Worksheet A Topic 2.1 Arithmetic And Geometric Sequences
Onlines
Mar 06, 2025 · 7 min read
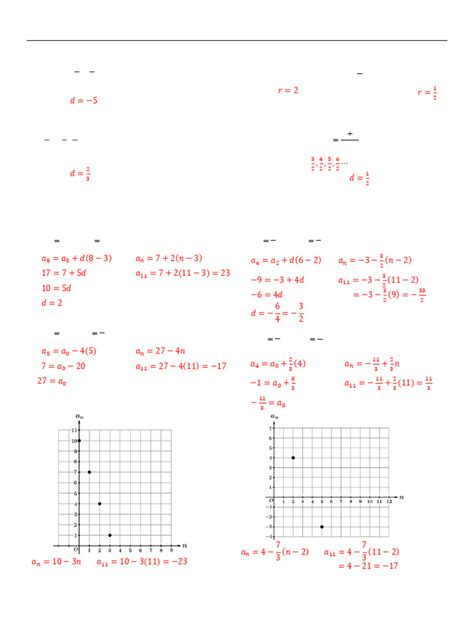
Table of Contents
Worksheet: Topic 2.1 Arithmetic and Geometric Sequences
This comprehensive guide delves into the fascinating world of arithmetic and geometric sequences, providing a thorough understanding of their properties, formulas, and applications. We'll explore various examples and practice problems to solidify your grasp of these fundamental mathematical concepts. This worksheet is designed to be used alongside your textbook and class notes, providing supplementary exercises and explanations to enhance your learning experience.
Understanding Sequences: The Foundation
Before we dive into the specifics of arithmetic and geometric sequences, let's establish a common understanding of what a sequence is. A sequence is simply an ordered list of numbers, called terms. These terms often follow a specific pattern or rule. We represent the terms of a sequence using subscripts: a<sub>1</sub> represents the first term, a<sub>2</sub> the second term, and so on. The general term is often denoted as a<sub>n</sub>, where 'n' represents the position of the term in the sequence.
Identifying Sequences: A Quick Glance
Let's look at a few examples to illustrate different types of sequences:
-
2, 4, 6, 8, 10... This sequence is clearly increasing by a constant amount (2) between consecutive terms. We'll see shortly that this is an example of an arithmetic sequence.
-
3, 6, 12, 24, 48... Here, each term is obtained by multiplying the previous term by a constant value (2). This is a classic example of a geometric sequence.
-
1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8... This sequence is the famous Fibonacci sequence, where each term is the sum of the two preceding terms. This is a more complex sequence, not covered in this specific worksheet.
Arithmetic Sequences: A Constant Difference
An arithmetic sequence is characterized by a constant difference between consecutive terms. This constant difference is called the common difference, often denoted by 'd'. To find the common difference, subtract any term from the term that immediately follows it.
Formula for the nth term of an Arithmetic Sequence:
The formula for finding the nth term (a<sub>n</sub>) of an arithmetic sequence is:
a<sub>n</sub> = a<sub>1</sub> + (n-1)d
Where:
- a<sub>n</sub> is the nth term
- a<sub>1</sub> is the first term
- n is the term number
- d is the common difference
Example 1:
Find the 10th term of the arithmetic sequence: 3, 7, 11, 15...
- Find the common difference (d): 7 - 3 = 4
- Identify the first term (a<sub>1</sub>): a<sub>1</sub> = 3
- Use the formula: a<sub>10</sub> = 3 + (10-1)4 = 3 + 36 = 39
Therefore, the 10th term is 39.
Sum of an Arithmetic Series:
An arithmetic series is the sum of the terms in an arithmetic sequence. The formula for the sum of the first 'n' terms (S<sub>n</sub>) of an arithmetic series is:
S<sub>n</sub> = n/2 [2a<sub>1</sub> + (n-1)d]
Or, alternatively:
S<sub>n</sub> = n/2 [a<sub>1</sub> + a<sub>n</sub>]
Example 2:
Find the sum of the first 20 terms of the arithmetic sequence: 2, 5, 8, 11...
- Find the common difference (d): 5 - 2 = 3
- Identify the first term (a<sub>1</sub>): a<sub>1</sub> = 2
- Use the formula: S<sub>20</sub> = 20/2 [2(2) + (20-1)3] = 10 [4 + 57] = 610
Therefore, the sum of the first 20 terms is 610.
Geometric Sequences: A Constant Ratio
A geometric sequence is characterized by a constant ratio between consecutive terms. This constant ratio is called the common ratio, often denoted by 'r'. To find the common ratio, divide any term by the term that immediately precedes it.
