Within Mindbridge What Is A Control Point
Onlines
Mar 24, 2025 · 6 min read
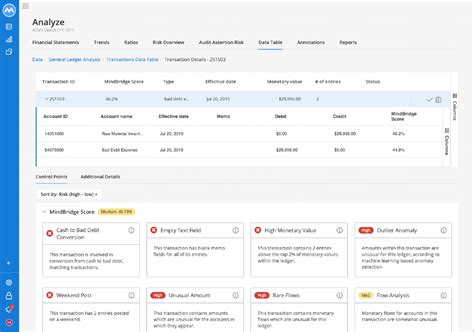
Table of Contents
Within MindBridge: What is a Control Point?
MindBridge Ai is a powerful audit automation tool leveraging artificial intelligence to detect anomalies and potential risks within financial datasets. A key component of its functionality is the concept of control points. Understanding control points is crucial to effectively utilizing MindBridge and interpreting its findings. This article dives deep into the meaning, function, and importance of control points within the MindBridge platform.
Understanding Control Points: The Foundation of MindBridge's Analysis
At its core, a control point in MindBridge represents a specific point in a transaction or a set of transactions where a company's internal controls should ideally intervene and prevent errors or fraudulent activities. These aren't manually defined by the user; instead, MindBridge's AI engine identifies them based on its analysis of the financial data and its understanding of common accounting principles and best practices. Think of them as potential red flags that the system highlights for further investigation.
How MindBridge Identifies Control Points
MindBridge's sophisticated algorithms analyze vast amounts of transactional data, identifying patterns and relationships. It doesn't just look at individual transactions; it considers the context, comparing transactions to historical data, industry benchmarks, and predefined risk models. The AI identifies potential control failures by recognizing discrepancies or irregularities that deviate from established norms. These deviations are then flagged as control points.
Key factors contributing to MindBridge's identification of control points include:
- Unusual transaction patterns: Sudden spikes in spending, unusual volumes, or transactions outside of normal business hours.
- Unusual relationships between accounts: Unexpected connections between different accounts or unexpected activity involving specific accounts known to be high-risk.
- Deviation from historical trends: Transactions that significantly deviate from established patterns observed in previous periods.
- Missing or incomplete data: The absence of crucial information that would normally be expected in a legitimate transaction.
- Inconsistent data: Contradictory information within or across different datasets.
Examples of Control Points
The types of control points identified can vary significantly based on the nature of the data and the industry. Here are some illustrative examples:
- A large, unusual journal entry: A significant journal entry without sufficient supporting documentation or justification could be flagged as a control point, potentially indicating manipulation or fraud.
- Multiple transactions with the same vendor on the same day: While not inherently suspicious, a high volume of transactions with one vendor in a short timeframe might warrant further review, especially if the vendor is newly added or lacks a strong historical relationship.
- Transactions exceeding established thresholds: If a transaction exceeds a pre-defined limit (e.g., exceeding a specified purchase order amount), MindBridge might flag it as a control point.
- Transactions processed outside of normal business hours: Transactions processed outside standard business operating hours could indicate unauthorized access or fraudulent activity.
- Discrepancies between invoices and payment records: A mismatch between an invoice amount and the actual payment could suggest potential errors or even fraudulent activities.
- Transactions with unusual account coding: Incorrect or inconsistent account coding can indicate a lack of proper internal controls and potentially signal fraudulent behavior.
Interpreting Control Points: Understanding the Risk Level
MindBridge doesn't simply flag control points; it also assigns a risk level to each one. This risk level is based on a combination of factors, including:
- The magnitude of the anomaly: Larger discrepancies or deviations generally receive higher risk scores.
- The frequency of similar anomalies: Repeated occurrences of a similar type of anomaly increase the risk level.
- The complexity of the transaction: Complex transactions with many unusual aspects might be deemed riskier.
- The historical context: The absence of similar transactions in the past might signal an increased risk.
- The risk profile of the related accounts or individuals: Transactions involving accounts or individuals known to be high-risk will typically receive higher risk scores.
This risk scoring system helps auditors prioritize their investigations, focusing on the most potentially problematic areas first. Control points with high-risk scores warrant immediate attention, whereas those with low scores may require less urgent review.
The Role of Control Points in the Audit Process
Control points are not just flags; they're integral components of a streamlined, efficient audit process. They allow auditors to:
- Focus on high-risk areas: Instead of manually reviewing every transaction, auditors can concentrate their efforts on the areas identified by MindBridge as potentially problematic.
- Increase audit efficiency: Automation reduces the time spent on manual data analysis, enabling auditors to complete audits faster and more cost-effectively.
- Reduce audit risk: By identifying potential errors and fraudulent activities early, MindBridge helps mitigate risks associated with incomplete or inaccurate financial reporting.
- Enhance audit quality: The objective analysis provided by MindBridge improves the quality and reliability of audit findings.
- Improve internal controls: Identifying weaknesses in internal controls through control point analysis helps organizations strengthen their financial processes and reduce future risks.
Beyond Identification: Actionable Insights from Control Points
The value of MindBridge extends beyond simple control point identification. The platform provides context and supporting information for each flagged item. This supporting data includes:
- Detailed transaction information: This includes dates, amounts, accounts involved, and any associated notes.
- Visualizations: Graphs and charts that help visualize the anomalies and trends.
- Comparative analysis: Comparisons to historical data and industry benchmarks.
- Auditing trail: A complete record of the AI's analysis process.
This rich context allows auditors to quickly understand the nature of the identified issue and to formulate appropriate follow-up actions. This actionable intelligence empowers auditors to efficiently investigate and address any potential risks.
Working Effectively with MindBridge Control Points
To fully leverage the potential of MindBridge and its control point analysis, auditors should follow these best practices:
- Understand the context: Don't simply react to the alert; understand the underlying reasons and the potential implications.
- Prioritize investigations: Focus on high-risk control points first.
- Validate findings: Don't blindly trust the AI; always verify the findings through independent investigation.
- Document findings: Maintain detailed records of all investigations and conclusions.
- Use the platform's features: Utilize all of MindBridge's analytical and visualization tools to gain a comprehensive understanding of the data.
- Stay updated: Keep abreast of any updates and improvements to the MindBridge platform and its functionalities.
Conclusion: Control Points as a Catalyst for Efficient and Effective Audits
Control points, as identified by MindBridge, represent a significant advancement in audit methodologies. They provide a powerful tool for auditors to streamline their processes, focus on high-risk areas, and improve the overall quality and efficiency of their work. By understanding the principles behind control point identification and effectively interpreting the results, auditors can leverage MindBridge to enhance their audits and contribute to stronger financial reporting practices. The platform's ability to identify potentially problematic areas proactively allows organizations to mitigate risks and maintain robust financial integrity. The future of auditing is undoubtedly intertwined with the intelligent automation provided by platforms like MindBridge, and the concept of control points remains central to its effectiveness.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Rn Managing Client Care Assessment 2 0
Mar 26, 2025
-
From Ants To Grizzlies Worksheet Answers
Mar 26, 2025
-
Important Rbs Policies Should Be Reinforced Through Trainings And Meetings
Mar 26, 2025
-
If You Drive A Toyota You Are
Mar 26, 2025
-
Decision Making And Problem Solving Edapt
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Within Mindbridge What Is A Control Point . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
