You Have Been Performing Multiple-provider Cpr And Using An Aed
Onlines
Mar 24, 2025 · 5 min read
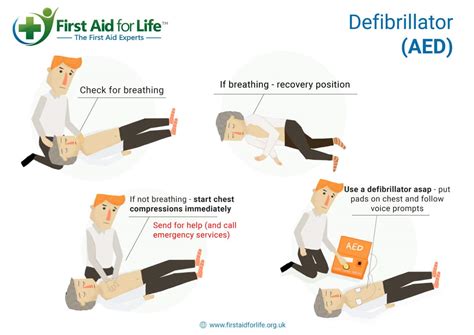
Table of Contents
Performing Multiple-Provider CPR and AED Use: A Comprehensive Guide
Performing cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and using an automated external defibrillator (AED) is a critical skill for healthcare providers and first responders. While single-provider CPR is often sufficient in some situations, multiple-provider CPR, especially when integrated with AED use, significantly improves the chances of successful resuscitation. This comprehensive guide will explore the intricacies of multiple-provider CPR and AED utilization, highlighting key aspects to enhance effectiveness and coordination.
Understanding the Importance of Multiple-Provider CPR
Multiple-provider CPR offers several advantages over single-provider CPR, especially during cardiac arrest:
Increased Efficiency and Effectiveness
With multiple providers, tasks can be divided, leading to increased efficiency. One provider can perform chest compressions while another manages the airway and delivers ventilations. This minimizes interruptions in chest compressions, a crucial factor in maintaining blood flow to the vital organs. Continuous, high-quality chest compressions are paramount and are significantly more likely to be achieved with a team.
Reduced Provider Fatigue
Single-provider CPR can be extremely physically demanding, leading to fatigue and reduced effectiveness over time. Multiple providers can rotate compression duties, reducing fatigue and maintaining the quality of chest compressions for a longer duration. This sustained effort greatly increases the likelihood of successful resuscitation.
Enhanced Coordination and Teamwork
Multiple-provider CPR necessitates effective teamwork and communication. A well-coordinated team can swiftly assess the situation, initiate CPR, and manage the airway and other critical aspects of resuscitation more efficiently. Clear communication and role assignment are critical to success.
Improved Patient Outcomes
Studies consistently demonstrate that multiple-provider CPR, particularly when combined with early defibrillation, significantly improves patient survival rates and neurological outcomes after cardiac arrest. The combined effect of continuous chest compressions, effective ventilations, and timely defibrillation maximizes the chances of restoring spontaneous circulation (ROSC).
Integrating AED Use in Multiple-Provider CPR
The use of an AED is crucial in multiple-provider CPR, as early defibrillation is a cornerstone of successful resuscitation. The integration of AED use within a team approach streamlines the process and ensures timely intervention.
Steps for Integrating AED Use:
-
Immediate recognition and activation of the emergency response system: Call for emergency medical services (EMS) immediately. This allows for professional help to arrive as soon as possible.
-
Rapid assessment of the victim: Check for responsiveness and breathing. If the victim is unresponsive and not breathing normally, begin CPR.
-
Chest compressions: Begin high-quality chest compressions at a rate of 100-120 compressions per minute, allowing for minimal interruptions.
-
Airway management: While chest compressions are performed, another provider should manage the airway, ensuring an open airway and providing ventilations. The recommended ratio for two-provider CPR is 30:2 (chest compressions to ventilations).
-
AED application and analysis: Once the AED arrives, swiftly turn it on and follow the device's prompts. Apply the pads to the victim's chest, ensuring proper placement. Allow the AED to analyze the heart rhythm.
-
Defibrillation (if advised): If the AED advises a shock, ensure everyone is clear of the victim before delivering the shock.
-
Continued CPR: After defibrillation, immediately resume high-quality CPR, following the same rhythm as before. Continue CPR until the victim shows signs of life or EMS arrives and takes over.
Roles and Responsibilities in a Multiple-Provider CPR Scenario:
In a two-provider scenario, the roles can be effectively divided:
-
Compressor: Focuses solely on delivering high-quality chest compressions, maintaining the correct rate and depth.
-
Ventilator/AED Operator: Manages the airway, delivers ventilations, operates the AED, and announces the rhythm analysis results.
In larger teams (three or more providers), roles can be further specialized:
-
Compressor: One or more providers focus exclusively on chest compressions.
-
Ventilator: One provider manages the airway and delivers ventilations.
-
AED Operator: One provider operates the AED and communicates with the team.
-
Team Leader: Organizes and coordinates the team's efforts, ensuring clear communication and efficient task management.
Advanced Considerations in Multiple-Provider CPR
Several advanced considerations can significantly improve the effectiveness of multiple-provider CPR and AED use:
High-Quality Chest Compressions:
-
Correct hand placement: The heel of one hand should be placed in the center of the chest, with the other hand on top, interlocking fingers.
-
Proper depth and rate: Compressions should be at least 2 inches deep and at a rate of 100-120 per minute.
-
Full chest recoil: Allow the chest to fully recoil after each compression. Avoid leaning on the chest between compressions.
-
Minimizing interruptions: Interruptions in chest compressions should be minimized, as they can significantly reduce effectiveness.
Effective Airway Management:
-
Head-tilt-chin-lift maneuver: This maneuver helps open the airway.
-
Jaw thrust maneuver: Use this method if there is a suspected cervical spine injury.
-
Proper ventilation technique: Deliver ventilations smoothly over one second, ensuring adequate chest rise.
-
Monitoring for adequate ventilation: Observe chest rise and fall to ensure effective ventilations.
Advanced Airway Management Techniques:
In scenarios requiring more advanced airway management, techniques such as oropharyngeal airways, nasopharyngeal airways, or endotracheal intubation may be necessary. These techniques require specialized training and should only be performed by qualified personnel.
Post-Cardiac Arrest Care:
After successful resuscitation, the focus shifts to post-cardiac arrest care. This includes monitoring vital signs, providing oxygen, and transporting the victim to a hospital for further treatment.
Ongoing Training and Competency Maintenance:
CPR and AED use require regular training and competency maintenance. Participating in regular refresher courses ensures that providers maintain proficiency in these life-saving skills.
Conclusion
Multiple-provider CPR, coupled with the timely use of an AED, dramatically improves survival rates after cardiac arrest. Effective teamwork, clear communication, and a focus on high-quality chest compressions and airway management are essential for successful resuscitation. By understanding the roles and responsibilities of each team member and adhering to established guidelines, healthcare providers and first responders can enhance their ability to save lives. Regular training and competency maintenance are crucial for maintaining the skills and knowledge needed to perform these life-saving interventions effectively. The coordinated efforts of a well-trained team can significantly improve outcomes for victims of cardiac arrest.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Wealth Building Is Not A Game Of Chance Answer Key
Mar 25, 2025
-
Vvc Now Is Best Suited For Which Situation
Mar 25, 2025
-
Which Of These Addresses Identify A Computer On The Network
Mar 25, 2025
-
Which Example From A Visit Of Charity
Mar 25, 2025
-
Which Of These Is An Example Of Internal Motivations
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about You Have Been Performing Multiple-provider Cpr And Using An Aed . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