Formula for the nth term of a Geometric Sequence:
The formula for finding the nth term (a<sub>n</sub>) of a geometric sequence is:
a<sub>n</sub> = a<sub>1</sub> * r<sup>(n-1)</sup>
Where:
- a<sub>n</sub> is the nth term
- a<sub>1</sub> is the first term
- n is the term number
- r is the common ratio
Example 3:
Find the 7th term of the geometric sequence: 2, 6, 18, 54...
- Find the common ratio (r): 6 / 2 = 3
- Identify the first term (a<sub>1</sub>): a<sub>1</sub> = 2
- Use the formula: a<sub>7</sub> = 2 * 3<sup>(7-1)</sup> = 2 * 3<sup>6</sup> = 2 * 729 = 1458
Therefore, the 7th term is 1458.
Sum of a Geometric Series:
A geometric series is the sum of the terms in a geometric sequence. The formula for the sum of the first 'n' terms (S<sub>n</sub>) of a geometric series is:
S<sub>n</sub> = a<sub>1</sub> * (1 - r<sup>n</sup>) / (1 - r) (where r ≠ 1)
Example 4:
Find the sum of the first 5 terms of the geometric sequence: 1, 3, 9, 27...
- Find the common ratio (r): 3 / 1 = 3
- Identify the first term (a<sub>1</sub>): a<sub>1</sub> = 1
- Use the formula: S<sub>5</sub> = 1 * (1 - 3<sup>5</sup>) / (1 - 3) = (1 - 243) / (-2) = 242 / 2 = 121
Therefore, the sum of the first 5 terms is 121.
Infinite Geometric Series: A Special Case
When dealing with an infinite geometric series, the sum only converges (approaches a finite value) if the absolute value of the common ratio (|r|) is less than 1 (|r| < 1). If this condition is met, the formula for the sum of an infinite geometric series is:
S<sub>∞</sub> = a<sub>1</sub> / (1 - r)
Example 5:
Find the sum of the infinite geometric series: 1, 1/2, 1/4, 1/8...
- Find the common ratio (r): (1/2) / 1 = 1/2
- Identify the first term (a<sub>1</sub>): a<sub>1</sub> = 1
- Use the formula: S<sub>∞</sub> = 1 / (1 - 1/2) = 1 / (1/2) = 2
Therefore, the sum of this infinite geometric series is 2.
Applications of Arithmetic and Geometric Sequences
Arithmetic and geometric sequences are not just theoretical concepts; they have numerous real-world applications across various fields:
-
Finance: Calculating compound interest involves geometric sequences. Each year, the interest is added to the principal, and the next year's interest is calculated on the larger amount.
-
Physics: Modeling projectile motion and analyzing oscillations often utilizes arithmetic or geometric sequences.
-
Computer Science: Analyzing algorithms and data structures sometimes involves understanding the growth patterns of sequences.
-
Engineering: Determining the structural integrity of certain designs can depend on the understanding of sequences.
-
Biology: Modeling population growth (under specific conditions) can utilize geometric sequences.
Practice Problems: Test Your Understanding
Now it's time to put your knowledge into practice. Solve the following problems:
- Find the 15th term of the arithmetic sequence: 5, 11, 17, 23...
- Find the sum of the first 10 terms of the arithmetic sequence: 2, 7, 12, 17...
- Find the 8th term of the geometric sequence: 3, 6, 12, 24...
- Find the sum of the first 6 terms of the geometric sequence: 1, 2, 4, 8...
- Determine if the following sequence is arithmetic or geometric: 4, 12, 36, 108... Find the next term.
- Find the sum of the infinite geometric series: 4, 2, 1, 1/2...
- A ball is dropped from a height of 10 meters. Each time it bounces, it reaches a height that is 3/4 of its previous height. What height does the ball reach after the third bounce? (Hint: Geometric sequence)
- A person saves $100 in the first month, $110 in the second month, $120 in the third month, and so on. How much money will they have saved after 12 months? (Hint: Arithmetic sequence)
These problems offer a range of complexities, allowing you to test your understanding of both arithmetic and geometric sequences and series. Remember to carefully identify the first term, common difference (for arithmetic), or common ratio (for geometric) before applying the appropriate formulas. Good luck!
This detailed worksheet provides a comprehensive overview of arithmetic and geometric sequences, equipping you with the knowledge and practice needed to master these essential mathematical concepts. Remember, consistent practice is key to solidifying your understanding. Use this worksheet as a resource, revisit the examples, and challenge yourself with additional problems to further strengthen your skills.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Left Hand Of Darkness Notes
Mar 06, 2025
-
The Turn Of The Screw Chapter Summary
Mar 06, 2025
-
Cat On A Hot Tin Roof Summary
Mar 06, 2025
-
Serendipity Love In The Time Of Cholera
Mar 06, 2025
-
Quantitative Reasoning Math Nova Community College
Mar 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Worksheet A Topic 2.1 Arithmetic And Geometric Sequences . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
