Written Assignment 7 Dilations And Symmetry
Onlines
Mar 10, 2025 · 6 min read
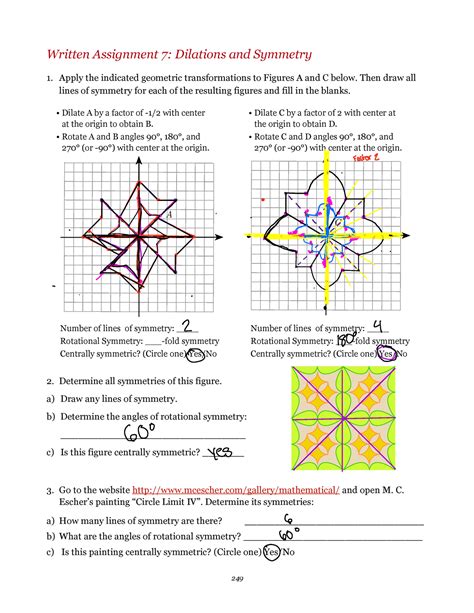
Table of Contents
Written Assignment 7: Dilations and Symmetry – A Deep Dive
This comprehensive guide delves into the fascinating world of dilations and symmetry, two fundamental concepts in geometry. We'll explore their definitions, properties, and applications, providing a robust understanding suitable for students tackling written assignments on this topic. This detailed exploration will cover various aspects, including different types of symmetry, the effects of dilations on shapes, and practical examples to solidify your understanding. Prepare to master dilations and symmetry!
Understanding Dilations: Resizing Shapes Mathematically
A dilation is a transformation that changes the size of a figure but not its shape. It's like using a magnifying glass – you enlarge or reduce the image, maintaining its proportions. The key elements of a dilation are:
-
Center of Dilation: This is a fixed point around which the transformation occurs. Imagine this as the center of your magnifying glass.
-
Scale Factor: This is the ratio of the distance from the center of dilation to a point on the transformed figure to the distance from the center of dilation to the corresponding point on the original figure. A scale factor greater than 1 enlarges the figure (enlargement), while a scale factor between 0 and 1 reduces it (reduction). A scale factor of exactly 1 results in no change.
Example: If the scale factor is 2, each distance from the center of dilation to a point on the original figure is doubled in the transformed figure.
Properties of Dilations: What Stays the Same?
While dilations change the size, several properties remain invariant (unchanged):
-
Shape: The shape of the figure remains the same; it's just bigger or smaller.
-
Angle Measures: The angles within the figure remain congruent (equal in measure).
-
Parallelism: If two lines are parallel in the original figure, their corresponding lines in the dilated figure will also be parallel.
-
Collinearity: If three or more points are collinear (lie on the same line) in the original figure, their corresponding points in the dilated figure will also be collinear.
Types of Dilations: Enlargements and Reductions
As mentioned earlier, dilations are categorized based on the scale factor:
-
Enlargement: A dilation with a scale factor greater than 1. The image is larger than the pre-image.
-
Reduction: A dilation with a scale factor between 0 and 1. The image is smaller than the pre-image.
Exploring Symmetry: The Beauty of Balance
Symmetry, in mathematics, describes a balanced arrangement of parts of a figure. Several types of symmetry exist:
1. Line Symmetry (Reflectional Symmetry): Mirror, Mirror
Line symmetry, also known as reflectional symmetry, occurs when a figure can be folded along a line (the line of symmetry) such that the two halves coincide perfectly. This line acts like a mirror.
2. Rotational Symmetry: Turning and Matching
Rotational symmetry exists when a figure can be rotated less than 360 degrees about a central point (the center of rotation) and still look exactly the same. The order of rotational symmetry refers to the number of times the figure matches itself during a 360-degree rotation. For example, a square has rotational symmetry of order 4.
3. Point Symmetry (Rotational Symmetry of Order 2): 180-Degree Turn
Point symmetry is a special case of rotational symmetry. A figure has point symmetry if it looks the same after a 180-degree rotation around a central point. This means that for every point (x, y) in the figure, the point (-x, -y) is also in the figure.
4. Translational Symmetry: Repeating Patterns
Translational symmetry occurs when a figure can be translated (moved) a certain distance and direction and still look the same. This is commonly seen in repeating patterns like wallpaper designs or tessellations.
