Which Statement About This Figure Is True
Onlines
Mar 25, 2025 · 5 min read
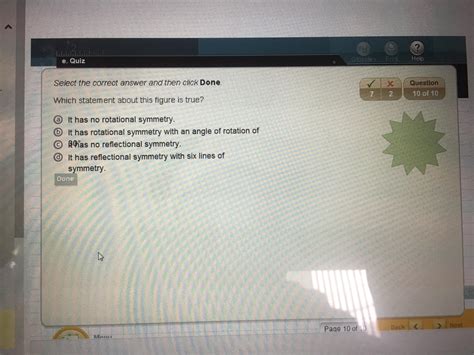
Table of Contents
Decoding Visual Data: Determining the Truth Behind a Figure
Analyzing figures, charts, and graphs is a crucial skill in many fields, from academic research to business analysis. Understanding how to interpret visual data effectively allows us to draw meaningful conclusions and make informed decisions. However, the process isn't always straightforward. Often, multiple statements might seem plausible when analyzing a single figure, making it crucial to identify the truly accurate statements. This article explores various techniques and considerations for determining which statement about a specific figure holds true, focusing on the critical thinking and analytical skills necessary for effective data interpretation.
The Importance of Context:
Before diving into the analysis of any figure, understanding the context is paramount. This includes:
-
The Source: Who created the figure, and what is their potential bias? Understanding the source can help identify potential motivations behind the data presentation. A figure from a company's marketing materials might emphasize positive trends, while a figure from an independent research group may offer a more objective perspective.
-
The Data: What type of data is being presented? Is it categorical, numerical, or a combination? Knowing the data type will inform the appropriate analytical methods and interpretations. For example, a bar chart represents categorical data, while a scatter plot shows the relationship between two numerical variables.
-
The Axes and Labels: Clearly understanding the axes and their labels (including units) is fundamental. Incorrect labeling or scaling can significantly distort the interpretation of the figure.
-
The Legend: If the figure contains multiple data series or categories, the legend is critical for distinguishing between them.
-
The Overall Message: What is the figure trying to communicate? Understanding the intended message can help guide the analysis and identify potential misleading elements.
Types of Figures and Analysis Techniques:
Different types of figures require different analytical approaches. Let's consider some common examples:
1. Bar Charts:
Bar charts are used to compare different categories of data. When analyzing a bar chart, consider:
-
The Height of the Bars: The height directly represents the magnitude of the data for each category. Direct comparisons between bars are straightforward.
-
The Relative Differences: Focus on the relative differences between bars, not just their absolute values. A small difference between two large bars might be less significant than a larger difference between two small bars.
-
Potential Outliers: Are there any bars that significantly deviate from the others? Outliers can indicate unusual data points that might warrant further investigation.
2. Line Graphs:
Line graphs showcase trends and changes over time or across a continuous variable. Key aspects to consider:
-
The Slope of the Line: A steep positive slope indicates a rapid increase, while a shallow positive slope suggests a slower increase. Similarly, negative slopes represent decreases.
-
Turning Points: Points where the slope changes direction (from positive to negative or vice-versa) are significant as they indicate shifts in trends.
-
Extrapolation: Avoid extrapolating beyond the range of the data. Predictions based on extending the line beyond the observed data points are often unreliable.
3. Scatter Plots:
Scatter plots illustrate the relationship between two numerical variables. Analysis focuses on:
-
Correlation: Does a clear relationship exist between the two variables? Is the relationship positive (as one variable increases, the other increases), negative (as one variable increases, the other decreases), or nonexistent?
-
Clustering: Are the data points clustered in specific regions of the plot? Clusters can suggest underlying subgroups or patterns.
-
Outliers: Are there any data points that lie far from the general trend? Outliers can significantly influence the interpretation of the correlation.
4. Pie Charts:
Pie charts represent proportions of a whole. Pay close attention to:
-
Segment Sizes: The size of each segment directly reflects its proportion of the whole.
-
Labels and Percentages: Ensure accurate labeling and percentage calculations to avoid misinterpretations.
-
Clarity: Too many segments can make a pie chart difficult to interpret.
Identifying True Statements: A Step-by-Step Approach:
To determine which statement about a figure is true, follow these steps:
-
Understand the Figure: Carefully examine all aspects of the figure, including the title, axes, labels, legend, and data points.
-
Analyze the Data: Apply the appropriate analytical techniques based on the type of figure. Identify key trends, patterns, and outliers.
-
Evaluate Each Statement: Carefully consider each statement in relation to the data in the figure. Does the statement accurately reflect the trends and patterns observed?
-
Verify with Calculations: If necessary, perform calculations to verify the accuracy of the statements. For example, you might need to calculate percentages, averages, or slopes.
-
Consider Potential Biases: Be aware of potential biases in the data presentation. Does the figure accurately represent the data, or are there elements that might mislead the viewer?
-
Eliminate False Statements: Systematically eliminate statements that are not supported by the data or that contain logical fallacies.
-
Identify the True Statement(s): The remaining statement(s) should be those that accurately reflect the information presented in the figure.
Example Scenario:
Imagine a bar chart showing the sales of four different products (A, B, C, and D) over a year. Consider the following statements:
- Statement 1: Product A had the highest sales throughout the year.
- Statement 2: Product B's sales increased steadily throughout the year.
- Statement 3: Product C had lower sales than Product D in the first quarter, but higher sales in the last quarter.
- Statement 4: The total sales of all products increased by 15% over the year.
To determine which statement is true, you would analyze the bar chart's data for each product across each quarter. You'd compare the heights of the bars representing sales for each product and check if the statements align with those observations. You would also calculate the total sales for each quarter and the year-over-year increase to verify Statement 4.
Conclusion:
Determining which statement about a figure is true requires careful observation, critical thinking, and a thorough understanding of data analysis techniques. By following the steps outlined above and applying appropriate analytical methods, you can effectively interpret visual data and draw accurate conclusions. Remember that context is crucial, and always be wary of potential biases. With practice, you will become proficient in deciphering the truth hidden within figures, enabling you to make well-informed decisions based on reliable data analysis.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Guest Enjoying A Few Cocktails
Mar 25, 2025
-
Select All The Descriptions That Apply To The Rondo Form
Mar 25, 2025
-
Exploring Anatomy And Physiology In The Laboratory 4th Edition
Mar 25, 2025
-
Hannah Arendt The Human Condition Summary
Mar 25, 2025
-
Why Does Macbeth Want Banquo And Fleance Dead
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Statement About This Figure Is True . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
