Within The Context Of Christianity Faith And Belief Involve
Onlines
Mar 30, 2025 · 8 min read
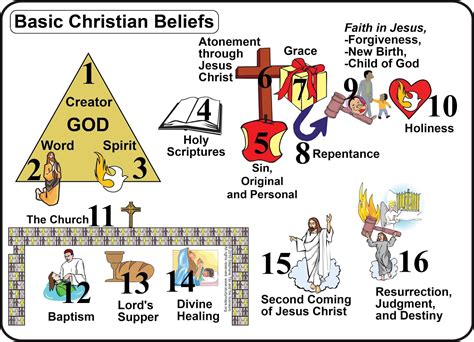
Table of Contents
Delving Deep: Exploring the Core of Christian Faith and Belief
Christianity, one of the world's largest religions, boasts a rich tapestry of beliefs, practices, and traditions spanning two millennia. Understanding its core tenets requires exploring its foundational texts, historical context, and diverse interpretations. This comprehensive exploration delves into the central pillars of Christian faith and belief, examining key concepts and their significance for believers.
The Holy Trinity: One God in Three Persons
A cornerstone of Christian doctrine is the belief in the Holy Trinity – God existing as three co-equal, co-eternal persons: the Father, the Son (Jesus Christ), and the Holy Spirit. This complex concept is often challenging to grasp, yet it's fundamental to Christian understanding of God. The Trinity isn't three separate gods but rather one unified God manifested in three distinct yet interconnected persons.
- The Father: Represented as the creator of the universe and the source of all things. He's the ultimate authority and the embodiment of divine power.
- The Son (Jesus Christ): The incarnate God, believed to be fully God and fully human. His life, death, and resurrection are central to Christian salvation. He is seen as the mediator between God and humanity.
- The Holy Spirit: The active presence of God in the world, empowering believers and guiding the church. The Spirit is often described as the comforter, the advocate, and the sanctifier.
Understanding the Trinity requires grappling with the mystery of God's nature, acknowledging that some aspects remain beyond human comprehension. However, the concept underlines God's unity and multifaceted nature, demonstrating his love, power, and grace simultaneously. Various theological perspectives exist on interpreting the Trinity, yet the core belief in one God in three persons remains a unifying theme.
The Bible: The Inspired Word of God
The Bible, comprising the Old and New Testaments, serves as the ultimate authority for Christian belief and practice. Christians believe it to be divinely inspired, the word of God communicated through human authors. This belief underscores the Bible's significance as the primary source of theological understanding and ethical guidance.
- The Old Testament: Narrates the history of God's covenant with his chosen people, Israel, including accounts of creation, the patriarchs, the exodus from Egypt, and the establishment of the kingdom of Israel. It contains prophetic writings foretelling the coming of the Messiah.
- The New Testament: Focuses on the life, ministry, death, resurrection, and ascension of Jesus Christ, along with the early development of the Christian church. It includes the Gospels (accounts of Jesus' life), the Acts of the Apostles, epistles (letters from Paul and other apostles), and the Book of Revelation.
The interpretation of the Bible has varied across different denominations and throughout history. However, the core belief in its divine inspiration remains a central element of Christian faith. Different approaches to biblical interpretation exist, ranging from literal interpretations to more nuanced, contextual readings. Understanding the historical and cultural contexts surrounding the biblical texts is crucial for accurate interpretation.
The Incarnation, Crucifixion, and Resurrection of Jesus Christ
The life, death, and resurrection of Jesus Christ form the heart of Christian belief. These events are not merely historical occurrences but are considered pivotal in God's plan for humanity's salvation.
- The Incarnation: The belief that God became human in the person of Jesus Christ. This event demonstrates God's love and willingness to enter human experience, bridging the gap between the divine and the human.
- The Crucifixion: Jesus' death on the cross is seen as a sacrificial act, atoning for the sins of humanity. This sacrifice is understood to reconcile humanity with God.
- The Resurrection: Jesus' rising from the dead is considered the ultimate victory over sin and death, offering hope for eternal life and validating his claims of divinity.
These three events are intrinsically linked, forming the narrative of salvation in Christian theology. The incarnation highlights God's love, the crucifixion demonstrates his sacrifice, and the resurrection offers the promise of new life and eternal hope. The significance of these events has been interpreted and celebrated in countless ways throughout Christian history, shaping theology, liturgy, and the lives of individual believers.
Salvation Through Faith in Jesus Christ
A core belief within Christianity centers on the concept of salvation – deliverance from sin and its consequences. Christians believe that salvation is achieved through faith in Jesus Christ, accepting him as Lord and Savior. This faith is seen as a gift from God, not something earned through human merit.
- Grace: The undeserved favor and love of God offered freely to humanity. Salvation is understood as a gift of God's grace, not a reward for good works.
- Repentance: Turning away from sin and embracing a life of obedience to God. It involves acknowledging one's shortcomings and seeking forgiveness.
