Which Statement Best Compares The Laws Of Supply And Demand
Onlines
Mar 25, 2025 · 6 min read
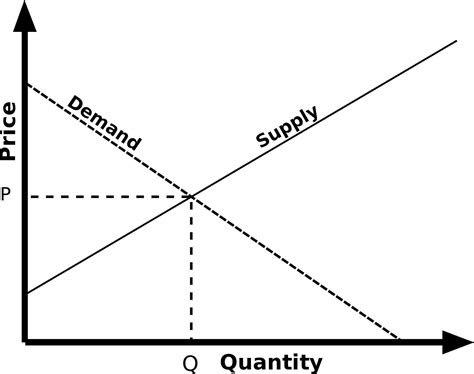
Table of Contents
Which Statement Best Compares the Laws of Supply and Demand? Understanding the Interplay of Market Forces
The laws of supply and demand are fundamental concepts in economics that explain how the price of a good or service is determined in a free market. While often presented separately, they are inextricably linked, working in tandem to create a dynamic equilibrium. Understanding their interplay is crucial for grasping market behavior, predicting price fluctuations, and making informed economic decisions. This article will delve deep into the individual laws, comparing and contrasting them to arrive at the statement that best encapsulates their relationship.
The Law of Supply: More for More
The law of supply states that, all other factors being equal, as the price of a good or service increases, the quantity supplied will also increase. Producers are motivated by profit; a higher price means greater potential profit, incentivizing them to produce and offer more of the product. Conversely, a lower price diminishes profit margins, leading to a decrease in the quantity supplied.
Key Factors Influencing Supply:
-
Price of Inputs: The cost of raw materials, labor, and other resources directly impacts the profitability of production. Rising input costs can shift the supply curve to the left (decrease in supply), even if the market price remains constant.
-
Technology: Technological advancements can significantly improve production efficiency, lowering costs and increasing the quantity supplied at any given price. This shifts the supply curve to the right (increase in supply).
-
Government Regulations: Taxes, subsidies, and licensing requirements can influence the cost and ease of production, affecting the overall supply. For example, a tax on production will shift the supply curve to the left.
-
Producer Expectations: Anticipated future price changes can influence current supply decisions. If producers expect prices to rise, they might withhold supply to sell at a higher price later, decreasing current supply.
-
Number of Sellers: A greater number of producers in the market will generally lead to a higher quantity supplied at each price level, shifting the supply curve to the right.
The Law of Demand: Less for More
The law of demand dictates that, all other factors being equal, as the price of a good or service increases, the quantity demanded will decrease. Consumers, facing higher prices, will tend to reduce their consumption, seeking substitutes or forgoing the purchase altogether. Conversely, a lower price makes the good or service more affordable and attractive, leading to an increase in the quantity demanded.
Key Factors Influencing Demand:
-
Consumer Income: A rise in disposable income generally leads to increased demand for normal goods, while demand for inferior goods may decrease.
-
Consumer Tastes and Preferences: Changes in fashion, trends, and consumer preferences can drastically alter demand. A product that becomes trendy will see a surge in demand, irrespective of price changes within a certain range.
-
Prices of Related Goods: The demand for a product can be affected by the prices of complements (goods used together) and substitutes (goods that can be used in place of each other). For example, an increase in the price of coffee might decrease the demand for coffee creamer (complement).
-
Consumer Expectations: Similar to producers, consumer expectations about future price changes can impact current demand. Anticipation of a price increase might lead to increased current demand.
-
Number of Buyers: A larger market with more consumers will naturally lead to higher overall demand at any given price.
Comparing and Contrasting Supply and Demand: A Tale of Two Forces
While seemingly opposite, the laws of supply and demand are inherently intertwined. They interact to determine the market equilibrium price – the point where the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded. This equilibrium is a constantly shifting balance, reacting to changes in the factors influencing both supply and demand.
Similarities:
-
Both are based on the principle of "ceteris paribus": Both laws assume that all other factors remain constant when analyzing the relationship between price and quantity. This simplification allows for a clearer understanding of the core relationship.
-
Both are fundamental to price determination: The interplay of supply and demand ultimately decides the market price of a good or service.
-
Both are influenced by numerous factors: While price is the primary driver, a multitude of external factors can shift the supply and demand curves, impacting the equilibrium price and quantity.
Differences:
-
Perspective: The law of supply focuses on the producer's perspective (how much they are willing to supply at different prices), while the law of demand focuses on the consumer's perspective (how much they are willing to buy at different prices).
-
Direction of Relationship: Supply has a positive relationship with price (higher price, higher quantity), while demand has a negative relationship (higher price, lower quantity).
-
Curve Shape: The supply curve typically slopes upwards, while the demand curve slopes downwards.
The Statement that Best Compares the Laws of Supply and Demand
Several statements could attempt to compare these laws, but the most accurate and comprehensive captures their dynamic interaction and inherent interdependence. The best statement would be something like this:
"The laws of supply and demand are inversely related forces that interact to determine the market equilibrium price and quantity. Supply, driven by producer profitability, shows a positive relationship with price, while demand, reflecting consumer affordability and preference, shows a negative relationship. The intersection of the supply and demand curves represents the market equilibrium, a constantly shifting balance that reflects the interplay of these fundamental economic forces."
This statement accurately reflects the core concepts:
- Inverse relationship: It explicitly points out the inverse relationship between the two forces.
- Market equilibrium: It highlights the crucial role of both laws in determining market equilibrium.
- Producer and consumer perspectives: It incorporates the different perspectives of producers and consumers.
- Dynamic nature: It emphasizes the dynamic and ever-changing nature of market equilibrium.
Beyond the Basics: Understanding Market Shifts
Analyzing market equilibrium only scratches the surface of understanding the interplay of supply and demand. Significant shifts in either supply or demand can lead to substantial changes in the market price and quantity.
For instance, a sudden increase in demand (perhaps due to a new trend or positive media attention) can drive up prices if supply remains relatively constant. Conversely, an unexpected surge in supply (like a bumper crop) can lead to lower prices if demand doesn't correspondingly increase. Analyzing these shifts requires a deeper understanding of the factors influencing both supply and demand, allowing for more accurate predictions and informed decision-making.
Understanding how the factors listed above interact allows for more nuanced economic predictions. For example, a technological advancement reducing production costs (increasing supply) coupled with a rise in consumer income (increasing demand) would lead to a complex interplay of forces, resulting in an uncertain change to the market equilibrium price. The magnitude of the shifts in supply and demand would determine the ultimate outcome.
Conclusion: Mastering the Market Mechanism
The laws of supply and demand are not merely abstract economic theories; they are the bedrock of market dynamics. They are the invisible hand guiding prices and resource allocation in free markets. By understanding their interplay – the inverse relationship, the concept of market equilibrium, and the myriad factors influencing each – we gain a powerful tool for understanding how markets function, predicting price fluctuations, and making sound economic decisions. The best statement comparing these laws is one that encapsulates this dynamic interplay and highlights their crucial role in shaping market outcomes. The more we understand this dynamic interaction, the better equipped we are to navigate the complexities of the modern economy.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Match Each Intelligence Product Category To Its Brief Description
Mar 29, 2025
-
Summary Of Chapter 15 Of The Giver
Mar 29, 2025
-
Letrs Unit 1 Bridge To Practice Answers
Mar 29, 2025
-
Identify All The Cavities For Each Organ As Follows
Mar 29, 2025
-
Core Curriculum Introductory Craft Skills Trade Terms Quiz Answer Key
Mar 29, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Statement Best Compares The Laws Of Supply And Demand . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
