overall usability.
- Workflow Optimization: Designers can identify bottlenecks in the design and development process and suggest enablers that streamline workflows and improve collaboration.
- Tooling and Process Improvements: Designers evaluate the impact of new tools and processes on the design team's efficiency and output. They can suggest enablers that improve design handoff, collaboration, and feedback loops.
- Accessibility and Inclusivity: The design lead ensures that prioritized enablers contribute to a more accessible and inclusive product experience for all users.
Expanding the Circle: Collaboration Beyond the Core Team
While the core team lays the foundation for enabler prioritization, successful implementation necessitates collaboration with a wider range of roles:
1. Data Science and Analytics:
Data scientists and analysts provide valuable insights into user behavior, product performance, and areas for improvement. Their contribution to enabler prioritization includes:
- Identifying bottlenecks: Data analysis can highlight areas where processes or technology are hindering product development or user experience.
- Measuring the impact of enablers: Data can be used to track the effectiveness of implemented enablers and measure their impact on key metrics.
- Predictive modeling: Data-driven models can help forecast the potential impact of different enablers, informing prioritization decisions.
2. Operations and Infrastructure:
The operations and infrastructure teams are essential for implementing and maintaining the technical enablers:
- Resource availability: They assess the availability of resources (servers, networks, etc.) required for implementing enablers.
- Technical feasibility: They provide insights into the technical challenges and potential risks associated with implementing enablers.
- Maintenance and support: They provide ongoing support and maintenance for the implemented enablers, ensuring their continued effectiveness.
3. Security:
Security professionals are crucial for ensuring that enablers do not compromise the security of the product or user data:
- Security risk assessment: They evaluate the security implications of each enabler, identifying potential vulnerabilities and recommending mitigation strategies.
- Compliance requirements: They ensure that enablers comply with relevant security regulations and standards.
- Security testing: They conduct security testing to identify and address any security flaws in the implemented enablers.
4. Marketing and Sales:
Marketing and sales teams contribute to enabler prioritization by providing insights into market trends and customer needs:
- Market trends: They identify market trends and customer needs that could be addressed by implementing certain enablers.
- Sales process optimization: They can identify bottlenecks in the sales process that could be addressed by improving tools or processes.
- Customer feedback: They gather customer feedback and use it to inform the prioritization of enablers that improve the customer experience.
5. Legal and Compliance:
Legal and compliance teams ensure that the implemented enablers comply with all applicable laws and regulations:
- Legal and regulatory requirements: They assess the legal and regulatory implications of each enabler, ensuring compliance with all relevant laws and regulations.
- Data privacy: They ensure that enablers comply with data privacy regulations, protecting user data.
- Contractual obligations: They ensure that enablers comply with any contractual obligations.
6. Finance:
The finance team plays a critical role in allocating resources for enabler implementation:
- Budget allocation: They allocate budget for the implementation of prioritized enablers.
- Return on investment (ROI): They assess the potential ROI of different enablers, helping prioritize those with the highest potential return.
- Cost-benefit analysis: They conduct cost-benefit analyses to ensure that the cost of implementing enablers is justified by the benefits.
Prioritization Frameworks and Techniques
Effective enabler prioritization requires a structured approach. Several frameworks and techniques can be employed:
- MoSCoW Method: Categorizes enablers into Must have, Should have, Could have, and Won't have categories based on their importance and feasibility.
- RICE Scoring: Ranks enablers based on Reach, Impact, Confidence, and Effort.
- Value vs. Effort Matrix: Plots enablers on a graph based on their value and effort required for implementation, prioritizing those with high value and low effort.
- Weighted Scoring System: Assigns weights to different criteria (e.g., business value, technical feasibility, risk) and calculates a weighted score for each enabler.
Continuous Iteration and Feedback
Enabler prioritization is not a one-time event. It's an ongoing process that requires continuous iteration and feedback. Regularly reviewing and adjusting the prioritization based on new information, changing priorities, and feedback from stakeholders is crucial for maintaining alignment and achieving product goals.
Conclusion
Prioritizing enablers is a crucial aspect of successful product management. It necessitates collaboration across a broad range of roles, each contributing unique expertise and perspectives. By effectively engaging with these roles, employing appropriate prioritization frameworks, and fostering continuous feedback loops, product managers can ensure that the right enablers are prioritized, ultimately leading to faster product development, improved user experience, and enhanced business outcomes. This collaborative approach ensures that the foundation of successful product development is strong and resilient, supporting continuous growth and innovation. Remember, the goal is not just to prioritize enablers, but to leverage them to propel the product and the entire organization forward.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Medications Noted On The Discharge Summary Must Include
Apr 11, 2025
-
What Game Did Tarzan Like To Play Answers
Apr 11, 2025
-
What Was The Primary Motivation For Inventing The Quad Skate
Apr 11, 2025
-
What Fear Can Teach Us Commonlit Answers
Apr 11, 2025
-
What Is The Theme Of The Secret Garden
Apr 11, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Role Does Product Management Work With To Prioritize Enablers . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.