Identifying Symmetry in Various Shapes
Let's explore symmetry in different geometric shapes:
-
Equilateral Triangle: Possesses 3 lines of symmetry and rotational symmetry of order 3.
-
Square: Possesses 4 lines of symmetry, and rotational symmetry of order 4, and point symmetry.
-
Rectangle (non-square): Possesses 2 lines of symmetry.
-
Circle: Has infinite lines of symmetry and rotational symmetry of infinite order.
-
Regular Pentagon: Possesses 5 lines of symmetry and rotational symmetry of order 5.
The Interplay of Dilations and Symmetry
Dilations and symmetry are often studied together because dilations can affect the symmetry of a figure. Consider these points:
-
Preservation of Symmetry: Applying a dilation to a figure with line symmetry will often result in a dilated figure that also possesses line symmetry. The lines of symmetry may change location but not their number. Similarly, rotational symmetry is often preserved.
-
Scale Factor and Symmetry: The scale factor of a dilation does not directly influence the type of symmetry but affects the size and location of the elements of symmetry.
-
Complex Shapes and Symmetry: With complex shapes, examining the impact of a dilation on the symmetry requires careful analysis of the individual components and how they relate to each other after transformation.
Practical Applications: Where Dilations and Symmetry Shine
Dilations and symmetry are not merely abstract concepts; they have far-reaching practical applications in various fields:
-
Architecture: Symmetrical designs are aesthetically pleasing and often create a sense of balance and harmony. Dilations are used in scaling blueprints and architectural models.
-
Art and Design: Artists use symmetry and dilations to create patterns, logos, and visually appealing designs. The concept of fractals relies heavily on dilation and self-similarity.
-
Computer Graphics: Dilations are fundamental in computer graphics for scaling images and objects. Symmetry plays a role in creating realistic and balanced virtual environments.
-
Engineering: Symmetrical designs are often used in engineering to distribute weight evenly and enhance structural stability. Dilations are utilized in scaling models and designs.
Solving Problems Involving Dilations and Symmetry: Step-by-Step Guidance
Let's tackle some common problems involving dilations and symmetry:
Problem 1: A triangle with vertices A(1, 1), B(3, 1), and C(2, 3) is dilated with a scale factor of 2 and a center of dilation at the origin (0, 0). Find the coordinates of the vertices of the dilated triangle.
Solution: Multiply the coordinates of each vertex by the scale factor:
- A'(2, 2)
- B'(6, 2)
- C'(4, 6)
Problem 2: Determine the lines of symmetry of a regular hexagon.
Solution: A regular hexagon has 6 lines of symmetry, three connecting opposite vertices and three connecting midpoints of opposite sides.
Problem 3: A square with side length 5 is dilated by a scale factor of 0.5. What is the area of the dilated square?
Solution: The side length of the dilated square will be 5 * 0.5 = 2.5. The area of the dilated square will be 2.5² = 6.25 square units. Note that the area is scaled by the square of the scale factor (0.5² = 0.25).
Problem 4: A figure has rotational symmetry of order 3. How many times does the figure match itself during a complete rotation of 360 degrees?
Solution: Three times.
Conclusion: Mastering Dilations and Symmetry
This in-depth exploration of dilations and symmetry provides a solid foundation for understanding these geometric concepts. By grasping their definitions, properties, and applications, you can confidently approach written assignments and real-world problems involving these transformations. Remember to practice consistently, applying the knowledge gained to various shapes and scenarios. This practice will solidify your understanding and boost your problem-solving skills in geometry. The interplay between these two concepts is rich and rewarding to explore, opening up possibilities for deeper mathematical understanding and creative applications in various fields. Through consistent effort and exploration, you'll master these vital concepts and appreciate their significance in the broader context of mathematics and its applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Puss In Boots The Bloody Chamber Narrator
Mar 10, 2025
-
Unit 3 Progress Check Mcq Apush
Mar 10, 2025
-
In The Hands Of An Angry God Summary
Mar 10, 2025
-
Till We Have Faces Summary Chapter 1
Mar 10, 2025
-
Angela And Carlos Are Asked To Determine The Relationship
Mar 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Written Assignment 7 Dilations And Symmetry . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