- Faith: Trusting in Jesus Christ and his sacrifice on the cross. It involves a personal commitment to follow him and live according to his teachings.
Different denominations and theological perspectives offer varying interpretations of the nature and process of salvation. However, the core belief in salvation through faith in Jesus Christ remains central to Christian teaching. This belief provides hope and purpose for believers, offering forgiveness, reconciliation with God, and the promise of eternal life.
The Church: The Body of Christ
The church is understood as the community of believers, the body of Christ on earth. It's not just a building but a living organism, united by faith in Jesus Christ. The church plays a crucial role in Christian life, providing fellowship, support, and opportunities for spiritual growth.
- Fellowship: The sharing of life and faith within a community of believers. This involves mutual support, encouragement, and accountability.
- Worship: The act of praising and honoring God through prayer, song, and other forms of spiritual expression. Worship provides an opportunity to connect with God and experience his presence.
- Mission: The call to share the gospel of Jesus Christ with others. This involves evangelism, service, and acts of compassion.
The church has diverse expressions, with various denominations and traditions reflecting different interpretations of Christian theology and practice. However, the core belief in the church as the body of Christ, a community united by faith, remains a common thread among Christians worldwide.
The Holy Spirit: The Active Presence of God
The Holy Spirit is considered the third person of the Trinity, actively present in the world and in the lives of believers. The Spirit is seen as the source of power and guidance, empowering Christians to live out their faith and fulfilling God's purpose.
- Guidance: The Spirit leads and directs believers in their lives, providing wisdom, discernment, and understanding.
- Empowerment: The Spirit equips believers with spiritual gifts to serve God and others.
- Sanctification: The process of becoming holy, conforming to the image of Christ through the transformative power of the Spirit.
The experience and understanding of the Holy Spirit vary among different denominations and individual believers. However, the belief in the Spirit's active presence and transformative power is central to Christian faith. This belief encourages believers to seek spiritual growth, engage in service, and experience the fullness of God's presence in their lives.
Heaven and Hell: Eternal Destiny
Christian belief includes the concept of eternal destiny, encompassing heaven and hell. These are not simply locations but represent the ultimate consequences of one's choices and relationship with God.
- Heaven: The eternal dwelling place of God and those who have accepted Jesus Christ as their Savior. It's described as a place of perfect peace, joy, and communion with God.
- Hell: The eternal separation from God, often described as a place of suffering and torment. It's understood as the ultimate consequence of rejecting God's offer of salvation.
The specific nature of heaven and hell is a subject of diverse interpretations within Christianity. However, the core belief in an eternal destiny, determined by one's relationship with God, remains a significant aspect of Christian faith. This belief emphasizes the importance of living a life that reflects one's faith and making choices that align with God's will.
The End Times and Second Coming of Christ
Christian eschatology, the study of end times, involves the belief in the future return of Jesus Christ. This event is anticipated with varying degrees of detail and interpretation across different denominations.
- Second Coming: The belief that Jesus Christ will return to earth to judge the living and the dead. This event is often associated with significant upheaval and transformation.
- Millennium: Some interpretations anticipate a thousand-year reign of Christ on earth before the final judgment.
- New Heavens and New Earth: The belief that God will create a new heaven and a new earth, free from sin and suffering.
The specifics of end-time events are often debated and interpreted differently among various Christian groups. However, the belief in the second coming of Christ and the ultimate establishment of God's kingdom remains a significant aspect of Christian hope and anticipation.
Living Out the Christian Faith: A Life of Service and Obedience
Christianity is not merely a set of beliefs but a way of life. Living out the faith involves striving to follow Jesus' teachings and serving God and others. This involves various aspects of daily life.
- Prayer: Communication with God, expressing gratitude, seeking guidance, and confessing sins.
- Fellowship: Connecting with other believers in a church community.
- Service: Using one's gifts and talents to serve others.
- Obedience: Following God's commandments and living according to his will.
- Witness: Sharing one's faith with others, both through words and actions.
Living a Christian life is a continuous journey of growth and discipleship. It involves seeking to live out the values and teachings of Jesus Christ, making a positive impact on the world, and striving for holiness in one's daily life.
This comprehensive exploration provides a broad overview of the core beliefs and practices within Christianity. The depth and complexity of Christian faith require ongoing study and reflection, inviting believers to continually deepen their understanding and live out their faith authentically. Remember, diverse interpretations and expressions of Christianity exist, reflecting the richness and dynamic nature of this faith tradition.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Cardholders Who Hold An Ordering Officer Delegation
Apr 01, 2025
-
How To Read Literature Like A Professor Chapters
Apr 01, 2025
-
Summary Of The Gilded Six Bits
Apr 01, 2025
-
The Earliest Form Of Intraverbal Training Is
Apr 01, 2025
-
Guided Reading Activity Industrialization 1865 To 1901 Answers
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Within The Context Of Christianity Faith And Belief Involve . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
