Which Statement About Longitude And Latitude Is True
Onlines
Mar 17, 2025 · 6 min read
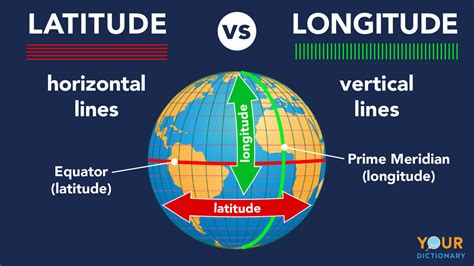
Table of Contents
Which Statement About Longitude and Latitude is True? A Deep Dive into Geographic Coordinates
Understanding longitude and latitude is fundamental to geography, navigation, and numerous applications using location-based services. While the basic concepts seem straightforward – lines that crisscross the globe – the intricacies of these coordinate systems often lead to confusion. This comprehensive guide will clarify common misconceptions and definitively answer the question: which statement about longitude and latitude is true? We'll delve into the precise definitions, explore their interrelationships, and examine various applications to solidify your understanding.
Defining Longitude and Latitude: The Foundation of Geographic Coordinates
Before we tackle true/false statements, let's establish a solid base.
Latitude: Measuring North and South
Latitude refers to the angular distance of a point north or south of the Earth's equator. It's measured in degrees (°), minutes ('), and seconds ("), ranging from 0° at the equator to 90° at the North and South Poles. Lines of constant latitude are called parallels, as they run parallel to each other and to the equator. The equator itself is the only great circle among the parallels. All other parallels are smaller circles, gradually diminishing in circumference as one approaches the poles.
- Key characteristics of latitude:
- Ranges from 0° (equator) to 90° (North or South Pole)
- Parallels are parallel to the equator
- All points on a parallel share the same latitude
- Crucial for determining climate zones and solar radiation
Longitude: Measuring East and West
Longitude, on the other hand, measures the angular distance of a point east or west of the Prime Meridian. The Prime Meridian, by international agreement, passes through the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, England. Lines of constant longitude are called meridians, which all converge at the North and South Poles. Unlike parallels, all meridians are great circles.
- Key characteristics of longitude:
- Ranges from 0° (Prime Meridian) to 180° (International Date Line) east or west
- Meridians converge at the poles
- All points on a meridian share the same longitude
- Essential for determining time zones and global positioning
Common Misconceptions and True Statements
Now, let's address some common misconceptions and identify accurate statements regarding longitude and latitude:
Statement 1: All meridians are of equal length, while parallels vary in length.
TRUE. This statement accurately reflects the fundamental geometric differences between meridians and parallels. Meridians are great circles, all passing through the North and South Poles and thus having equal length. Parallels, however, are smaller circles (except for the equator) and decrease in length as they approach the poles. This difference significantly influences map projections and distance calculations.
Statement 2: Latitude lines run east-west, and longitude lines run north-south.
TRUE. This is a straightforward and accurate description of the orientation of latitude and longitude lines on a map or globe. Latitude lines (parallels) circle the Earth parallel to the equator, while longitude lines (meridians) run from the North Pole to the South Pole.
Statement 3: The equator is a line of latitude, and the Prime Meridian is a line of longitude.
TRUE. The equator, at 0° latitude, serves as the fundamental reference line for measuring latitude. Similarly, the Prime Meridian, at 0° longitude, acts as the fundamental reference line for measuring longitude. Both are essential components of the global coordinate system.
Statement 4: Longitude determines time zones, and latitude influences climate.
TRUE. The Earth rotates 360° in approximately 24 hours, leading to a roughly 15° shift per hour. Longitude is therefore crucial in determining time zones, with each zone typically spanning approximately 15° of longitude. Latitude, on the other hand, significantly impacts climate. Locations closer to the equator receive more direct sunlight and thus experience warmer temperatures than those at higher latitudes.
Statement 5: Two points with the same latitude but different longitudes will always lie on the same parallel.
TRUE. This highlights the nature of parallels. Points sharing the same latitude are located on the same parallel, regardless of their longitude. This allows for easy identification and grouping of locations at the same north-south distance from the equator.
Statement 6: All points on the Earth can be uniquely identified by a single pair of latitude and longitude coordinates.
TRUE. This is the fundamental principle underlying the geographic coordinate system. Each point on the Earth’s surface can be pinpointed by a unique latitude and longitude pair, providing a precise location reference. This makes it a cornerstone for navigation, mapping, and countless other applications.
Statement 7: The International Date Line generally follows the 180th meridian.
TRUE. The International Date Line, marking the transition between calendar days, largely follows the 180th meridian. However, deviations exist to accommodate political boundaries and island groups. This line isn't a strictly geometric line but rather a political and practical demarcation.
Statement 8: Longitude is measured from 0° to 360°, while latitude is measured from -90° to +90°.
FALSE. This statement is incorrect. Longitude is measured from 0° to 180° east and 0° to 180° west, while latitude is measured from 0° (equator) to 90° North and 0° to 90° South. The use of positive and negative signs for latitude and longitude is common in some coordinate systems but isn't fundamental to the basic definition.
Statement 9: A change in latitude results in a change in both distance and direction from a reference point, whereas a change in longitude only affects the distance.
FALSE. A change in latitude directly impacts both distance and direction from a reference point, as it signifies movement north or south. A change in longitude affects distance and also direction; a change in longitude at higher latitudes results in a smaller distance change compared to the same longitudinal change at lower latitudes.
Statement 10: The shortest distance between two points on the Earth's surface is always along a line of constant latitude or longitude.
FALSE. The shortest distance between two points on the Earth’s surface is along a great-circle route. Great circles are circles whose centers coincide with the Earth's center, and a great-circle route is the portion of a great circle lying between two points. While meridians are great circles, parallels (except for the equator) are not. Therefore, shortest distance calculations often involve complex geodesy.
Applications of Longitude and Latitude
The applications of longitude and latitude are vast and impactful across numerous fields:
- Navigation: Essential for ships, aircraft, and even land vehicles using GPS.
- Mapping: Forms the basis of all map projections and coordinate systems.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): Used extensively for spatial data analysis and management.
- Remote Sensing: Critical for georeferencing satellite imagery and other remote sensing data.
- Weather Forecasting: Precise location information is vital for weather observations and predictions.
- Astronomy: Used to locate celestial objects and track their movements.
- Telecommunications: Crucial for locating and connecting communication devices.
Conclusion: Mastering Geographic Coordinates
Understanding the intricacies of longitude and latitude is crucial for anyone working with location-based data or navigating the world. By clarifying the key definitions and dispelling common misconceptions, this guide aims to provide a solid foundation for grasping these fundamental geographic concepts. Remember, the accurate measurement and use of longitude and latitude are paramount for precision in numerous applications, from navigation to advanced spatial analysis. This deep dive should leave you confidently equipped to tackle any statement regarding longitude and latitude with precision and accuracy.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Christian High School Equivalency Exam Answers
Mar 17, 2025
-
Introduction To Health Assessment 3 0 Test
Mar 17, 2025
-
Lord Of The Flies Student Workbook Answers Pdf
Mar 17, 2025
-
In Time Of The Butterflies Quotes
Mar 17, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Not Part Of Feminist Psychology
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Statement About Longitude And Latitude Is True . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
