Which Sentence Uses Correct Parallel Structure
Onlines
Mar 04, 2025 · 5 min read
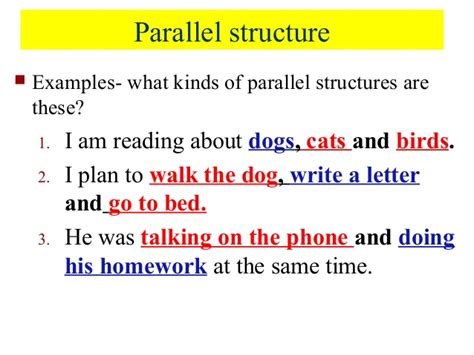
Table of Contents
Which Sentence Uses Correct Parallel Structure? Mastering Parallelism for Clear and Concise Writing
Parallel structure, also known as parallelism, is a powerful tool for creating clear, concise, and impactful writing. It involves using the same grammatical structure for similar items in a list, series, or comparison. Mastering parallel structure significantly enhances readability and strengthens the overall impact of your writing, making it more persuasive and easier to understand. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of parallel structure, providing you with the knowledge and examples to confidently identify and create grammatically correct parallel sentences.
Understanding Parallel Structure: The Basics
Parallelism is about balance and consistency. When elements within a sentence have a similar grammatical function (e.g., all are verbs, nouns, or adjectives), they should have a parallel grammatical form. This means they should follow the same pattern in terms of tense, voice, and parts of speech. Ignoring parallel structure often leads to awkward, confusing, and grammatically incorrect sentences.
Example of Correct Parallel Structure:
She enjoys swimming, hiking, and cycling.
In this sentence, all three elements ("swimming," "hiking," and "cycling") are gerunds (verbs acting as nouns). The parallel structure creates a smooth, easily understood flow.
Example of Incorrect Parallel Structure:
She enjoys swimming, to hike, and cycling.
Here, the parallelism is broken. "Swimming" and "cycling" are gerunds, but "to hike" is an infinitive. This inconsistency creates a jarring effect and detracts from the clarity of the sentence.
Common Types of Parallel Structure
Parallelism can be applied to various sentence structures:
1. Items in a Series or List
When listing items, ensure each item maintains the same grammatical form. This could involve a series of nouns, verbs, adjectives, or phrases.
Correct: He is intelligent, kind, and generous. (All adjectives)
Incorrect: He is intelligent, shows kindness, and generous. (Mix of adjective and verb phrase)
2. Correlative Conjunctions
Correlative conjunctions (e.g., both…and, either…or, neither…nor, not only…but also) require parallel structure in the phrases they connect.
Correct: She is both talented and dedicated.
Incorrect: She is both talented and shows dedication.
3. Comparisons Using than or as
When making comparisons using than or as, ensure the elements being compared have parallel structure.
Correct: He is taller than his brother is.
Incorrect: He is taller than his brother. (This is grammatically correct but can be improved for stronger parallelism.) A better version would be: He is taller than his brother is tall.
4. Compound Predicates
Compound predicates consist of two or more verbs sharing the same subject. These verbs must be parallel in form.
Correct: She sang and danced at the party.
Incorrect: She sang and was dancing at the party. (Mix of simple past and past continuous tenses)
Identifying and Correcting Parallelism Errors
To effectively identify and correct parallelism errors, follow these steps:
-
Identify the items that should be parallel: Look for lists, series, comparisons, or correlative conjunctions.
-
Determine the grammatical form of each item: Is it a noun, verb, adjective, adverb, phrase, or clause?
-
Ensure consistency: Check if all items have the same grammatical form and tense. If not, adjust the structure to achieve parallelism.
Advanced Parallelism Techniques and Nuances
While basic parallelism focuses on matching grammatical structures, achieving elegant parallelism often involves subtle considerations:
-
Balancing sentence length and complexity: Aim for a balance in the length and complexity of parallel elements. Avoid excessively long or complicated structures that disrupt the flow.
-
Maintaining consistent voice: When using verbs, maintain a consistent active or passive voice throughout the parallel structure.
-
Using parallel prepositional phrases: When using prepositional phrases in parallel, ensure the prepositions are the same and the objects of the prepositions are parallel.
-
Parallel clauses: Clauses (subject + verb) can also be parallel. Ensure each clause has a similar structure and grammatical function.
Examples of Correct and Incorrect Parallel Structure in Sentences
Let's analyze several sentences, highlighting the correct and incorrect use of parallel structure:
Correct:
- He likes to read, to write, and to travel. (All infinitives)
- She is intelligent, creative, and hardworking. (All adjectives)
- The dog ran quickly, jumped high, and barked loudly. (All verb phrases)
- Not only did he study hard, but he also sought help from his teachers. (Parallel clauses)
- The presentation was both informative and engaging. (Parallel adjectives)
Incorrect:
- He likes to read, writing, and to travel. (Mix of infinitive and gerund)
- She is intelligent, creative, and works hard. (Mix of adjective and verb phrase)
- The dog ran quickly, jumped high, and barking loudly. (Mix of verb phrase and participle)
- Not only did he study hard, but also sought help from his teachers. (Missing parallel verb phrase "he did")
- The presentation was informative and it was engaging. (Inconsistent structure)
The Importance of Parallelism in Effective Communication
Beyond the grammatical correctness, parallel structure significantly improves the clarity, readability, and impact of your writing. It aids comprehension by creating a rhythmic and predictable flow, enabling the reader to effortlessly follow the ideas being presented. Parallel structure makes your writing more persuasive by emphasizing the interconnectedness of your ideas, creating a more coherent and impactful message. It contributes significantly to the overall professional quality of your writing.
Practical Application: Improving Your Writing with Parallelism
Improving your writing through the application of parallel structure involves:
-
Careful review: Habitually review your writing for potential parallelism errors.
-
Active rewriting: Be prepared to rewrite sentences to achieve proper parallelism. Don't hesitate to adjust the phrasing to ensure grammatical consistency.
-
Seeking feedback: Ask others to review your work for parallelism issues. A fresh pair of eyes can often spot errors you may have missed.
Conclusion: Mastering Parallel Structure for Enhanced Writing
Mastering parallel structure is an essential skill for any writer seeking to produce clear, concise, and impactful communication. By understanding the principles of parallelism and practicing their application, you can significantly enhance the quality and effectiveness of your written work. Consistent use of parallelism transforms your writing from merely grammatically correct to elegant and persuasive, making your message stand out and resonate with your readers. Regular practice and conscious attention to parallel structure will elevate your writing to a new level of clarity and sophistication. Through diligent effort and mindful application, you can transform your writing style and cultivate a more polished, professional voice.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Take A Break By Nicole Peluse
Mar 04, 2025
-
Julia Is An Engineer For A Cleared Defense Contractor
Mar 04, 2025
-
Educators Can Find Out More About Age Appropriate Dietary Guidelines Via
Mar 04, 2025
-
Rn 3 0 Clinical Judgment Practice 3
Mar 04, 2025
-
Lesson 3 4 Solving Complex 1 Variable Equations Answer Key
Mar 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Sentence Uses Correct Parallel Structure . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
