Which Solutions Showed The Greatest Change In Ph Why
Onlines
Mar 15, 2025 · 6 min read
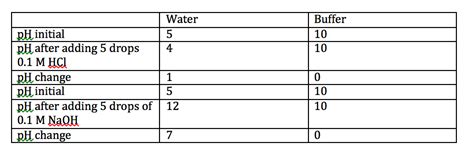
Table of Contents
Which Solutions Showed the Greatest Change in pH? Why?
Understanding pH changes is crucial in numerous fields, from chemistry and biology to environmental science and medicine. A solution's pH, representing its acidity or alkalinity, is a logarithmic measure of the hydrogen ion concentration. Significant pH shifts indicate substantial chemical reactions or alterations in the solution's composition. This article will delve into various scenarios where solutions exhibit dramatic pH changes, exploring the underlying chemical principles and practical implications.
Strong Acids and Strong Bases: The Most Dramatic pH Shifts
The most pronounced pH changes occur when strong acids or strong bases are added to water or solutions with initially neutral or near-neutral pH. Strong acids, like hydrochloric acid (HCl) and sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄), completely dissociate in water, releasing a high concentration of hydrogen ions (H⁺). This drastically lowers the pH. Conversely, strong bases, such as sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and potassium hydroxide (KOH), completely dissociate, releasing a high concentration of hydroxide ions (OH⁻), which significantly raises the pH.
Why the dramatic change? The logarithmic nature of the pH scale amplifies the impact of even small changes in H⁺ concentration. A one-unit decrease in pH represents a tenfold increase in H⁺ concentration. Adding a strong acid or base directly alters this concentration, resulting in a substantial pH shift. The complete dissociation is key; a weak acid or base would not produce the same drastic effect.
Example: Consider adding 1 mole of HCl to 1 liter of pure water. The pH of pure water is 7. HCl completely dissociates, yielding 1 mole of H⁺ ions. The resulting pH will be approximately 0, a massive change of 7 pH units. Similarly, adding 1 mole of NaOH to 1 liter of water would raise the pH to approximately 14.
Buffer Solutions: Resisting pH Changes
While strong acids and bases cause dramatic pH changes, buffer solutions exhibit remarkable resistance to these shifts. Buffer solutions contain a weak acid and its conjugate base (or a weak base and its conjugate acid) in roughly equal concentrations. When a small amount of strong acid or base is added, the buffer components react to neutralize the added ions, minimizing the change in pH.
Why the resistance? The weak acid or base in the buffer reacts with the added strong acid or base, forming its conjugate base or acid. This reaction consumes the added H⁺ or OH⁻ ions, preventing a large change in the overall H⁺ concentration and thus the pH. This buffering capacity is most effective when the pH is close to the pKa (acid dissociation constant) of the weak acid in the buffer.
Acid-Base Reactions: Neutralization and pH Shifts
Acid-base reactions, where an acid and a base react to form salt and water, can lead to significant pH changes, especially when strong acids and strong bases are involved. The neutralization reaction consumes H⁺ and OH⁻ ions, leading to a shift towards a more neutral pH (closer to 7).
Why the change? The reaction between H⁺ and OH⁻ ions effectively reduces the concentration of both, resulting in a less extreme pH. The extent of the pH change depends on the strengths and concentrations of the acid and base involved. A reaction between a strong acid and a strong base will result in a more dramatic shift towards neutrality compared to a reaction involving weak acids or bases.
Precipitation Reactions: Indirect pH Influence
Precipitation reactions, while not directly affecting H⁺ or OH⁻ concentrations, can indirectly impact pH. If a reaction produces a salt that undergoes hydrolysis (reacts with water to produce H⁺ or OH⁻ ions), the pH of the solution can change.
Why the indirect influence? The hydrolysis of certain salts can increase or decrease the H⁺ or OH⁻ concentration, thereby altering the pH. For instance, the hydrolysis of a salt formed from a weak acid and a strong base will produce a basic solution, raising the pH. Conversely, the hydrolysis of a salt formed from a strong acid and a weak base will produce an acidic solution, lowering the pH.
Dilution Effects: Gradual pH Changes
Diluting an acidic or basic solution with water can gradually change its pH. The dilution reduces the concentration of H⁺ or OH⁻ ions, leading to a less extreme pH.
Why the gradual change? Dilution spreads the existing H⁺ or OH⁻ ions over a larger volume, lowering their concentration. The logarithmic nature of the pH scale means that even a significant dilution might only result in a moderate pH change. This effect is less dramatic than adding a strong acid or base, but it's still a notable factor in many chemical processes.
Enzymatic Reactions: pH-Dependent Activity
Many biological systems rely on enzymatic reactions, and enzyme activity is highly pH-dependent. Changes in pH can drastically alter enzyme function, leading to significant changes in the rates of biological reactions.
Why the pH dependence? Enzyme structures, particularly the active sites where reactions occur, are sensitive to pH changes. Alterations in pH can affect the ionization state of amino acid residues in the enzyme, leading to conformational changes that either activate or inhibit the enzyme's catalytic activity. This can lead to dramatic changes in product formation and other biological processes.
Environmental Factors: Rain, Soil, and Aquatic Systems
pH changes significantly impact environmental systems. Acid rain, caused by atmospheric pollutants, drastically lowers the pH of lakes, rivers, and soil, affecting aquatic life and plant growth. Similarly, industrial discharges can cause significant shifts in pH, leading to environmental damage.
Why the environmental impact? Many organisms have narrow pH tolerances; significant deviations can be detrimental or lethal. Changes in pH can alter the solubility of various minerals and nutrients in soil and water, affecting plant and animal nutrition. The altered pH can also disrupt the delicate balance of various ecological processes.
Industrial Applications: pH Control and Monitoring
Many industrial processes require precise pH control. The manufacturing of pharmaceuticals, food processing, and wastewater treatment all involve meticulous monitoring and adjustment of pH to ensure optimal product quality, safety, and environmental compliance.
Why the need for control? In many industries, even small pH fluctuations can have significant consequences. For instance, changes in pH can affect reaction rates, product stability, or the effectiveness of treatment processes. Sophisticated pH monitoring and control systems are used to maintain desired pH levels.
Conclusion: Understanding the Nuances of pH Change
The magnitude of pH changes depends on numerous factors, including the strength and concentration of acids and bases, the presence of buffer solutions, the occurrence of chemical reactions, and dilution effects. Understanding the underlying chemical principles governing these changes is crucial in various scientific, environmental, and industrial applications. Whether it's the dramatic shifts caused by strong acids and bases, the subtle changes in buffer solutions, or the indirect influence of precipitation reactions, the consequences of pH fluctuations are far-reaching and underscore the importance of accurate pH measurement and control. Continuous research and technological advancements in pH measurement and control will continue to refine our understanding and ability to manage these crucial changes across diverse fields.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Drag The Historical Style Periods To The Corresponding Musical Examples
Mar 15, 2025
-
Joe Turners Come And Gone Summary
Mar 15, 2025
-
7 05 Unit Test The United States And Globalization
Mar 15, 2025
-
John And Mary Hazlitt Left The Airport Taxi
Mar 15, 2025
-
Calculating Specific Heat Extra Practice Worksheet
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Solutions Showed The Greatest Change In Ph Why . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
